(Press-News.org) There is a new way to design computer chips and electronic circuitry for extreme environments: make them out of diamond.
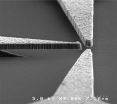
A team of electrical engineers at Vanderbilt University has developed all the basic components needed to create microelectronic devices out of thin films of nanodiamond. They have created diamond versions of transistors and, most recently, logical gates, which are a key element in computers.
"Diamond-based devices have the potential to operate at higher speeds and require less power than silicon-based devices," Research Professor of Electrical Engineering Jimmy Davidson said. "Diamond is the most inert material known, so our devices are largely immune to radiation damage and can operate at much higher temperatures than those made from silicon."
Their design of a logical gate is described in the Aug. 4 issue of the journal Electronics Letters. Co-authors of the paper are graduate student Nikkon Ghosh, Professor of Electrical Engineering Weng Poo Kang.
Not an engagement ring
Davidson was quick to point out that even though their design uses diamond film, it is not exorbitantly expensive. The devices are so small that about one billion of them can be fabricated from one carat of diamond. The films are made from hydrogen and methane using a method called chemical vapor deposition that is widely used in the microelectronics industry for other purposes. This deposited form of diamond is less than one-thousandth the cost of "jewelry" diamond, which has made it inexpensive enough so that companies are putting diamond coatings on tools, cookware and other industrial products. As a result, the cost of producing nanodiamond devices should be competitive with silicon.
Potential applications include military electronics, circuitry that operates in space, ultra-high speed switches, ultra-low power applications and sensors that operate in high radiation environments, at extremely high temperatures up to 900 degrees Fahrenheit and extremely low temperatures down to minus 300 degrees Fahrenheit.
Hybrid of old and new
The nanodiamond circuits are a hybrid of old fashioned vacuum tubes and modern solid-state microelectronics and combine some of the best qualities of both technologies.
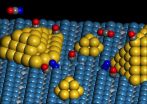
Nanodiamond devices consist of a thin film of nanodiamond that is laid down on a layer of silicon dioxide. Much as they do in vacuum tubes, the electrons move through vacuum between the nanodiamond components, instead of flowing through solid material the way they do in normal microelectronic devices. As a result, they require vacuum packaging to operate.
"The reason your laptop gets hot is because the electrons pumping through its transistors bump into the atoms in the semiconductor and heat them up," Davidson said. "Because our devices use electron transport in vacuum they don't produce nearly as much heat."
This transmission efficiency is also one reason why the new devices can run on very small amounts of electrical current. Another is that diamond is the best electron emitter in the world so it doesn't take much energy to produce strong electron beams. "We think we can make devices that use one tenth the power of the most efficient silicon devices," said Davidson.
The design is also largely immune to radiation damage. Radiation disrupts the operation of transistors by inducing unwanted charge in the silicon, causing an effect like tripping the circuit breaker in your home. In the nanodiamond device, on the other hand, the electrons flow through vacuum so there is nothing for energetic particles to disrupt. If the particles strike the nanodiamond anode or cathode, the impact is limited to a small fluctuation in the electron flow, not complete disruption, as is the case with silicon devices.
"When I read about the problems at the Fukushima power plant after the Japanese tsunami, I realized that nanodiamond circuits would be perfect for failsafe circuitry in nuclear reactors," Davidson said. "It wouldn't be affected by high radiation levels or the high temperatures created by the explosions."
Nanodiamond devices can be manufactured by processes that the semiconductor industry currently uses. The one exception is the requirement to operate in vacuum, which would require some modification in the packaging process. Currently, semiconductor chips are sealed in packages filled with an inert gas like argon or simply encapsulated in plastic, protecting them from chemical degradation. Davidson and his colleagues have investigated the packaging process and have found that the metallic seals used in military-grade circuitry are strong enough to hold an adequate vacuum for centuries.
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by grants from the U.S. Army.
Visit Research News @ Vanderbilt for more research news from Vanderbilt.
Designing diamond circuits for extreme environments
2011-08-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New study shows how to eliminate motion sickness on tilting trains
2011-08-06
An international team of researchers led by scientists at Mount Sinai School of Medicine have found that motion sickness on tilting trains can be essentially eliminated by adjusting the timing of when the cars tilt as they enter and leave the curves. They found that when the cars tilt just at the beginning of the curves instead of while they are making the turns, there was no motion sickness. The findings were published online Monday, July 25 in the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB) Journal.
When a tilting train enters a curve, sensors ...
A patient's own skin cells may one day treat multiple diseases
2011-08-06
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — The possibility of developing stem cells from a patient's own skin and using them to treat conditions as diverse as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and cancer has generated tremendous excitement in the stem cell research community in recent years. Such therapies would avoid the controversial need for using stem cells derived from human embryos, and in theory, also bypass immunological problems inherent in using cells from one person to treat another.
However, in the nearly five years since the first article describing the development of ...
US physician practices spend 4 times Canadian practices
2011-08-06
NEW YORK (Aug. 4, 2011) -- Physicians in the United States spend nearly four times as much dealing with health insurers and payers compared with doctors in Canada. Most of the difference stems from the fact that Canadian physicians deal with a single payer, in contrast to the multiple payers in the United States.
These findings are published in the August issue of the journal Health Affairs -- the result of a research collaboration among Weill Cornell Medical College, Cornell University–Ithaca, the University of Toronto, and the Medical Group Management Association.
Administrative ...
Wireless network in hospital monitors vital signs
2011-08-06
A clinical warning system that uses wireless sensors to track the vital signs of at-risk patients is undergoing a feasibility study at Barnes-Jewish Hospital in St. Louis.
When the full system is operational sensors will take blood oxygenation and heart-rate readings from at-risk patients once or twice a minute. The data will be transmitted to a base station, where they will be combined with other data in the patient's electronic medical record, such as lab test results.
The incoming vital signs and data in the medical record will be continually scrutinized by a machine-learning ...
U of Minnesota researchers discover a natural food preservative that kills food-borne bacteria
2011-08-06
University of Minnesota researchers have discovered and received a patent for a naturally occurring lantibiotic — a peptide produced by a harmless bacteria — that could be added to food to kill harmful bacteria like salmonella, E. coli and listeria.
The U of M lantibiotic is the first natural preservative found to kill gram-negative bacteria, typically the harmful kind. "It's aimed at protecting foods from a broad range of bugs that cause disease," said Dan O'Sullivan, a professor of food science and nutrition in the university's College of Food, Agricultural and Natural ...
Females can place limits on evolution of attractive features in males, research shows
2011-08-06
AUDIO:
Male túngara frogs producing their distinctive "whine " and "chuck " calls to attract females.
Click here for more information.
AUSTIN, Texas—Female cognitive ability can limit how melodious or handsome males become over evolutionary time, biologists from The University of Texas at Austin, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center and the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute have observed.
Males across the animal world have evolved ...
University of Virginia researchers uncover new catalysis site
2011-08-06
Mention catalyst and most people will think of the catalytic converter, an emissions control device in the exhaust system of automobiles that reduces pollution.
But catalysts are used for a broad variety of purposes, including the conversion of petroleum and renewable resources into fuel, as well as the production of plastics, fertilizers, paints, solvents, pharmaceuticals and more. About 20 percent of the gross domestic product in the United States depends upon catalysts to facilitate the chemical reactions needed to create products for everyday life.
Catalysts are ...
Potential new eye tumor treatment discovered
2011-08-06
Baltimore, MD — New research from a team including several Carnegie scientists demonstrates that a specific small segment of RNA could play a key role in the growth of a type of malignant childhood eye tumor called retinoblastoma. The tumor is associated with mutations of a protein called Rb, or retinoblastoma protein. Dysfunctional Rb is also involved with other types of cancers, including lung, brain, breast and bone. Their work, which will be the cover story of the August 15th issue of Genes & Development, could result in a new therapeutic target for treating this rare ...
Targeting innate immunity in malaria
2011-08-06
WORCESTER, Mass. – Scientists at the University of Massachusetts Medical School have uncovered a novel DNA-sensing pathway important to the triggering of an innate immune response for malaria. Activation of this pathway appears to stimulate production of an overabundance of type-1 interferon by the immune system that may contribute to inflammation and fever in malaria patients and could play a part in susceptibility for the most common and lethal form of malaria known as plasmodium falciparum. Published online by Immunity this week, the study offers the first evidence that ...
Questions to Ask Your Plastic Surgeon Before Breast Augmentation
2011-08-06
The decision to have breast augmentation surgery is an important one that involves multiple factors. Breast augmentation has the ability to improve your self-esteem, increase self-confidence and feelings of appeal, and even improve your clothing options. It also has physical and aesthetic risks which should be fully considered prior to undergoing the procedure.
Breast augmentation is the most popular form of plastic surgery in the United States, with more than 250,000 performed every year. This does not mean that the procedure is right for you and, like any elective ...