(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR, Mich.---A study links low vitamin D in young girls with early menstruation, which is a risk factor for a host of health problems for teen girls as well as women later in life.
Researchers from the University of Michigan School of Public Health measured the blood vitamin D levels in 242 girls ages 5-12 from Bogota, Colombia, and followed them for 30 months. Girls low on vitamin D were twice as likely to start menstruation during the study than those with sufficient vitamin D, said epidemiologist Eduardo Villamor, associate professor in the U-M SPH.
This is important for several reasons, Villamor said. Worldwide, there has been a slow decline in the age of the first menstruation, or menarche, for years, which Villamor says suggests an environmental cause, since the genetics that trigger puberty haven't changed.
"We know relatively little about what triggers puberty from an environmental perspective," Villamor said. "If we learn what is causing the decline in age of first menstruation, we may be able to develop interventions" to prevent premature menarche.
Early menstruation is a risk factor for behavioral and psychosocial problems in teens. Also, girls who have an earlier menarche appear to have increased risk of developing cardiometabolic diseases and cancer---particularly breast cancer, as adults.
This study formally explored the link between vitamin D status of girls and the time of their first menstruation. Previous research has suggested that menarche happens later in girls living closer to the Equator than girls living in northern countries. Coincidentally, girls in northern countries may harbor high rates of vitamin D deficiencyduring winter months because of limited sun exposure.
In the research by Villamor and colleagues, 57 percent of the girls in the vitamin D-deficient group reached menarche during the study, compared to 23 percent in the vitamin D-sufficient group. In terms of age, girls who were low in vitamin D were about 11.8 years old when they started menstruating, compared to the other group at about age 12.6 years old. This 10-month difference is substantial, Villamor said, because even though 10 months may not seem like a long time, at that age a lot is happening rapidly to a young girl's body.
Still, while the results suggest a link between vitamin D and menarche, they have not established a causal relationship. It's necessary to do more studies to show if interventions that change girls' vitamin D status result in a change in their age of menarche.
###
For more on Villamor: http://www.sph.umich.edu/iscr/faculty/profile.cfm?uniqname=villamor
To access the paper: http://www.ajcn.org/content/early/2011/08/10/ajcn.111.018168.full.pdf+html
The University of Michigan School of Public Health has been promoting health and preventing disease since 1941, and is ranked among the top public health schools in the nation. Whether making new discoveries in the lab or researching and educating in the field, our faculty, students, and alumni are deployed around the globe to promote and protect our health http://www.sph.umich.edu/
EDITORS: Watch and link to a video with Villamor: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qSzzFJUxi1I&feature=player_embedded
END
Golf courses and coffee plantations are some of the unlikely bat habitats that could be considered in conservation plans, say scientists presenting research at the Ecological Society of America's (ESA) 96th Annual Meeting from August 7-12, 2011. Using Doppler weather radar and other technologies relatively new to the field of ecology, ecologists will discuss the role of atmospheric conditions in bat behavior and the effectiveness of acoustic deterrents in reducing bat fatalities at wind farms. ESA's August 2011 meeting will take place in Austin, Texas, home to North America's ...
Analyses of the metabolic profile of blood serum have revealed significant differences in metabolites between men and women. In a study to be published on August 11 in the open-access journal PLoS Genetics, scientists at the Helmholtz Zentrum München have concluded that there is a need for gender-specific therapies.
Gender-specific therapies may be required for some diseases as there are significant differences between male and female metabolism. Such differences were shown to exist for 101 of the 131 metabolites – above all in lipid and amino acid species – in the sera ...
AUSTIN, Texas – Just as the rainy season is driving a new surge of cholera cases in Haiti, a new computational model could forecast where outbreaks are likely to occur.
Researchers at Ohio State University are working with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) on the project, in the hopes of targeting anti-cholera efforts where they are most needed in the earthquake-ravaged country.
Just back from a 10-day trip to the Artibonite Valley in Haiti, Ohio State researcher Marisa Eisenberg described the model's early results at the Ecological Society of America ...
Ice and frozen ground at the North and South Poles are affected by climate change induced warming, but the consequences of thawing at each pole differ due to the geography and geology, according to a Penn State hydrologist.
"The polar regions, particularly the Arctic, are warming faster than the rest of the world," Michael N. Gooseff, associate professor of civil and environmental engineering, told attendees today (Aug. 11) at the 96th annual meeting of the Ecological Society of America in Austin, Texas. "As a consequence, polar ecosystems respond directly to changes ...
In both chimpanzees and humans, portions of the brain that are critical for complex cognitive functions, including decision-making, self-awareness and creativity, are immature at birth. But there are important differences, too. Baby chimpanzees don't show the same dramatic increase in the volume of prefrontal white matter in the brain that human infants do.
Those are the conclusions of a study reported in the August 11th Current Biology, a Cell Press publication, that is the first to track the development of the chimpanzee brain over time and to make the comparison to ...
Bacteria may have bad reputations but in fact, all animals -- us included -- rely on them in critical ways. In the case of sap-feeding insects, intimate associations with microbes offer a source for essential nutrients that their sugary diets just don't include. Now, researchers reporting in the August 11th Current Biology, a Cell Press publication, have new insight into organisms that have taken this symbiotic lifestyle to the extreme; they have sequenced the genomes of two species of bacteria that live together, one inside of the other, inside mealybugs.
The effort ...
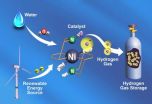
RICHLAND, Wash. -- Looking to nature for their muse, researchers have used a common protein to guide the design of a material that can make energy-storing hydrogen gas. The synthetic material works 10 times faster than the original protein found in water-dwelling microbes, the researchers report in the August 12 issue of the journal Science, clocking in at 100,000 molecules of hydrogen gas every second.
This step is just one part of a series of reactions to split water and make hydrogen gas, but the researchers say the result shows they can learn from nature how to control ...
VIDEO:
The video describes the new epidermal electronics system and shows how it is applied to the skin.
Click here for more information.
Through a combination of careful theoretical modeling and precise micro-manufacturing, a team of engineers and scientists has developed a new type of ultra-thin, self-adhesive electronics device that can effectively measure data about the human heart, brain waves and muscle activity – all without the use of bulky equipment, conductive ...
- Revenue increased to US $ 1.035 billion, compared to US $ 663 million
in H1 2010
- Operating profit increased to US $ 288 million, compared to US $ 83 million
in H1 2010
- Adjusted EBITDA grew to US $ 337 million, compared to US $ 137 million
in H1 2010
- Net profit amounted to US $ 244 million, compared to net loss of US $ 13 million in H1 2010
URALCHEM Holding P.L.C. (hereinafter URALCHEM Holding or the Company), a Cypriot holding company of the URALCHEM Group (hereinafter called the Group), one of the largest producers of nitrogen and phosphate fertilisers ...
VIDEO:
A new form of electronics, small enough to fit under a temporary tattoo, changes the way scientists think about gathering data from the human body.
Click here for more information.
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Engineers have developed a device platform that combines electronic components for sensing, medical diagnostics, communications and human-machine interfaces, all on an ultrathin skin-like patch that mounts directly onto the skin with the ease, flexibility and comfort of ...