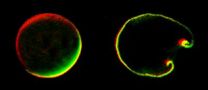
(Press-News.org) If you've ever spilled a drop of coffee on a surface, you might have noticed the curious way the color concentrates at the edges when the coffee dries. This is known as the "coffee ring effect," and recently, researchers have determined that the shape of the particles in the liquid is an important factor in creating this pattern. The research results could eventually translate into new techniques or formulations for product coatings, or better inks and paints.
This work, published in the August 18 issue of the journal Nature was performed by Arjun Yodh and colleagues at the University of Pennsylvania.
"We found that if you change the shape of the particles in the solution, the coffee ring effect goes away, and you end up with a uniform coating," said Peter Yunker, a graduate student in Yodh's lab.
First, a little fluid dynamics: As the liquid in a droplet evaporates, the edges remain fixed, so as the volume decreases, fluid flows outward from the middle of the droplet to its edges. This flow carries particles to the edges, and round particles at the edge will pack closely. By the time all of the liquid in the droplet evaporates, most of the particles will be at the edge, producing the coffee ring effect.
Both the shape that liquid droplets take, and the way the shape changes as the droplets evaporate, is greatly influenced by surface tension at the air-liquid interface. This tension is a property of the interface, based on how the molecules in the liquid interact with one another versus the air. For example, liquids with a high surface tension, like water, may form a raised droplet, because the molecules are very attracted to one another and not so attracted to the air. In contrast, liquids with lower surface tension, like alcohols, are more likely to form flat spots instead of curved droplets.
The Yodh group found that elongated particles in a liquid behave differently than round ones because of the way they are affected by the surface tension of the air-liquid interface. The forces at work are even observable in a common breakfast cereal.
"If you make the particles elongated or ellipsoidal, they deform the air-water interface, which causes the particles to strongly attract one another. You can observe this effect in a bowl of cheerios-if there are only a few left they clump together in the middle of the bowl, due to the surface tension of the milk," explained Yunker.
This clumping changes the way the particles distribute themselves within the droplet. Even if the clumped ellipsoidal particles reach the edge of the droplet, they do not pack as closely as round particles. The loosely packed clumps eventually spread to cover the entire surface, filling it so an even coating of particles is deposited when evaporation is complete.
"This work gives us a new idea about how to make a uniform coating, relatively simply. If you change the particle shape, you can change the way a particle is deposited. You can also make mixtures. In some cases, even just a small amount of ellipsoids can change the way the particles deposit when they dry," said Yodh.
In future studies, the research team will explore drying and deposition of different types of fluids. They will also investigate different particle sizes and shapes, and the interplay of particle mixtures.
"This is an exciting scientific result with potential commercial applications, which was in part enabled by support of the Materials Research Science and Engineering Center at the University of Pennsylvania," said Mary Galvin, program director for the division of materials research at the National Science Foundation, which partially funded the research. The centers program, recently renamed Materials Research Centers and Teams, provides support for interdisciplinary materials research and education while addressing fundamental problems in science and engineering.
INFORMATION:
The future of inks, paints and coatings takes shape
Researchers determine that particle shape affects the 'coffee ring effect'
2011-08-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Increased celiac disease prevalence in women with unexplained infertility
2011-08-19
A recent study demonstrated increased rates of celiac disease in women who present with unexplained infertility. Published in the May-June 2011 issue of The Journal of Reproductive Medicine, the study evaluated 191 female patients presenting with infertility. Each participant underwent serologic screening for celiac disease as well as routine infertility testing. The 4 patients who had positive serum test results were advised to seek evaluation with a gastroenterologist. All 4 patients were confirmed to have celiac disease. They then underwent nutritional counseling ...
New CU-Boulder study reveals bacteria from dog feces in outdoor air of urbanized air
2011-08-19
Bacteria from fecal material -- in particular, dog fecal material -- may constitute the dominant source of airborne bacteria in Cleveland's and Detroit's wintertime air, says a new University of Colorado Boulder study.
The CU-Boulder study showed that of the four Midwestern cities in the experiment, two cities had significant quantities of fecal bacteria in the atmosphere -- with dog feces being the most likely source.
"We found unexpectedly high bacterial diversity in all of our samples, but to our surprise the airborne bacterial communities of Detroit and Cleveland ...
Research examines the black-and-white issues surrounding executions in the South
2011-08-19
An examination of post-emancipation executions in the South is revealing how race played a significant and under-examined role in executions. Annulla Linders, a University of Cincinnati associate professor of sociology, will present the research on Aug. 21, at the 106th annual meeting of the American Sociological Association in Las Vegas.
Linders combed through newspaper archives in the Library of Congress to examine the meanings and understandings about race and justice that were produced in newspaper accounts of legal, public executions of African-American convicts ...
Battling job barriers with a tube of lipstick
2011-08-19
Generations of American women have turned to door-to-door sales when a male-dominated workforce and lack of education prevented them from entering the workforce. They were known as the Tupperware Lady or the Avon Lady as they showed off their newest products to the "Lady of the House."
New research out of the University of Cincinnati finds it's a strategy that is now bringing success to some women in third world countries facing discrimination in the formal job market. Erynn Masi de Casanova, a UC assistant professor of sociology, will present her research on Aug. 21 ...
Long-term, intimate partnerships can promote unhealthy habits
2011-08-19
For better or for worse, in sickness and in health – there's a long line of research that associates marriage with reducing unhealthy habits such as smoking, and promoting better health habits such as regular checkups. However, new research is emerging that suggests married straight couples and cohabiting gay and lesbian couples in long-term intimate relationships may pick up each other's unhealthy habits as well. University of Cincinnati research into how those behaviors evolve will be presented Aug. 23 at the 106th annual meeting of the American Sociological Association ...
NSF launches new engineering research centers with awards totaling $74.0 million
2011-08-19
The National Science Foundation (NSF) today announced the award of $74 million to create four new Engineering Research Centers (ERCs) that will advance interdisciplinary research and education in partnership with industry.
During the next five years, the ERCs will share the goal of creating knowledge and innovations that address significant societal issues such as health and sustainability challenges while advancing the competitiveness of U.S. industry. The centers will support research and innovation in solar energy, water infrastructure, neural engineering and energy ...
Penn molecular scientists develop color-changing stress sensor
2011-08-19
PHILADELPHIA — It is helpful — even life-saving — to have a warning sign before a structural system fails, but, when the system is only a few nanometers in size, having a sign that's easy to read is a challenge. Now, thanks to a clever bit of molecular design by University of Pennsylvania and Duke University bioengineers and chemists, such warning can come in the form of a simple color change.
The study was conducted by professor Daniel Hammer and graduate students Neha Kamat and Laurel Moses of the Department of Bioengineering in Penn's School of Engineering and ...
Online Parcel Delivery Firm Says Small Businesses Must Capitalise on Mobile Sales Boom
2011-08-19
Britain's leading online parcel delivery specialist has called on small businesses to take advantage of the boom in sales through smartphones.
Recent research has shown that more and more consumers are prepared to buy products through their mobile phones and are enjoying the freedom that mobile shopping offers. Bolton-based Parcel2Go helps businesses of all sizes organise shipping to countries across the world and suggests that small firms should take a proactive approach when it comes to building an online presence.
People are now using their mobile phones to do ...
Emergency workers will respond
2011-08-19
Headlines screamed in the days following Hurricane Katrina: Police Quitting, Overwhelmed by Chaos. Pundits squawked about the flight of the "notoriously corrupt" New Orleans police force. City and emergency planners outside the devastated areas envisioned disasters happening in their own cities and widespread desertion by their first responders.
But that's not a very realistic fear, according to UD's Joe Trainor, who recently conducted research on the subject.
"Fire companies and police stations and hospitals should stop being concerned about whether individuals will ...
English language ads better reach Latino audience
2011-08-19
English language ads have a greater impact in mobilizing Latino voters than Spanish language ads, according to a study recently published in American Political Research, a SAGE journal.
This study examined the effects of direct mail pieces on Latino voters. The direct mail piece, which was written in either English or Spanish, was sent to two separate groups while a third who received no mailing was used as a control group. The experiment was conducted in New York City Council District 21 prior to the February 2009 special election to fill a vacancy on the New York ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
[Press-News.org] The future of inks, paints and coatings takes shapeResearchers determine that particle shape affects the 'coffee ring effect'