(Press-News.org) SPRINGFIELD, MO—The American elderberry is showing promise as a profitable commercial fruit crop. Traditionally used for making jelly, juice, and wine, elderberry is becoming increasing important in North America's burgeoning "nutraceutical" industry. Historically, elderberries have mostly been harvested from the wild; researchers have made recently made efforts to select or develop improved cultivars. Increased interest and emerging markets are encouraging scientists to develop improved elderberry cultivars that yield consistent, superior production. Scientists from the University of Missouri have introduced a new variety named 'Wyldewood', a tall, vigorous elderberry plant that consistently produces heavy yields, is efficient to harvest, and produces fruit well-suited for processing.
The Elderberry Improvement Project was initiated at Missouri State University and the University of Missouri in 1997 with the goal of developing American elderberry cultivars adapted to Midwestern environments. 'Wyldewood' is the first cultivar released from the program. Originally described and tested as 'Brush Hills 1' and 'Wyldewood 1', the new release was identified and collected from the wild by Jack Millican in 1995 near the community of Brush Hill, Oklahoma. The cultivar was named in honor of Wyldewood Cellars Winery of Mulvane, Kansas, a leading promoter of elderberry production in the Midwest and a supporter of the Elderberry Improvement Project. 'Wyldewood' was tested and observed beginning in 1998 at two locations in southern Missouri.
According to corresponding author Patrick L. Byers of the University of Missouri Cooperative Extension Service in Springfield, 'Wyldewood' outperformed the standard 'Adams II' elderberry in yield potential and berry size; 'Wyldewood berry weights ranged from a low of 52 mg to a high of 111 mg. The harvest season for 'Wyldewood' is generally 14 to 26 days later than the standard 'Adams II', with harvest usually beginning in late July in Missouri.
A limited number of unrooted cuttings of 'Wyldewood' are available for test purposes to federal and state experiment stations from University of Missouri and Missouri State University by contacting the authors.
###
The complete study and abstract are available on the ASHS HortScience electronic journal web site: http://hortsci.ashspublications.org/cgi/content/full/45/2/312
Founded in 1903, the American Society for Horticultural Science (ASHS) is the largest organization dedicated to advancing all facets of horticultural research, education, and application. More information at ashs.org
'Wyldewood,' first release from Elderberry Improvement Project
Long-term research produces results for Missouri fruit breeding program
2010-09-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
'Blue Suede' premiers: New blueberry recommended for home gardeners
2010-09-21
GRIFFIN, GA—Blueberry aficionados will soon have a tasty, colorful new variety for their backyard gardens. Blueberry experts D. Scott NeSmith and Mark K. Ehlenfeldt introduced 'Blue Suede™' in a recent issue of HortScience. The new southern highbush blueberry (Vaccinium hybrid) was released by the University of Georgia's College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, the University of Georgia Agricultural Experiment Station, and the U.S. Department of Agriculture–Agricultural Research Service. 'Blue Suede™' is targeted for sales to the home gardener market.
According ...
Purdue researcher cracks open secret of oysters' ability to stick together
2010-09-21
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A Purdue University-led research team has uncovered the chemical components of the adhesive produced by oysters, providing information that could be useful for fisheries, boating and medicine.
A better understanding of oysters' ability to stick together to form complex reefs would help those trying to boost the dwindling oyster population, aid in the creation of materials to keep boat hulls clean without harming the environment, and bring researchers one step closer to creating wet-setting adhesives for use in medicine and construction.
Jonathan ...
Rotating high-pressure sodium lamps provide flowering plants for spring markets
2010-09-21
EAST LANSING, MI—When consumers visit garden centers in spring they will most likely buy flowering ornamental plants that are ready for their home gardens. Studies have shown that consumers favor plants that are already in flower rather than those that are "vegetative"—a preference that can present multiple challenges for commercial growers.
To satisfy consumers' wishes, producers of ready-to-flower ornamentals like bedding plants and perennials start growing crops far in advance of the spring buying season, often during the dark and short days of winter. When the days ...
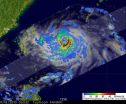
NASA sees Tropical Storm Julia getting 'dusted'
2010-09-21
Dust has been blowing into the Eastern Atlantic Ocean from Africa's Saharan Desert, and a NASA satellite captured some of that dust east of Tropical Storm Julia.
NASA's Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument on the Terra satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Julia on Sept. 18 at 13:50 UTC (9:50 a.m. EDT) and noticed a large area of Saharan dust over the Atlantic Ocean, to Julia's east.
On Sept. 20 at 5 a.m. EDT, Julia was still holding on to tropical storm status with maximum sustained winds near 45 mph. Julia was located about ...
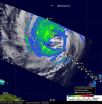
NASA satellites and aircraft studied Hurricane Karl before it faded
2010-09-21
Hurricane Karl made landfall near Veracruz, Mexico on Friday, Sept. 17 and moved inland over Mexico's rugged terrain, which took the punch out of the storm. As Karl was moving into Mexico, NASA aircraft and NASA satellites were gathering data from this storm that jumped from a tropical storm to a Category 3 hurricane the day before.
Karl had maximum sustained winds of 115 mph when it made landfall on Friday afternoon, Sept. 17. That made Karl a Category three hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson scale, and a major hurricane to boot.
On that day, NASA's Genesis and Rapid ...
Winter drought stress can delay flowering, prevent fruit loss in orange crops
2010-09-21
LAKE ALFRED, FL—Successful mechanical harvesting of perennial fruit crops requires efficient, economical harvesting systems that do not reduce trees' production life or diminish fruit quality. Most of the world's citrus is now harvested manually, but the use of efficient and lower-cost mechanical harvesting techniques is expected to increase in the next few years, especially in the large citrus plantations in Florida and Brazil. The citrus industry is ramping up efforts to extend the harvest season past June, when the following year's crop becomes large enough to be susceptible ...
NASA captures very heavy rain in Typhoon Fanapi and 2 landfalls
2010-09-21
Taiwan experienced a landfall and a soaking from Typhoon Fanapi, and NASA and JAXA's TRMM satellite noted a large area of very heavy rain in the system before it made landfall this weekend. NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites also captured impressive visible images of Fanapi just before the Taiwan landfall, and as it was making landfall in eastern China very early today.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM captured an image of Typhoon Fanapi's rainfall on Sept. 18 at 0653 UTC (2:53 a.m. EDT) after the typhoon had intensified to 105 knots (~121 ...
Introducing 'Champagne', new disease-resistant fig
2010-09-21
BATON ROUGE, LA—The ancient fig tree, first imported to the United States during the 16th century, thrives in areas of California and the South Atlantic and Gulf Coast areas of the U.S. One of the most popular trees grown in Southern backyards, fig is favored for its versatile fruit and low-maintenance production.
Charles E. Johnson, Ed O'Rourke, and James E. Boudreaux, from the Louisiana State University Agricultural Center in Baton Rouge, introduced a new fig they named "Champagne" in a recent issue of HortScience. According to the report, the new fig performed well ...
NASA's MODIS and AIRS instruments watch Igor changing shape, warming over 3 days
2010-09-21
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS, is an instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites and provides incredible views of tropical cyclones like Hurricane Igor, from its vantage point in space. Imagery from the MODIS instruments on these two satellites captured from Sept. 18 to 20 showed that powerful Hurricane Igor in the Atlantic Ocean is morphing from a rounded storm to more of a comma-shaped storm.
The MODIS instrument on NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of Igor at 11:30 am on Sept. 18, while MODIS in the Aqua satellite ...
Food for thought, er, well...
2010-09-21
Ever wonder why it's such an effort to forget about work while on vacation or to silence that annoying song that's playing over and over in your head?
Mathematicians at Case Western Reserve University may have part of the answer.
They've found that just as thinking burns energy, stopping a thought burns energy - like stopping a truck on a downhill slope.
"Maybe this explains why it is so tiring to relax and think about nothing," said Daniela Calvetti, professor of mathematics, and one of the authors of a new brain study. Their work is published in an advanced online ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
Team led by UC San Diego researchers selected for prestigious global cancer prize
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
[Press-News.org] 'Wyldewood,' first release from Elderberry Improvement ProjectLong-term research produces results for Missouri fruit breeding program