(Press-News.org) Scientists have discovered a genetic cause of extreme thinness for the first time, in a study published today in the journal Nature.
The research shows that people with extra copies of certain genes are much more likely to be very skinny. In one in 2000 people, part of chromosome 16 is duplicated, making men 23 times and women five times more likely to be underweight.
Each person normally has a copy of each chromosome from each parent, so we have two copies of each gene. But sometimes sections of a chromosome can be duplicated or deleted, resulting in an abnormal 'dosage' of genes.
In a study examining the DNA of over 95,000 people, researchers at Imperial College London and the University of Lausanne have identified that duplication of a part of chromosome 16 is associated with being underweight, defined as a a body mass index below 18.5. Half of all children with the duplication in the study have been diagnosed with a 'failure to thrive', meaning that their rate of weight gain is significantly lower than normal. A quarter of people with the duplication have microcephaly, a condition in which the head and brain are abnormally small, which is associated with neurological defects and shorter life expectancy. Last year, the same researchers discovered that people with a missing copy of these genes are 43 times more likely to be morbidly obese.
Professor Philippe Froguel, from the School of Public Health at Imperial College London, who led the study, said: "The dogma is that we have two copies of each gene, but this isn't really true. The genome is full of holes where genes are lost, and in other places we have extra copies of genes. In many cases, duplications and deletions have no effect, but occasionally they can lead to disease.
"So far, we have discovered a large number of genetic changes that lead to obesity. It seems that we have plenty of systems that increase appetite since eating is so important – you can suppress one and nothing happens. This is the first genetic cause of extreme thinness that has been identified.
"One reason this is important is that it shows that failure to thrive in childhood can be genetically driven. If a child is not eating, it's not necessarily the parents' fault.
"It's also the first example of a deletion and a duplication of one part of the genome having opposite effects. At the moment we don't know anything about the genes in this region. If we can work out why gene duplication in this region causes thinness, it might throw up new potential treatments for obesity and appetite disorders. We now plan to sequence these genes and find out what they do, so we can get an idea of which ones are involved in regulating appetite."
The part of chromosome 16 identified in the study contains 28 genes. Duplications in this region have previously been linked with schizophrenia, and deletions with autism.
###The study was funded by the Medical Research Council, the Wellcome Trust, and other sources.
Notes to editors:
1. Journal reference: S. Jacquemont et al. 'Mirror extreme BMI phenotypes associated with gene dosage at the chromosome 16p11.2 locus.' Nature, 31 August 2011.
2. About Imperial College London
Consistently rated amongst the world's best universities, Imperial College London is a science-based institution with a reputation for excellence in teaching and research that attracts 14,000 students and 6,000 staff of the highest international quality. Innovative research at the College explores the interface between science, medicine, engineering and business, delivering practical solutions that improve quality of life and the environment - underpinned by a dynamic enterprise culture.
Since its foundation in 1907, Imperial's contributions to society have included the discovery of penicillin, the development of holography and the foundations of fibre optics. This commitment to the application of research for the benefit of all continues today, with current focuses including interdisciplinary collaborations to improve global health, tackle climate change, develop sustainable sources of energy and address security challenges.
In 2007, Imperial College London and Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust formed the UK's first Academic Health Science Centre. This unique partnership aims to improve the quality of life of patients and populations by taking new discoveries and translating them into new therapies as quickly as possible.
Website: www.imperial.ac.uk
3. About the Medical Research Council
For almost 100 years the Medical Research Council has improved the health of people in the UK and around the world by supporting the highest quality science. The MRC invests in world-class scientists. It has produced 29 Nobel Prize winners and sustains a flourishing environment for internationally recognised research. The MRC focuses on making an impact and provides the financial muscle and scientific expertise behind medical breakthroughs, including one of the first antibiotics penicillin, the structure of DNA and the lethal link between smoking and cancer. Today MRC funded scientists tackle research into the major health challenges of the 21st century. www.mrc.ac.uk
4. About the Wellcome Trust
The Wellcome Trust is a global charitable foundation dedicated to achieving extraordinary improvements in human and animal health. It supports the brightest minds in biomedical research and the medical humanities. The Trust's breadth of support includes public engagement, education and the application of research to improve health. It is independent of both political and commercial interests.
Website: www.wellcome.ac.uk
'Gene overdose' causes extreme thinness
2011-09-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Doctors' and nurses' hospital uniforms contain dangerous bacteria majority of the time, study shows
2011-09-01
Washington, DC, August 31, 2011 – More than 60 percent of hospital nurses' and doctors' uniforms tested positive for potentially dangerous bacteria, according to a study published in the September issue of the American Journal of Infection Control, the official publication of APIC - the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology.
A team of researchers led by Yonit Wiener-Well, MD, from the Shaare Zedek Medical Center in Jerusalem, Israel, collected swab samples from three parts of the uniforms of 75 registered nurses (RNs) and 60 medical doctors ...
MIABE standard opens up new opportunities in drug discovery
2011-09-01
AUDIO:
This audio file is a brief interview with MIABE coauthors Sandra Orchard, John Overington, Dominic Clark and Christoph Steinbeck of the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute. They briefly discuss the potential impact...
Click here for more information.
An international consortium of pharmaceutical companies, public and commercial data providers and academic groups has agreed on a new standard for describing the effect of a compound on a biological entity. Published in ...
ESC Congress 2011 highlights
2011-09-01
Paris, France, 31 August 2011: "The ESC Congress 2011 in Paris has been a record breaking event" said Prof Michael Böhm, chairman of the ESC Congress Programme Committee. "With a total attendance of 32 946 participants, this is our largest congress ever. We are especially pleased to see that more and more delegates are coming from outside Europe. Large delegations came from Brazil, Japan, China and India this year," said Prof Böhm.
"The quality of the scientific content at the ESC Congress attracts more and more participants each year," explained Prof Böhm. "The medical ...
Researcher identifies nearly 100 studies supporting use of thermal ablation to treat lung cancer
2011-09-01
(Providence, R.I.) – The journal Radiology will publish in its September issue an article written by Damian E. Dupuy, M.D., director of tumor ablation at Rhode Island Hospital, supporting the use of ablation procedures for the treatment of lung cancer. The article, "Image-guided Thermal Ablation of Lung Malignancies," reviews the results of nearly 100 studies conducted between 1991 and 2011 that conclude that image-guided ablation for lung cancer is a successful alternative for patients who cannot withstand surgery due to advanced age or medical comorbidities.
Percutaneous ...
Successful rainwater harvesting systems should combine new technology with old social habits
2011-09-01
As a crippling drought grips much of the Southern and Southwestern United States, the population continues to grow and water resources become scarcer. One way to address the problem is by a combination of modern engineering and ancient social principles, outlined in a new paper on rainwater harvesting that will be presented at the 2011 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition.
Author John Whear, biomedical engineer at the Cancer Therapy & Research Center at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, examines how to manage rainwater ...
NIST achieves record-low error rate for quantum information processing with one qubit
2011-09-01
Thanks to advances in experimental design, physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have achieved a record-low probability of error in quantum information processing with a single quantum bit (qubit)—the first published error rate small enough to meet theoretical requirements for building viable quantum computers.
A quantum computer could potentially solve certain problems that are intractable using today's technology, even supercomputers. The NIST experiment with a single beryllium ion qubit, described in a forthcoming paper,* is a milestone ...
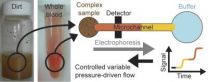
Researchers expand capabilities of miniature analyzer for complex samples
2011-09-01
It's not often that someone can claim that going from a positive to a negative is a step forward, but that's the case for a team of scientists from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and private industry. In a recent paper,* the group significantly extended the reach of their novel microfluidic system for analyzing the chemical components of complex samples. The new work shows how the system, meant to analyze real-world, crude mixtures such as dirt or whole blood, can work for negatively charged components as well as it has in the past for positively ...
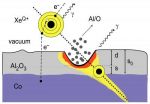
Ion armageddon: Measuring the impact energy of highly charged ions
2011-09-01
Much like a meteor impacting a planet, highly charged ions hit really hard and can do a lot of damage, albeit on a much smaller scale. And much like geologists determine the size and speed of the meteor by looking at the hole it left, physicists can learn a lot about a highly charged ion's energy by looking at the divots it makes in thin films.
Building upon their work for which they were recently awarded a patent,* scientists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and Clemson University have measured the energy of highly charged ion impacts on a ...
Solar industry responsible for lead emissions in developing countries
2011-09-01
Solar power is not all sunshine. It has a dark side—particularly in developing countries, according to a new study by a University of Tennessee, Knoxville, engineering professor.
A study by Chris Cherry, assistant professor in civil and environmental engineering, found that solar power heavily reliant on lead batteries has the potential to release more than 2.4 million tons of lead pollution in China and India.
Lead poisoning causes numerous adverse health effects, including damage to the central nervous system, the kidneys, the cardiovascular system, and the reproductive ...
Word association: Princeton study matches brain scans with complex thought
2011-09-01
In an effort to understand what happens in the brain when a person reads or considers such abstract ideas as love or justice, Princeton researchers have for the first time matched images of brain activity with categories of words related to the concepts a person is thinking about. The results could lead to a better understanding of how people consider meaning and context when reading or thinking.
The researchers report in the journal Frontiers in Human Neuroscience that they used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to identify areas of the brain activated when ...