(Press-News.org) Much like a meteor impacting a planet, highly charged ions hit really hard and can do a lot of damage, albeit on a much smaller scale. And much like geologists determine the size and speed of the meteor by looking at the hole it left, physicists can learn a lot about a highly charged ion's energy by looking at the divots it makes in thin films.
Building upon their work for which they were recently awarded a patent,* scientists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and Clemson University have measured the energy of highly charged ion impacts on a thin film surface for the first time in detail.** Understanding how ions discharge their energy upon impact will help researchers to make better predictive models of how the particles affect surfaces.
The question isn't trivial. Ions are used in exactly that way for a variety of micro- and nanoscale production processes, techniques such as ion milling and etching. Better predictive models may also help researchers curtail ionic erosion where it would be a bad thing, such as inside a fusion reactor.
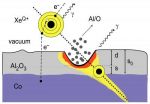
The research team used xenon atoms from which they had stripped all but 10 of the atoms' original 54 electrons. Making an atom so highly ionized takes a lot of energy—about 50,000 electron volts. The atom soaks up all the energy that went into freeing the electrons until it is capable of imparting more energy, and thus more damage, than could be done with kinetic energy—mass and speed—alone.
"When the highly charged ion is finally released and hurtles into its target, most of its energy, about 60 percent, blows back in the 'splash' and dissipates into the vacuum," says Josh Pomeroy. "According to our measurements, 27 percent of the remaining 40 percent of the ion's energy goes into changing the shape of the material—making divots."
Pomeroy says that the remaining 13 percent is most likely converted to heat.
The group first began looking into nanoscale pitting of thin films to help improve the performance of data storage hard drives, which used aluminum oxide thin films as an insulator between magnetic plates. They used ions to pockmark the surface of these films and showed that the depth of the pitting could be determined by measuring minute changes in electrical conductance through the film.
The original motivation for the work has abated, but the group's method and materials remain useful for measuring the energy transfer of highly charged ions and calibrating industrial systems using high-energy ion beams.
INFORMATION:
* United States Patent 7,914,915, "Highly charged ion modified oxide device and method of making same." Inventors: J.M. Pomeroy, H. Grube and A. Perrella. Issued March 29, 2011.
** R.E. Lake, J.M. Pomeroy, H. Grube and C.E. Sosolik. Charge state dependent energy deposition by ion impact. Physical Review Letters. August 5, 2011. http://prl.aps.org/abstract/PRL/v107/i6/e063202.
Ion armageddon: Measuring the impact energy of highly charged ions
2011-09-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Solar industry responsible for lead emissions in developing countries
2011-09-01
Solar power is not all sunshine. It has a dark side—particularly in developing countries, according to a new study by a University of Tennessee, Knoxville, engineering professor.
A study by Chris Cherry, assistant professor in civil and environmental engineering, found that solar power heavily reliant on lead batteries has the potential to release more than 2.4 million tons of lead pollution in China and India.
Lead poisoning causes numerous adverse health effects, including damage to the central nervous system, the kidneys, the cardiovascular system, and the reproductive ...
Word association: Princeton study matches brain scans with complex thought
2011-09-01
In an effort to understand what happens in the brain when a person reads or considers such abstract ideas as love or justice, Princeton researchers have for the first time matched images of brain activity with categories of words related to the concepts a person is thinking about. The results could lead to a better understanding of how people consider meaning and context when reading or thinking.
The researchers report in the journal Frontiers in Human Neuroscience that they used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to identify areas of the brain activated when ...
Iron 'Veins' Are Secret of Promising New Hydrogen Storage Material
2011-09-01
With a nod to biology, scientists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have a new approach to the problem of safely storing hydrogen in future fuel-cell-powered cars. Their idea: molecular scale "veins" of iron permeating grains of magnesium like a network of capillaries. The iron veins may transform magnesium from a promising candidate for hydrogen storage into a real-world winner.
Hydrogen has been touted as a clean and efficient alternative to gasoline, but it has one big drawback: the lack of a safe, fast way to store it onboard a vehicle. ...
Registration Opens September 1 for 4th Annual Renton FilmFrenzy, a 50-Hour Filmmaking Competition with $1,700 in Cash Prizes; Filmmakers will Take Over Renton from Oct. 7-9
2011-09-01
It will be "lights, camera, action" in Renton from October 7-9, when aspiring, ahead of the curve filmmakers take over the city for the fourth annual Renton FilmFrenzy, a 50-hour filmmaking competition. Last year, 25 filmmaking teams competed for $1,700 in cash prizes and the coveted Curvee Awards.
"Thanks to our partnerships with SIFF, Reel Grrls, theFilmSchool, area filmmaking programs, and the Renton Arts Commission, the Renton FilmFrenzy continues to expand and has become an integral part of the growing and strong Renton arts community," said ...
Sandfly saliva provides important clues for new Leishmaniasis treatments
2011-09-01
Bethesda, MD—For millions of people who live under the constant threat of Leishmania infection, a new discovery by Brazilian scientists may lead to new breakthroughs, preventing these parasites from taking hold in the body or reducing the severity of infections once they occur. In a new report appearing in the Journal of Leukocyte Biology (http://www.jleukbio.org), scientists show that specific molecules found in the saliva of the sandfly—a small flying insect that is the vector for the parasite—make it possible for Leishmania to evade neutrophils and live within human ...
Celebrate the Seventh Annual Cobra Polo Classic Benefiting Ronald McDonald House Charities
2011-09-01
Polo is possibly the oldest sport, period. The first experience with a mallet, pony and a round object were recorded nearly two thousand years ago. Polo is the sport known to royalty around the world.
On Sunday, September 11th over twelve-hundred guests will celebrate the seventh annual Cobra Polo Classic benefiting Ronald McDonald House Charities of Spokane. "It is the most prestigious event in the Inland Northwest," reports Mike Forness, RMHC of Spokane Executive Director. Sky divers, gourmet food and wine, cigar and Dry Fly whiskey tent, safari escape women's ...
SER2011 Mexico call to action
2011-09-01
The delegates of the Society for Ecological Restoration´s 4th World Conference on Ecological Restoration (SER2011) congratulate the Parties of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) for their practical and forward looking Strategic Plan 2011-2020, including Targets 14 and 15 in which the Parties have agreed that by 2020, ecosystems of particular importance to water security, human health, and sustainable livelihoods are restored, and their resilience and contribution to carbon stocks enhanced, through conservation and restoration, including the restoration of at ...
2011 AAO-HNSF new oral research daily highlights
2011-09-01
San Francisco, CA – The 2011 Annual Meeting & OTO EXPO of the American Academy of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery Foundation (AAO-HNSF), the largest meeting of ear, nose, and throat doctors in the world, will convene September 11-14, 2011, in San Francisco, CA.
Featuring more than 386 scientific research sessions, 468 posters, and several hundred instruction course hours for attendees, the annual meeting is a unique opportunity for journalists from around the world to cover breaking science and medical news. Reporters will have access to the latest research and ...
Scientists unravel the cause of rare genetic disease: Goldman-Favre Syndrome explained
2011-09-01
Bethesda, MD—A new research report published in The FASEB Journal (https://www.fasebj.org) will help ophthalmologists and scientists better understand a rare genetic disease that causes increased susceptibility to blue light, night blindness, and decreased vision called Enhanced S-Cone Syndrome or Goldman-Favre Syndrome. In the report, scientists found that the expression of genes responsible for the healthy renewal of rods and cones in the retina was reduced and that this problem originates in the photoreceptors themselves rather than in the adjacent retinal pigment epithelial ...
'Pink ribbon dollars' help fill financial gaps for breast cancer programs
2011-09-01
A new study shows that donations collected by check boxes on state income tax forms, fees from license plates and revenue from state lottery tickets have raised millions for breast cancer research and prevention programs across the country, according to researchers at Washington University in St. Louis.
"We found that revenue-generating breast cancer initiatives can be a successful strategy for states to raise funds, or 'pink ribbon dollars,' for prevention and early detection programs," says Amy A. Eyler, PhD, research associate professor at the Brown School of Social ...