New harmonized cardiovascular treatment guidelines make heart disease treatment easier
2011-09-13
(Press-News.org) A new set of harmonized guidelines for the management of risk factors for cardiovascular disease will make it much easier for physicians to care for their patients, according to the authors of the C-CHANGE guidelines published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) (pre-embargo link only) http://www.cmaj.ca/site/embargo/cmaj101508.pdf.
The Canadian Cardiovascular Harmonized National Guideline Endeavour (C-CHANGE) Initiative harmonized and integrated more than 400 separate recommendations from 8 sets of guidelines into one comprehensive but simplified resource. Differing guidelines can lead to conflicting recommendations and become barriers to good treatment, and the guidelines group simplified and distilled practice and evidence down to 89 recommendations to help clinicians diagnose and manage risk factors for cardiovascular disease in their patients.
"With an aging patient population burdened with multiple chronic diseases, practitioners are challenged to provide the most effective guidelines-based medical management for their patients with multiple comorbidities," writes Dr. Peter Liu, cardiologist at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre, University Health Network and University of Toronto, with coauthors. The complexity and discrepancy of the recommendations paradoxically became a barrier to good health care.
Harmonization and integration of guidelines is becoming increasingly important because of the growing emphasis on multidisciplinary care. Other regions and countries such as Europe, the United States and New Zealand are moving to harmonize guidelines.
"The [C-CHANGE] harmonized set of recommendations is intended to be consistent, scientifically rigorous and nonredundant, and to positively influence health outcomes," state the authors. This should lead to a more evidence-based approach and effective health care for our patients.
The guidelines provide recommendations on screening, diagnostic strategies and treatment, including changes to health behaviours and pharmaceutical treatments for all the major cardiovascular risk factors that can lead to complications such as stroke, heart attack and sudden cardiac death.
INFORMATION:
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2011-09-13
Young children who watch fast-paced, fantastical television shows may become handicapped in their readiness for learning, according to a new University of Virginia study published in the October issue of the journal Pediatrics.
U.Va. psychologists tested 4-year-old children immediately after they had watched nine minutes of the popular show "SpongeBob SquarePants" and found that their executive function – the ability to pay attention, solve problems and moderate behavior – had been severely compromised when compared to 4-year-olds who had either watched nine minutes of ...
2011-09-13
Monmouth Junction, NJ (September 12, 2011): A new study finds that infections following cardiac device implantations or replacement result in extremely high costs, both financially and in terms of patient mortality, even months after affected patients return home. Infections associated with pacemakers and defibrillators led to 4.8 to 7.7-fold increases in admission mortality, 1.6 to 2.1-fold increases long term mortality, 2.5 to 4.0-fold increases in hospital length of stay, and 1.4 to 1.8-fold increases in cost compared to pacemaker and defibrillator implantations without ...
2011-09-13
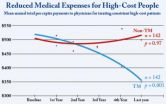
According to a study published this week in the September/October 2011 issue of the American Journal of Health Promotion (Vol. 26, No. 1, pp. 56-60), people with consistently high health care costs experienced a 28 percent cumulative decrease in physician fees after an average of five years practicing the stress-reducing Transcendental Meditation technique compared with their baseline. Both between and within group comparisons were statistically significant. This study has major policy implications.
In most populations, a small fraction of people account for the majority ...
2011-09-13
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- An airplane's digital flight-data recorder, or "black box," holds massive amounts of data, documenting the performance of engines, cockpit controls, hydraulic equipment and GPS systems, typically at regular one-second intervals throughout a flight. Inspectors use such data to reconstruct the final moments of an accident, looking for telltale defects that may explain a crash.
More recently, analysts have probed black-box data in an effort to prevent such accidents from ever occurring. Using software tools that can rapidly search data, operators can ...
2011-09-13
Among the many ways that participation in Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) helps its members stay sober, two appear to be most important – spending more time with individuals who support efforts towards sobriety and increased confidence in the ability to maintain abstinence in social situations. In a paper that will appear in the journal Addiction and has been released online, researchers report the first study to examine the relative importance to successful recovery of the behavior changes associated with participation in AA.
"AA is the most commonly sought source of help ...
2011-09-13
CHICAGO – Lifestyle modifications and pharmaceutical treatment of risk factors for cardiovascular disease are associated with improvement in sexual function among men with erectile dysfunction (ED), according to a meta-analysis posted Online First today in Archives of Internal Medicine, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
"Erectile dysfunction shares modifiable risks factors with atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease (CAD), including hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, cigarette smoking, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and sedentary behavior," according to background ...
2011-09-13
This press release is available in Spanish.
A commercial enzyme could reduce overall costs linked with producing ethanol from grain, and also reduce associated emissions of greenhouse gases, according to a study by U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists and colleagues.
The researchers found that the enzyme helps extract water from an ethanol byproduct used to make dried distillers grains with solubles (DDGS), which can be used as feed supplements for cattle, swine and poultry. This could significantly reduce the amount of electricity, natural gas, energy and ...
2011-09-13
CHICAGO – Repeated exposure of the eye to ophthalmic antibiotics appears to be associated with the emergence of resistant strains of microbes among patients undergoing intraocular injection therapy for neovascular retinal disease, according to a report in the September issue of Archives of Ophthalmology, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
According to background information in the article, more than 8 million people in the United States are affected by age-related macular degeneration, the leading cause of blindness among individuals older than 65 years in this country. ...
2011-09-13
Berkeley – Engineers at the University of California, Berkeley, have shown that it is possible to reduce the minimum voltage necessary to store charge in a capacitor, an achievement that could reduce the power draw and heat generation of today's electronics.
"Just like a Formula One car, the faster you run your computer, the hotter it gets. So the key to having a fast microprocessor is to make its building block, the transistor, more energy efficient," said Asif Khan, UC Berkeley graduate student in electrical engineering and computer sciences. "Unfortunately, a transistor's ...
2011-09-13
Quebec City, September 12, 2011—A study presented today by Université Laval researchers at the 4th World Congress on Sleep Medicine currently underway in Quebec City revealed that the risk of insomnia is 67% higher in people from families in which at least one member is an insomniac.
The research team, directed by Dr. Charles M. Morin of Université Laval's School of Psychology, came to these conclusions following a study involving 3,485 people. The participants were asked to answer a telephone survey on their sleep quality and that of their immediate families. On three ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New harmonized cardiovascular treatment guidelines make heart disease treatment easier