(Press-News.org) ST. PAUL, Minn. – In a first of its kind study, researchers have found that using two way audio-video telemedicine to deliver stroke care, also known as telestroke, appears to be cost-effective for rural hospitals that don't have an around-the-clock neurologist, or stroke expert, on staff. The research is published in the September 14, 2011, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
"In an era of spiraling health care costs, our findings give critical information to medical policy makers," said Jennifer J. Majersik, MD, MS, with the University of Utah School of Medicine in Salt Lake City and a member of the American Academy of Neurology. "If barriers to using telestroke, such as low reimbursement rates and high equipment costs are improved, telestroke has the potential to greatly diminish the striking disparity in stroke care for rural America."
For the study, researchers used existing data from previous telestroke studies, as well as data from large multi-hospital telestroke network databases at the University of Utah Hospitals and Clinics in Salt Lake City and Mayo Clinic in Phoenix. They calculated the cost-effectiveness of telestroke by comparing the costs and quality-adjusted life years of stroke patients treated by telestroke to those treated by usual care such as a rural emergency department without telestroke or a stroke expert available. Quality-adjusted life year is a measure of disease burden based on the number of years of life that would be added by using telestroke and the quality of life during those years.
The study found that the cost of telestroke over a person's lifetime was less than $2,500 per quality-adjusted life year. The threshold of $50,000 per quality-adjusted life year is commonly cited as the cut-off for cost-effectiveness.
In addition, Majersik says telestroke can help with increasing the low number of stroke patients in rural areas receiving tPA, which is the clot-busting drug that can reduce death and disability from stroke but must be given within the first three to 4.5 hours after symptoms begin. "Only two to four percent of stroke patients receive this treatment, with the lowest percentage in rural areas largely because there aren't enough stroke experts with experience using tPA," said Majersik. "Telestroke has the potential to lower this barrier by providing long-distance consultation to rural areas, increasing the expertise and quality of stroke care at rural hospitals."
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute.
The American Academy of Neurology, an association of more than 24,000 neurologists and neuroscience professionals, is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, brain injury, Parkinson's disease and epilepsy. For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit http://www.aan.com.
END
Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Eating low-fat yoghurt whilst pregnant can increase the risk of your child developing asthma and allergic rhinitis (hay fever), according to recent findings.
The study will be presented at the European Respiratory Society's (ERS) Annual Congress in Amsterdam on 25 September 2011. All the abstracts for the ERS Congress will be publicly available online from today (17 September 2011).
The study aimed to assess whether fatty acids found in dairy products could protect against the development of allergic diseases in children.
The researchers ...
The crystal structure of the dynamin protein — one of the molecular machines that makes cells work — has been revealed, bringing insights into a class of molecules with a wide influence on health and disease.
"It's a really cool structure," said Jodi Nunnari, professor and chair of molecular and cellular biology at UC Davis and senior author of the paper, to be published Sept. 18 in the journal Nature. "This is a really important class of molecules for regulating membrane dynamics."
The detailed structure reveals exactly how the dynamin protein can form large assemblies ...
SAN DIEGO, CA and PHILADELPHIA, PA – September 18, 2011 —Tarsa Therapeutics today presented positive safety and efficacy data from its Phase III ORACAL trial of OSTORA™, the company's oral recombinant salmon calcitonin tablet in development for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. These data were presented at the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research 2011 Annual Meeting by ORACAL investigator Neil Binkley, MD, who is an Associate Professor of Endocrinology and Geriatrics at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health in Madison, ...
VIDEO:
Receptors on the cell's surface crowd around the nanotube, effectively standing it upright. The cell mistakes the tube for a sphere and begins to engulf it.
Click here for more information.
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — It's been long known that asbestos spells trouble for human cells. Scientists have seen cells stabbed with spiky, long asbestos fibers, and the image is gory: Part of the fiber is protruding from the cell, like a quivering arrow that's found ...
Researchers have developed a new method to sequence and analyze the dark matter of life—the genomes of thousands of bacteria species previously beyond scientists' reach, from microorganisms that produce antibiotics and biofuels to microbes living in the human body.
Scientists from UC San Diego, the J. Craig Venter Institute and Illumina Inc., published their findings in the Sept. 18 online issue of the journal Nature Biotechnology. The breakthrough will enable researchers to assemble virtually complete genomes from DNA extracted from a single bacterial cell. By contrast, ...
BOULDER -- The planet's deep oceans at times may absorb enough heat to flatten the rate of global warming for periods of as long as a decade even in the midst of longer-term warming, according to a new analysis led by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR).
The study, based on computer simulations of global climate, points to ocean layers deeper than 1,000 feet (300 meters) as the main location of the "missing heat" during periods such as the past decade when global air temperatures showed little trend. The findings also suggest that several more intervals ...
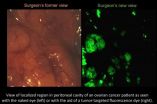
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - The first fluorescence-guided surgery on an ovarian cancer patient was performed using a cancer cell "homing device" and imaging agent created by a Purdue University researcher.
The surgery was one of 10 performed as part of the first phase of a clinical trial to evaluate a new technology to aid surgeons in the removal of malignant tissue from ovarian cancer patients. The method illuminates cancer cells to help surgeons identify and remove smaller tumors that could otherwise be missed.
Philip Low, the Ralph C. Corely Distinguished Professor of ...
Scientists at the University of Plymouth have shown, for the first time in an animal, that nanoparticles have a detrimental effect on the brain and other parts of the central nervous system.
They subjected rainbow trout to titanium oxide nanoparticles which are widely used as a whitening agent in many products including paints, some personal care products, and with applications being considered for the food industry. They found that the particles caused vacuoles (holes) to form in parts of the brain and for nerve cells in the brain to die. Although some effects of nanoparticles ...
Production of crop milk, a secretion from the crops of parent birds, is rare among birds and, apart from pigeons, is only found in flamingos and male emperor penguins. Essential for the growth and development of the young pigeon squab, pigeon 'milk' is produced by both parents from fluid-filled cells lining the crop that are rich in fat and protein. Research published in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Genomics uses new technology to study the genes and proteins involved in pigeon 'milk' production and shows that pigeon 'milk' contains antioxidants and immune-enhancing ...
Researchers whose findings on the detrimental impact of some common medicines on elderly people were widely reported earlier in the summer have found that taking a few of these medicines does not appear to cause further cognitive impairment in those already suffering from dementia.
In a paper published today by the journal Age and Ageing, Dr Chris Fox of the University of East Anglia (UEA) and colleagues from a number of other universities and the NHS describe how they studied a clinically representative sample of 224 people with established Alzheimer's dementia who ...