(Press-News.org) WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Sept. 16, 2011 – A study by epidemiologists at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center and colleagues suggests that a high intake of calcium causes prostate cancer among African-American men who are genetically good absorbers of the mineral.
"High dietary intake of calcium has long been linked to prostate cancer but the explanation for this observation has been elusive," said Gary G. Schwartz, Ph.D., associate professor of cancer biology, urology, and public health sciences at Wake Forest Baptist and co-author on the study.
Schwartz and colleagues from the Keck School of Medicine at the University of Southern California (USC) and the Cancer Prevention Institute of California studied 783 African-American men living in the San Francisco and Los Angeles areas, 533 of whom were diagnosed with prostate cancer. They studied the effects of genotype, calcium intake and diet-gene interactions.
The study is one of the few to explore genes related to calcium absorption or to examine diet in a large African-American population. Although prostate cancer is 36 percent more common among African-Americans than in non-Hispanic whites, data on the diet-cancer link primarily comes from Caucasian populations. The team targeted a genetic allele that is more common in populations of African origin than in other populations and which is associated with regulating the absorption of calcium.
In the United States, more than 240,000 men are diagnosed annually with prostate cancer and about 33,720 die from the disease, according to the National Cancer Institute. Only lung cancer kills more American men. According to the Prostate Cancer Foundation, there are no proven strategies for preventing the disease, but changes in diet and lifestyle have shown to reduce the risk of disease progression.
The study, which is now available in the online issue of the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, found that men who reported the highest intake of calcium were two times more likely to have localized and advanced prostate cancer than those who reported the lowest. Men with a genotype associated with poor calcium absorption were 59 percent less likely to have been diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer than men who genetically were the best absorbers of calcium. And, among men with calcium intake below the median, genetically poor absorbers had a 50 percent decreased risk of having advanced prostate cancer than the best absorbers. The final paper is scheduled to appear in the January 2012 print issue.
The results pose somewhat of a "conundrum," said Sue Ann Ingles, Dr.P.H., associate professor of preventive medicine at USC and principal investigator of the study. Although calcium appears to increase risk for prostate cancer, it is essential for bone health and appears to protect against colorectal cancer, she said.
"It may be possible in the future to personalize prevention using this type of genetic knowledge," Schwartz said of the research findings. "But first, we will need to confirm this genetic result among men of other races to be sure that it is the allele that increases the risk of disease, rather than the possibility that we're seeing this result simply because we are studying an allele that is highly associated with African-American men."
He added the findings provide some clarity about the link between calcium and prostate cancer. Unlike age and race, which are fixed risk factors for prostate cancer, diet is modifiable.
"We now have a better understanding of why calcium in diet may increase the risk for prostate cancer and who is at increased risk," Schwartz said. "If our results are confirmed, it gives much better insight into the preventable causes of prostate cancer. So if I know I'm a good absorber of calcium, I may want to be careful about my diet and about the use of calcium supplements."
###The study was funded by grants from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, The Cancer Research Fund of the California Department of Health Services Cancer Research Program and the National Cancer Institute. Co-authors on the paper, in addition to Schwartz and Ingles, include: Glovioell W. Rowland, from USC; and Esther M. John, from the Cancer Prevention Institute and the Department of Health Research and Policy at Stanford University School of Medicine and Stanford Cancer Center.
Media Relations Contacts: Jessica Guenzel, jguenzel@wakehealth.edu, (336) 716-3487; or Bonnie Davis, bdavis@wakehealth.edu, (336) 716-4977.
Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center (www.wakehealth.edu) is a fully integrated academic medical center located in Winston-Salem, N.C. Wake Forest School of Medicine directs the education and research components, with the medical school ranked among the nation's best and recognized as a leading research center in regenerative medicine, cancer, the neurosciences, aging, addiction and public health sciences. Piedmont Triad Research Park, a division of Wake Forest Baptist, fosters biotechnology innovation in an urban park community. Wake Forest Baptist Health, the clinical enterprise, includes a flagship tertiary care hospital for adults, Brenner Children's Hospital, a network of affiliated community-based hospitals, physician practices and outpatient services. The institution's clinical programs and the medical school are consistently recognized as among the best in the country by U.S.News & World Report.
Genetics may explain why calcium increases risk for prostate cancer
Researchers target gene common among African-American men
2011-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Virus a potential future cancer medicine
2011-09-19
In a new project, researchers from LIFE – the Faculty of Life Sciences at the University of Copenhagen – document that the vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) plays a previously unknown dual role in the prevention of a number of cancers. The new findings show that the virus both kills cancer cells and stops the expression of the molecules which certain types of cancer cells produce to hide from the immune system.
Certain types of cancer cells express far too many liquid immunostimulatory molecules, blocking the immune system's ability to recognise them, and enabling them ...
MRI research demonstrates ALS attacks multiple parts of the brain
2011-09-19
Recently published studies by a researcher in the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry demonstrate that ALS – known as Lou Gehrig's disease – damages neurons in parts of the brain responsible for cognition and behaviour.
ALS, which stands for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, is a fatal neurodegenerative disease that eventually leaves patients unable to move, breathe or swallow. Previous research has shown about 50 per cent of patients with ALS also have mild cognitive and behavioural changes, but between five and 15 per cent of patients can have severe changes resulting in dementia. ...
Researchers identify potential molecular target to prevent growth of cancer cells
2011-09-19
GALVESTON, September 16, 2011 – Researchers have shown for the first time that the protein fortilin promotes growth of cancer cells by binding to and rendering inert protein p53, a known tumor suppressor. This finding by researchers at the University of Texas Medical Branch may lead to treatments for a range of cancers and atherosclerosis, which p53 also helps prevent, and appears in the current print issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
"The p53 protein is a critical defense against cancer because it activates genes that induce apoptosis, or the death of cells. ...
Are genes our destiny?
2011-09-19
LA JOLLA, CA -- A "hidden" code linked to the DNA of plants allows them to develop and pass down new biological traits far more rapidly than previously thought, according to the findings of a groundbreaking study by researchers at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies.
The study, published today in the journal Science, provides the first evidence that an organism's "epigenetic" code - an extra layer of biochemical instructions in DNA - can evolve more quickly than the genetic code and can strongly influence biological traits.
While the study was limited to a single ...
Scab resistance in durum wheat
2011-09-19
MADISON, WI, SEPTEMBER 16, 2011 -- Durum wheat is a valuable cereal crop widely used for human consumption in the United States, Canada, and several European countries. Scab or Fusarium head blight is one of the crop's most serious diseases, reducing its grain yield and quality. Current durum cultivars don't have resistance to this widespread disease.
While working on the Durum Germplasm Enhancement Project (DGE), Dr. Prem Jauhar and staff at the USDA-ARS Northern Crop Research Laboratory, Fargo, ND discovered that a diploid wheatgrass contains the genes needed for scab ...
Balloon-based experiment to measure gamma rays 6,500 light years distant
2011-09-19
DURHAM, N.H. – Beginning Sunday, September 18, 2011 at NASA's launch facility in Fort Sumner, New Mexico, space scientists from the University of New Hampshire will attempt to send a balloon up to 130,000 feet with a one-ton instrument payload to measure gamma rays from the Crab Pulsar, the remains of a supernova explosion that lies 6,500 light years from Earth. The launch is highly dependent on weather and wind conditions, and the launch window closes at the end of next week.
The Gamma Ray Polarimeter Experiment (GRAPE), which was designed and built at the Space Science ...
Breeding soybeans for improved feed
2011-09-19
MADISON, WI, SEPTMEBER 12, 2011 -- Modifying soybean seed to increase phosphorus content can improve animal nutrition and reduce feed costs and nutrient pollution. However, further research is needed to commercialize this valuable technology. Knowledge of soybean and other crops such as maize suggest that reducing phytate, the principle storage form of phosphorus in plant tissue, in seeds reduces seed germination and emergence of seedlings in the field. In soybean, however, researchers debate whether this problem exists, and suggest that other factors may be the cause.
New ...
Lasers could be used to detect roadside bombs
2011-09-19
EAST LANSING, Mich. — A research team at Michigan State University has developed a laser that could detect roadside bombs – the deadliest enemy weapon encountered in Iraq and Afghanistan.
The laser, which has comparable output to a simple presentation pointer, potentially has the sensitivity and selectivity to canvas large areas and detect improvised explosive devices – weapons that account for around 60 percent of coalition soldiers' deaths. Marcos Dantus, chemistry professor and founder of BioPhotonic Solutions, led the team and has published the results in the current ...
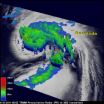
NASA sees power within hurricane Maria as it heads for a landfall in Newfoundland
2011-09-19
VIDEO:
This animation of NOAA's GOES-13 satellite observations from Sept. 6 at 8:45 a.m. EDT through Sept. 16 at 7:45 a.m. EDT shows the movement of Hurricane Katia followed by Tropical...
Click here for more information.
Hurricane Maria joins twelve other hurricanes on record to make landfall in Newfoundland, Canada, and NASA satellite imagery revealed its inner strength.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed over Hurricane Maria on Sept. ...
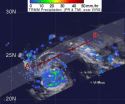
NASA's TRMM satellite sees moderate rainfall Tropical Storm Sonca
2011-09-19
When the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite flew over Tropical Storm Sonca on Friday, Sept. 16 it found moderate rainfall mostly on the southern side of the storm. Chichi Jima can expect some of that rainfall over the weekend as Sonca passes east of the island.
TRMM passed over Tropical Storm Sonca and its precipitation radar instrument saw moderate rainfall occurring mostly on the southern side of the storm, while light-to-moderate rainfall was occurring throughout the storm. The southern edge of the storm had rainfall rates between .78 to 1.57 inches ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Industrial research labs were invented in Europe but made the U.S. a tech superpower
Enzymes work as Maxwell's demon by using memory stored as motion
Methane’s missing emissions: The underestimated impact of small sources
Beating cancer by eating cancer
How sleep disruption impairs social memory: Oxytocin circuits reveal mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities
Natural compound from pomegranate leaves disrupts disease-causing amyloid
A depression treatment that once took eight weeks may work just as well in one
New study calls for personalized, tiered approach to postpartum care
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
Signs on Stone Age objects: Precursor to written language dates back 40,000 years
MIT study reveals climatic fingerprints of wildfires and volcanic eruptions
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
The hidden infections that refuse to go away: how household practices can stop deadly diseases
Ochsner MD Anderson uses groundbreaking TIL therapy to treat advanced melanoma in adults
A heatshield for ‘never-wet’ surfaces: Rice engineering team repels even near-boiling water with low-cost, scalable coating
Skills from being a birder may change—and benefit—your brain
Waterloo researchers turning plastic waste into vinegar
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
[Press-News.org] Genetics may explain why calcium increases risk for prostate cancerResearchers target gene common among African-American men