(Press-News.org) EAST LANSING, Mich. — A research team at Michigan State University has developed a laser that could detect roadside bombs – the deadliest enemy weapon encountered in Iraq and Afghanistan.
The laser, which has comparable output to a simple presentation pointer, potentially has the sensitivity and selectivity to canvas large areas and detect improvised explosive devices – weapons that account for around 60 percent of coalition soldiers' deaths. Marcos Dantus, chemistry professor and founder of BioPhotonic Solutions, led the team and has published the results in the current issue of Applied Physics Letters.
The detection of IEDs in the field is extremely important and challenging because the environment introduces a large number of chemical compounds that mask the select few molecules that one is trying to detect, Dantus said.
"Having molecular structure sensitivity is critical for identifying explosives and avoiding unnecessary evacuation of buildings and closing roads due to false alarms," he said
Since IEDs can be found in populated areas, the methods to detect these weapons must be nondestructive. They also must be able to distinguish explosives from vast arrays of similar compounds that can be found in urban environments. Dantus' latest laser can make these distinctions even for quantities as small as a fraction of a billionth of a gram.
The laser beam combines short pulses that kick the molecules and make them vibrate, as well as long pulses that are used to "listen" and identify the different "chords." The chords include different vibrational frequencies that uniquely identify every molecule, much like a fingerprint. The high-sensitivity laser can work in tandem with cameras and allows users to scan questionable areas from a safe distance.
"The laser and the method we've developed were originally intended for microscopes, but we were able to adapt and broaden its use to demonstrate its effectiveness for standoff detection of explosives," said Dantus, who hopes to net additional funding to take this laser from the lab and into the field.
This research is funded in part by the Department of Homeland Security. BioPhotonic Solutions is a high-tech company Dantus launched in 2003 to commercialize technology invented in a spinoff from his research group at MSU.
###
Michigan State University has been working to advance the common good in uncommon ways for more than 150 years. One of the top research universities in the world, MSU focuses its vast resources on creating solutions to some of the world's most pressing challenges, while providing life-changing opportunities to a diverse and inclusive academic community through more than 200 programs of study in 17 degree-granting colleges.
Lasers could be used to detect roadside bombs
2011-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA sees power within hurricane Maria as it heads for a landfall in Newfoundland
2011-09-19
VIDEO:
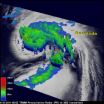
This animation of NOAA's GOES-13 satellite observations from Sept. 6 at 8:45 a.m. EDT through Sept. 16 at 7:45 a.m. EDT shows the movement of Hurricane Katia followed by Tropical...
Click here for more information.
Hurricane Maria joins twelve other hurricanes on record to make landfall in Newfoundland, Canada, and NASA satellite imagery revealed its inner strength.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed over Hurricane Maria on Sept. ...
NASA's TRMM satellite sees moderate rainfall Tropical Storm Sonca
2011-09-19
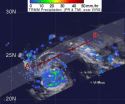
When the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite flew over Tropical Storm Sonca on Friday, Sept. 16 it found moderate rainfall mostly on the southern side of the storm. Chichi Jima can expect some of that rainfall over the weekend as Sonca passes east of the island.
TRMM passed over Tropical Storm Sonca and its precipitation radar instrument saw moderate rainfall occurring mostly on the southern side of the storm, while light-to-moderate rainfall was occurring throughout the storm. The southern edge of the storm had rainfall rates between .78 to 1.57 inches ...
Infrared satellite data shows Tropical Storm Roke strengthening
2011-09-19
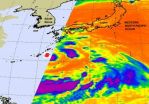
Tropical Storm Roke has changed in size and is starting to change in strength. Roke appears to be consolidating in infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite.
Roke began its life as a monsoon depression with a large low-level circulation center that over time consolidated and organized. The eastern half of Tropical Storm Roke was seen in an infrared image from NASA's Aqua satellite AIRS (Atmospheric Infrared Sounder) on Sept. 15, and it showed a more consolidated center with strong convection and very cold cloud-top temperatures.
Cloud-top temperatures are important ...
Study suggests possible link between two Type 2 diabetes drugs and pancreatic cancer
2011-09-19
Two newer drugs used to treat Type 2 diabetes could be linked to a significantly increased risk of developing pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer, and one could also be linked to an increased risk of thyroid cancer, according to a new UCLA study.
Researchers from the Larry L. Hillblom Islet Research Center at UCLA examined the U.S. Food and Drug Administration's database for adverse events reported between 2004 and 2009 among patients using the drugs sitagliptin and exenatide. They found a six-fold increase in the odds ratio for reported cases of pancreatitis with these ...
People born after World War II are more likely to binge drink and develop alcohol disorders
2011-09-19
September 15, 2011 --. In a review of 31 peer-reviewed and published studies, researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health looked generational and gender differences in alcohol consumption, alcohol disorders, and mortality. Findings indicate that people born after World War II are more likely to binge drink and develop alcohol use disorders. Researchers also found that the gender gap in alcoholism and problem drinking is narrowing in many countries.
Findings will be published in the December 2011 issue of Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research ...
Autism, intellectual disabilities related to parental age, education and ethnicity, not income
2011-09-19
SALT LAKE CITY – New research from the University of Utah in collaboration with the Utah Department of Health (UDOH) shows that the presence or absence of intellectual disability (ID) and autism spectrum disorders (ASD) varies with risk factors such as gender, parental age, maternal ethnicity, and maternal level of education. The study, published Sept. 15, 2011, in Autism Research, also shows that household income level has no association with either ID or ASD, in contrast to what other studies have suggested.
ASDs are a group of childhood neurodevelopmental disorders ...
Good news for rural stroke patients: Virtual stroke care appears cost-effective
2011-09-19
ST. PAUL, Minn. – In a first of its kind study, researchers have found that using two way audio-video telemedicine to deliver stroke care, also known as telestroke, appears to be cost-effective for rural hospitals that don't have an around-the-clock neurologist, or stroke expert, on staff. The research is published in the September 14, 2011, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
"In an era of spiraling health care costs, our findings give critical information to medical policy makers," said Jennifer J. Majersik, MD, MS, ...
Low-fat yogurt intake when pregnant may lead to child asthma and hay fever
2011-09-19
Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Eating low-fat yoghurt whilst pregnant can increase the risk of your child developing asthma and allergic rhinitis (hay fever), according to recent findings.
The study will be presented at the European Respiratory Society's (ERS) Annual Congress in Amsterdam on 25 September 2011. All the abstracts for the ERS Congress will be publicly available online from today (17 September 2011).
The study aimed to assess whether fatty acids found in dairy products could protect against the development of allergic diseases in children.
The researchers ...
Crystal structure shows how motor protein works
2011-09-19
The crystal structure of the dynamin protein — one of the molecular machines that makes cells work — has been revealed, bringing insights into a class of molecules with a wide influence on health and disease.
"It's a really cool structure," said Jodi Nunnari, professor and chair of molecular and cellular biology at UC Davis and senior author of the paper, to be published Sept. 18 in the journal Nature. "This is a really important class of molecules for regulating membrane dynamics."
The detailed structure reveals exactly how the dynamin protein can form large assemblies ...
Osteoporosis Phase III data at 2011 ASBMR Show oral calcitonin tablet is safe and effective
2011-09-19
SAN DIEGO, CA and PHILADELPHIA, PA – September 18, 2011 —Tarsa Therapeutics today presented positive safety and efficacy data from its Phase III ORACAL trial of OSTORA™, the company's oral recombinant salmon calcitonin tablet in development for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. These data were presented at the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research 2011 Annual Meeting by ORACAL investigator Neil Binkley, MD, who is an Associate Professor of Endocrinology and Geriatrics at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health in Madison, ...