(Press-News.org) Our life experiences -- the ups and downs, and everything in between -- shape us, stay with us and influence our emotional set point as adults, according to a new study led by Virginia Commonwealth University researchers.
The study suggests that, in addition to our genes, our life experiences are important influences on our levels of anxiety and depression.
"In this time of emphasis on genes for this and that trait, it is important to remember that our environmental experiences also make important contributions to who we are as people," said principal investigator Kenneth Kendler, M.D., director of the VCU Virginia Institute for Psychiatric and Behavioral Genetics.
"When I was growing up, in talking about the importance of a good diet, we used to say 'You are what you eat.' What this study shows is that to a substantial degree, 'you are what you have experienced.' That is, your life history stays with you in impacting on your background book, for good or for ill," he said.
Kendler, professor of psychiatry, and human and molecular genetics in the VCU School of Medicine, and an international team of researchers from VCU and other universities, analyzed nine data sets of more than 12,000 identical twins with symptoms of depression and/or anxiety through the lifespan.
By studying identical twins, researchers have a pair of individuals who are born with identical genetic compositions and a shared family environment. Their environments may begin to change as they begin to make divergent decisions as they get older that come with lifestyle, diet or friends.
Participants completed reports relating to their own symptoms of anxiety and depression in a five-to-six-year period. The participants varied in age and were from American and European population-based registries.
According to Kendler, statistical models, developed by his colleague Charles Gardner, Ph.D., a research associate in the VCU Department of Psychiatry, were used to observe how components of individual variation changed over time. The team observed that as the twins moved from childhood into late adult life, they increasingly diverged in their predicted levels of symptoms, but after that point, stopped further diverging. Further, they noted that environmental experiences contribute substantially to stable and predictable inter-individual differences in levels of anxiety and depression by mid-life in adults.
###
The study first appeared online Sept. 23, and in the October issue of Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Kendler collaborated with VCU researchers Lindon Eaves, Ph.D., Erik Loken, Ph.D., Judy Silberg, Ph.D., and Charles Gardner, Ph.D.; Nancy Pedersen, Ph.D., and Paul Lichtenstein, Ph.D., with the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden; Christel M. Middeldorp and Dorret Boomsma, with VU University, Amsterdam; and Chandra Reynolds, with the University of California, Riverside.
EDITOR'S NOTE: A copy of the study is available for reporters by email request from the journal Psychological Science by contacting Divya Menon at 202-293-9300 or dmenon@psychologicalscience.org.
About VCU and the VCU Medical Center
Virginia Commonwealth University is a major, urban public research university with national and international rankings in sponsored research. Located on two downtown campuses in Richmond, VCU enrolls more than 32,000 students in 211 certificate and degree programs in the arts, sciences and humanities. Sixty-nine of the programs are unique in Virginia, many of them crossing the disciplines of VCU's 13 schools and one college. MCV Hospitals and the health sciences schools of Virginia Commonwealth University compose the VCU Medical Center, one of the nation's leading academic medical centers. For more, see http://www.vcu.edu.
Virginia Commonwealth University study: We are what we experience
Life experiences influence set point for anxiety and depression
2011-10-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New potential therapeutic target for breast cancer
2011-10-06
New Rochelle, NY, October 5, 2011 -- A possible new target for breast cancer therapy comes from the discovery that the Tyk2 protein helps suppress the growth and metastasis of breast tumors, as reported in Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research, a peer-reviewed journal published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. The article is available free online for the next week at http://www.liebertpub.com/jir.
Qifang Zhang and Andrew Larner, Virginia Commonwealth University (Richmond, VA), and colleagues from VCU, Temple University School of Medicine (Philadelphia, PA), Jagiellonian ...
Atlanta Moving Company Atlanta Peach Movers Advise Extra Care for Moving Specialty Items
2011-10-06
The professionals at Atlanta Peach Movers, a full service Atlanta moving company specializing in local and long distance moves, remind Atlanta residents of the importance of hiring a professional moving service to move fragile or bulky items such as pianos, paintings, or arcade games. These items are valuable and often irreplaceable, and require special care when being moved. The Atlanta long distance movers at Atlanta Peach Movers are highly trained and experienced in moving all types of specialty items.
In addition to Atlanta moving services, Atlanta Peach Movers ...
New study shows inflammatory food toxins found in high levels in infants
2011-10-06
Researchers from Mount Sinai School of Medicine have found high levels of food toxins called Advanced Glycation End products (AGEs) in infants. Excessive food AGEs, through both maternal blood transmission and baby formula, could together significantly increase children's risk for diseases such as diabetes from a very young age. A second study of AGEs in adults found that cutting back on processed, grilled, and fried foods, which are high in AGEs, may improve insulin resistance in people with diabetes. AGEs -- toxic glucose byproducts previously tied to high blood sugar ...
Can peer mentors help teens lose weight? new strategies for combatting teen obesity
2011-10-06
New Rochelle, NY, October 5, 2011 -- Obesity among adolescents has more than tripled over the past 40 years, and recent estimates find that over 18% of teens in the U.S. are obese. Education and mentoring targeting obesity and delivered in high schools by peers has been shown to have a significant impact on teen diet and physical activity, according to a study published in Childhood Obesity, a peer-reviewed journal published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc.(http://www.liebertpub.com) The article "Effect of HealthCorps, a High School Peer Mentoring Program, on Youth Diet and Physical ...
I&K International Limited Offer Customers the Chance to Get a Free Makeup Bag
2011-10-06
I&K International Limited has announced an exciting new offer, whereby clients at Hairtrade.com will receive a free makeup bag when they buy any 3 items at the online store.
Customers shopping at Hairtrade.com - the UKs leading online hair care and hair extensions supplier - will be able to take advantage of the offer up until the 15th of October 2011.
Hairtrade.com has found a great deal of success since it started to supply all kinds of hair extension products back in 2005, and is now considered a must-visit for shoppers interested in hair extensions and wigs. ...
Invasive melanoma may be more likely in children than adults
2011-10-06
A Johns Hopkins Children's Center study of young people with melanoma, a deadly form of skin cancer, has found that some children have a higher risk of invasive disease than adults.
The study, published online Oct. 5 in the journal Cancer, is believed to be the first to compare disease spread in children and adults, and the results suggest some profound biological differences between childhood and adult melanoma, the researchers say.
The Johns Hopkins team analyzed five years of medical records tracking 717 children and 1,368 young adults (ages 20 through 24) diagnosed ...
Illusory memories can have salutary effects
2011-10-06
"False memories tend to get a bad rap," says developmental psychologist Mark L. Howe, of Lancaster University in England. Indeed, remembering events incorrectly or remembering events that didn't happen can have grave consequences, such as the criminal conviction of an innocent person. "But false memories are a natural outcropping of memory in general. They must have some positive effect, too."
That argument -- that memory illusions were evolutionarily adaptive and remain useful for psychological well being and problem-solving -- is the subject of an intriguing paper in ...
ForexTrading.net Releases New Videographic on the Forex Market
2011-10-06
ForexTrading.net, a new online forex magazine is aiming to keep users updated with all the latest happenings in the world of forex trading, through a videographic that has been published on the site.
The new videographic will give users of the site an overview of the forex trading market, and can even be embedded into users' personal websites or blogs where it can be shared with other interested internet users.
Recent years have seen a number of changes in the forex trading market; not only has the number of people who trade in this manner shot up, but the way in ...
Pitt biologists find 'surprising' number of unknown viruses in sewage
2011-10-06
Though viruses are the most abundant life form on Earth, our knowledge of the viral universe is limited to a tiny fraction of the viruses that likely exist. In a paper published this week in the online journal mBio, researchers from the University of Pittsburgh, Washington University in St. Louis, and the University of Barcelona found that raw sewage is home to thousands of novel, undiscovered viruses, some of which could relate to human health.
There are roughly 1.8 million species of organisms on our planet, and each one is host to untold numbers of unique viruses, ...
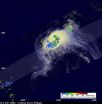
NASA sees wind shear and heavy rainfall in tropical storm Philippe
2011-10-06
Heavy rainfall was occurring in Tropical Storm Philippe's southeastern quadrant when NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite flew over it this week, and the storm continues to strengthen.
Philippe was still a tropical storm when the TRMM satellite passed above on October 3, 2011 at 1806 UTC (2:06 p.m. EDT) but the National Hurricane Center (NHC) predicts that the storm may become a hurricane in a couple days. TRMM's TMI and Precipitation Radar (PR) data showed that bands of powerful convective thunderstorms were still dropping rain at a rate of over ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Virginia Commonwealth University study: We are what we experienceLife experiences influence set point for anxiety and depression