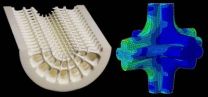
(Press-News.org) The exceptional strength of certain biological materials is due principally to their complex structure. Long bones, for instance, consist of a compact, solid outer casing filled with spongy tissue, which makes them particularly strong and resilient. Researchers from the Fraunhofer Institutes for Mechanics of Materials IWM and for Environmental, Safety and Energy Technology UMSICHT are collaborating on a project entitled "Bionic Manufacturing", which aims to develop products that are lightweight but strong and economic in their use of materials – imitating the perfected structures found in nature. The IWM scientists in Freiburg have taken on the task of identifying the best internal structures for manufactured components. "We have set ourselves the challenge of working as efficiently as nature: The finished component must not weigh more than necessary and yet still be able to perform its mechanical function reliably," explains Dr. Raimund Jaeger of IWM. This approach can be combined with a high degree of creative freedom: "Such components can be used to produce consumer goods with a high aesthetic value, such as designer chairs," adds Jaeger. And if by chance one of these bionically designed objects should break as the result of excessive loading, it will do so in a benign way – collapsing smoothly in localized areas rather than shattering into sharp splinters.
Whereas natural materials have evolved over numerous generations to reach the level of perfection we see today, engineers and product designers have to work much faster. The Freiburg research team has therefore developed a new design method. They start by constructing a virtual model of the future workpiece on the computer, filling out its contours with almost identical, cube-shaped, elementary cells. If the numerical simulation reveals that the grid structure does not satisfy requirements, the cell walls (trabecular microstructure) are refined accordingly. "We make them thicker if they are too weak and thinner if they need to be more pliable, or align them with the force lines along which the load is distributed," explains Jaeger. This method enables many different shapes to be designed around an inner cell structure that can then be evaluated and optimized using the simulation tool. To complement the simulations, the researchers carry out tests on real-life components to verify the structure's mechanical properties.
Jaeger reports that the method has worked very well every time they have used it to design any type of workpiece based on two-dimensional templates that can be pulled into the desired shape using the computer simulation. The same applies to components with a relatively regular shape. Despite their light weight, all of these components are very strong and resilient and capable of absorbing even substantial shocks. According to the scientists, they have potential applications wherever there is a need for products that combine a high level of mechanical stability and aesthetic appearance with low weight – for example medical orthopedic devices or anatomically formed body protectors such as lumbar support belts for skiers.
Fraunhofer UMSICHT is responsible for the technical implementation of the bionic design principles. The solution chosen by the project managers in Oberhausen involves the use of additive manufacturing techniques – in this case selective laser sintering of polymer materials. This technique enables workpieces to be fabricated by laying down successive layers of a fine polyamide powder, which are fused together in the desired configuration using a focused laser beam. It is the ideal method for creating complex internal structures and, at a later stage, components with a distributed pattern of material properties, which experts refer to as functionally graded materials. The resulting structures are similar to those observed in nature.
INFORMATION:
Components based on nature's example
2011-10-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Early C-Sections Place Mothers and Babies at Risk
2011-10-06
A growing number of pregnant American women and delivery doctors are choosing Cesarean sections (C-sections) before their babies reach full term (39 weeks) instead of vaginal birth for the delivery of babies. According to recent studies, the number of C-sections performed in the United States has risen to more than 36 percent.
Driving the increase are both mothers and their physicians. According to a study conducted by Yale researchers, women often choose Cesarean birth for convenience and for cosmetic reasons. Further, Dr. Uma M. Reddy, National Institute of Child ...
Premises Liability: Is a Property Owner Responsible for Your Injury?
2011-10-06
Who is responsible when a person is injured on a property owned by someone else? For example, is a landlord liable for tenant injuries? Premises liability law seeks to identify when the person in possession of the property must compensate someone for injuries that occur on that property.
Because various legal factors -- such as negligence, the status of the visitor or the role the injured person played in the incident -- determine when property owners are responsible, premises liability cases can become highly complex. This makes the advice of a premises liability / ...
Molecular sudoku
2011-10-06
As reported this week in Nature Communications, the researchers used the atomically-sharp tip of a scanning tunneling microscope to move 1-nanometer sized molecules on top of a silver substrate. The tip is controlled with such great accuracy that it is possible to precisely choose the position of each molecule and build tiny molecular squares, crosses, and chains of controlled size and orientation. The same tip is then used as a mobile electrode to probe the electrical conductivity of the molecules as a function of their position in the array. Figures a-d show an example ...
Earlier tracheostomies result in better patient outcomes
2011-10-06
A tracheostomy performed within the first seven days after a severe head injury results in better overall patient outcome, according to a team of Penn State College of Medicine researchers. This is especially true for patients who have a greater chance of surviving when admitted to the hospital.
A tracheostomy is an opening created in the front of the neck directly into the trachea to allow unimpeded breathing. (A tracheotomy is the act of making that opening.)
"The CDC estimates that more than 200,000 individuals are hospitalized annually for traumatic brain injury," ...
Appeals Court Overturns Sex Offender Registration Requirement
2011-10-06
In a recent ruling by the Massachusetts Court of Appeals, the Commonwealth's Sex Offender Registry Board may not require an individual to register as a Level 2 sex offender based solely on a conviction of possessing child pornography.
Massachusetts has three levels of sex offenders, which are based on a person's individual risk of reoffending and the perceived danger to the public. Level 1 offenders have a low risk of committing future crimes and pose a minimal public safety risk. The list of Level 1 offenders is not available to the general public. However, law enforcement ...
Crash-safe battery protection for electric cars
2011-10-06
If an electric car wants to be environmentally friendly it must weigh as little as possible, because when the light turns green every additional pound/kilogram must be accelerated with considerable energy expenditure. And the lighter the electric vehicle, the longer it can be on the road without having to be plugged back into a power outlet. To advance the symbiosis between electromobility and lightweight construction, engineers from the Fraunhofer Institute for Chemical Technology ICT in Pfinztal, Germany, are developing manufacturing concepts that have one goal – they ...
Keep Your Kids Safe This Halloween: Prepare for Common Dangers
2011-10-06
Trick-or-treating is a great way for kids to have fun, create cherished memories and indulge a youthful sweet tooth. But, when caught up in the spirit of the holiday, many parents forget that bumps, bruises and far more frightening injuries are also an unfortunate possibility when an unusual number of children take to the streets.
Pedestrian Accidents Involving Cars and Children Far More Common on October 31
Studies have shown that the number of pedestrian deaths involving children age 15 and younger is 4.5 times higher on Halloween night compared to all other nights ...
More aggressive treatment not necessary for men with a family history of prostate cancer
2011-10-06
MIAMA BEACH, FL (October 5, 2011)––Approximately 10-20 percent of prostate cancer patients have a family history of the disease. There are three major factors that are used to evaluate the extent and aggressiveness of prostate cancer, help make treatment decisions, and estimate prognosis: the Prostate Specific Antigen Level (PSA), Gleason score (GS) from the biopsy, and the digital rectal exam findings (DRE). However, men with a family history of prostate cancer have often been feared to have a more aggressive form of the disease not otherwise represented by these three ...
New research shows PET imaging effective in predicting lung cancer outcomes
2011-10-06
Advanced imaging with Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans shows great promise in predicting which patients with inoperable lung cancer have more aggressive tumors and need additional treatment following standard chemotherapy/radiation therapy, according to new research.
Mitch Machtay, MD, of the Seidman Cancer Center at University Hospitals (UH) Case Medical Center and principle investigator for the study, presented the significant data today at 2 pm at the annual meeting of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) in Miami Beach, Fla. The National Cancer ...
Divorcing During a Difficult Real Estate Market
2011-10-06
In these hard economic times, many couples are sticking together solely because of perceived monetary impediments to divorce. With the right help, however, you may not have to choose between happiness and financial wellbeing.
Divorce and the Economy
According to a study conducted by the University of Virginia, nearly 40 percent of married couples who were planning on a divorce or separation before the recession put their divorce on hold once the economy crashed. While the choice to abandon the pursuit of a divorce is no doubt complex and there are multiple reasons ...