(Press-News.org) A tracheostomy performed within the first seven days after a severe head injury results in better overall patient outcome, according to a team of Penn State College of Medicine researchers. This is especially true for patients who have a greater chance of surviving when admitted to the hospital.
A tracheostomy is an opening created in the front of the neck directly into the trachea to allow unimpeded breathing. (A tracheotomy is the act of making that opening.)
"The CDC estimates that more than 200,000 individuals are hospitalized annually for traumatic brain injury," said Kevin M. Cockroft, M.D., associate professor, neurosurgery. "Severely head-injured patients, particularly those with additional injuries, often require tracheostomy at some point during their hospital stay."
Previous studies have shown mixed results.
"Traditionally, tracheostomy, or 'trach,' has been recommended to prevent airway complications," Cockroft said. "Early trach has been advocated as a means to improve outcome, with various studies suggesting that it may decrease the incidence of pneumonia, reduce intensive care unit days and shorten overall length of stay. Some evidence also exists to suggest that early trach does not improve outcomes. As a result, the timing of trach in these critically ill patients remains controversial."
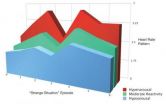
Early trach patients are defined as those who have a tracheostomy performed during the first seven hospital-stay days. Late trach patients are defined as those who have a tracheostomy performed at greater than seven days after admission.
Researchers used data collected from January 1990 through December 2005 by the Pennsylvania Trauma Society Foundation for its statewide trauma registry. Because of a lack of patients with only head injury, researchers looked at patients with injury to at least one other body system. In total, 3,104 patients were included in the study, with 1,577 in the early trach group and 1,527 in the late trach group. It is the largest study to date to report the effects of tracheostomy timing on outcome after a severe head injury.
In the study population, later trach patients were in the hospital three times longer than early trach patients and also spent an average of four times longer in the ICU. Early trach patients were 1.5 times more likely to be discharged in an independent state. However, later trach patients were twice as likely to live to be discharged from the hospital, potentially because more severe cases would receive an earlier trach.
In addition, later trach patients were about twice as likely to suffer from an adverse pulmonary occurrence such as pneumonia, about 1.5 times as likely to suffer a cardiac event such as a heart attack, and 1.5 times more likely to have an infection.
Researchers reported their results in the journal Neurocritical Care. The project was funded by the Departments of Neurosurgery and Public Health Sciences, Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center and Penn State College of Medicine.
"These results indicate a complex relationship between tracheostomy timing and outcome, but suggest that a strategy of early tracheostomy, particularly when performed on patients with a reasonable chance of survival, results in a better overall clinical outcome than when the tracheostomy is performed in a delayed manner," Cockroft said.
INFORMATION:
Other researchers are Elias B. Rizk and Akshal S. Patel, Department of Neurosurgery; Christina M. Stetter and Vernon M. Chinchilli, Department of Public Health Sciences.
END
In a recent ruling by the Massachusetts Court of Appeals, the Commonwealth's Sex Offender Registry Board may not require an individual to register as a Level 2 sex offender based solely on a conviction of possessing child pornography.
Massachusetts has three levels of sex offenders, which are based on a person's individual risk of reoffending and the perceived danger to the public. Level 1 offenders have a low risk of committing future crimes and pose a minimal public safety risk. The list of Level 1 offenders is not available to the general public. However, law enforcement ...
If an electric car wants to be environmentally friendly it must weigh as little as possible, because when the light turns green every additional pound/kilogram must be accelerated with considerable energy expenditure. And the lighter the electric vehicle, the longer it can be on the road without having to be plugged back into a power outlet. To advance the symbiosis between electromobility and lightweight construction, engineers from the Fraunhofer Institute for Chemical Technology ICT in Pfinztal, Germany, are developing manufacturing concepts that have one goal – they ...
Trick-or-treating is a great way for kids to have fun, create cherished memories and indulge a youthful sweet tooth. But, when caught up in the spirit of the holiday, many parents forget that bumps, bruises and far more frightening injuries are also an unfortunate possibility when an unusual number of children take to the streets.
Pedestrian Accidents Involving Cars and Children Far More Common on October 31
Studies have shown that the number of pedestrian deaths involving children age 15 and younger is 4.5 times higher on Halloween night compared to all other nights ...
MIAMA BEACH, FL (October 5, 2011)––Approximately 10-20 percent of prostate cancer patients have a family history of the disease. There are three major factors that are used to evaluate the extent and aggressiveness of prostate cancer, help make treatment decisions, and estimate prognosis: the Prostate Specific Antigen Level (PSA), Gleason score (GS) from the biopsy, and the digital rectal exam findings (DRE). However, men with a family history of prostate cancer have often been feared to have a more aggressive form of the disease not otherwise represented by these three ...
Advanced imaging with Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans shows great promise in predicting which patients with inoperable lung cancer have more aggressive tumors and need additional treatment following standard chemotherapy/radiation therapy, according to new research.
Mitch Machtay, MD, of the Seidman Cancer Center at University Hospitals (UH) Case Medical Center and principle investigator for the study, presented the significant data today at 2 pm at the annual meeting of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) in Miami Beach, Fla. The National Cancer ...
In these hard economic times, many couples are sticking together solely because of perceived monetary impediments to divorce. With the right help, however, you may not have to choose between happiness and financial wellbeing.
Divorce and the Economy
According to a study conducted by the University of Virginia, nearly 40 percent of married couples who were planning on a divorce or separation before the recession put their divorce on hold once the economy crashed. While the choice to abandon the pursuit of a divorce is no doubt complex and there are multiple reasons ...
In the best of circumstances, raising a toddler is a daunting undertaking. But parents under long-term stress often find it particularly challenging to tap into the patience, responsiveness, and energy required for effective child rearing.
Now research from a University of Rochester team helps to explain why chronic stress and parenting are such a toxic mix. The study finds that ongoing strains, like poverty or depression, disrupt the body's natural stress response, making mothers more likely to engage in a host of problematic parenting behaviors, including neglect, ...
In 2010, more than 2,000 businesses went through an immigration audit. And this year, ICE has already audited many more companies, including sending out 1,000 notification letters to businesses in early June alone. In a time when employers have enough to worry about, they must also make concerted efforts to ensure their employees are legally qualified to work in the U.S.
Under the Obama administration, the focus on illegal immigration has moved from undocumented immigrants to their potential employers. Gone are the days of loud immigration raids like the ones we saw ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers recently isolated 63 unique dust particles from their laboratory – and that's just the beginning.
The chemists were testing a new kind of sensor when dust got stuck inside it, and they discovered that they could measure the composition of single dust particles.
In a recent issue of The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, they describe how the discovery could aid the study respiratory diseases caused by airborne particles.
Most dust is natural in origin, explained James Coe, professor of chemistry at Ohio State University. The 63 particles ...
Property rights are one of the essential tenets of our society. According to one California eminent domain attorney, property owners are entitled to use their property how they see fit within the bounds of the law. However, there are instances where the government is entitled to infringe upon one's property to support the greater good of the community. This is called eminent domain.
Under the principle of eminent domain, it is the government's right to "take" private property for public use. When a "taking" occurs, a municipality must pay fair market ...