(Press-News.org) In the best of circumstances, raising a toddler is a daunting undertaking. But parents under long-term stress often find it particularly challenging to tap into the patience, responsiveness, and energy required for effective child rearing.
Now research from a University of Rochester team helps to explain why chronic stress and parenting are such a toxic mix. The study finds that ongoing strains, like poverty or depression, disrupt the body's natural stress response, making mothers more likely to engage in a host of problematic parenting behaviors, including neglect, hostility, and insensitivity.
"Stress gets under your skin," explains Melissa Sturge-Apple, assistant professor of psychology at the University of Rochester and lead author on the Development and Psychopathology paper to be published October 19. "It literally changes the way a mother's body responds to the normal demands of small children and those changes make it much harder to parent positively."
Although the effects of stress have been well documented in children and linked to a variety of diseases in adults, this is one of the first studies to look specifically at stress and parenting, according to the researchers. The findings point to the corrosive effects of poverty or depression on an individual's physiology and help to explain why people feel and act the way they do when faced with ongoing psychological or economic pressure, she says.
"Stress is not just in our heads, it's in our bodies," says Sturge-Apple.
This is also the first study to measure physiological stress response in real time, says Fred Rogosch, research director at the University of Rochester's Mt. Hope Family Center and a fellow author on the paper. Participants' reactions were captured using a novel wireless electrocardiograph (ECG) monitor developed for the study by University of Rochester engineers Zeljko Ignjatovic and Wendi Heinzelman. The unobtrusive device allowed the team to analyze subtle changes in participants' heart rhythms as they were happening, providing a non-behavioral window into how the study moms were reacting. Other methods, such as measuring the stress hormone cortisol, require a 20-minute delay and are not nearly as precise, explains Rogosch.
The new monitor could become an important tool for measuring stress outside of the lab, the authors write. For example, it could be used in clinical settings as a kind of emotional biofeedback monitor, giving therapists a way to quantitatively gage which therapies work best for alleviating negative emotions, according to the researchers.
In the study, the researchers observed 153 mothers and their 17-to-19-month-old children in individual two-hour sessions. Using the wireless ECG monitor, each mother's stress response was measured during a mildly distressing situation in which her child was left with a stranger for a few minutes. Later the mother and toddler were videotaped during unstructured playtime together.
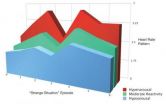
The study showed that a mother's stress system can be compromised by becoming either overactive or underactive. In mothers with higher depressive symptoms, stress responses were "hyperactive", the researchers found. These moms' heart rate patterns began higher, then spiked when their toddler was upset. After the mom was reunited with the child, their heart rate pattern remained elevated. During the free-play sessions, mothers with hyperactive stress responses engaged in the highest levels of hostility with their toddler, including derogatory comments, angry tone of voice, and rough physical interaction.
Although the popular image of depression is of someone who is listless and sad, Sturge-Apple points out that the study confirms what clinicians have long observed: that depression in mothers sometimes is linked to harsh, highly reactive parenting, not subdued mothering. This study helps to explain the biological basis of such behavior; the stress response systems of moms suffering from depression are on high alert, oversensitive to social stressors and unable to calm down, explains Sturge-Apple.
By contrast, study participants who struggled with poverty and lived in high-crime neighborhoods exhibited underactive, or "hypoactive," stress response systems. Their heart rates patterns began lower and rose little during their child's distress. During free play, these parents showed the highest levels of disengagement along with intrusive parenting. Although instructed to play with their children, these mothers were more likely to ignore their little ones and not respond to children's bids for attention or play. When they were engaged, mothers with hyporesponsive stress activity were overbearing. The researchers argue that the dampened physiological response to a child's anguish results from the "cumulative wear and tear … of living in poverty and dangerous neighborhoods." Faced with threats and concerns on a daily basis, these moms' stress systems simply become overwhelmed, concludes Sturge-Apple.
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by the National Institute of Nursing Research.
Michael Skibo, a doctoral student in social and clinical psychology at the University of Rochester, also contributed to the publication.
About the University of Rochester
The University of Rochester (www.rochester.edu) is one of the nation's leading private universities. Located in Rochester, N.Y., the University gives students exceptional opportunities for interdisciplinary study and close collaboration with faculty through its unique cluster-based curriculum. Its College, School of Arts and Sciences, and Hajim School of Engineering and Applied Sciences are complemented by its Eastman School of Music, Simon School of Business, Warner School of Education, Laboratory for Laser Energetics, School of Medicine and Dentistry, School of Nursing, Eastman Institute for Oral Health, and the Memorial Art Gallery.
How chronic stress short-circuits parenting
2011-10-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Immigration Audits and Your Business
2011-10-06
In 2010, more than 2,000 businesses went through an immigration audit. And this year, ICE has already audited many more companies, including sending out 1,000 notification letters to businesses in early June alone. In a time when employers have enough to worry about, they must also make concerted efforts to ensure their employees are legally qualified to work in the U.S.
Under the Obama administration, the focus on illegal immigration has moved from undocumented immigrants to their potential employers. Gone are the days of loud immigration raids like the ones we saw ...
1 room -- 63 different dust particles? Researchers aim to build dust library
2011-10-06
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers recently isolated 63 unique dust particles from their laboratory – and that's just the beginning.
The chemists were testing a new kind of sensor when dust got stuck inside it, and they discovered that they could measure the composition of single dust particles.
In a recent issue of The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, they describe how the discovery could aid the study respiratory diseases caused by airborne particles.
Most dust is natural in origin, explained James Coe, professor of chemistry at Ohio State University. The 63 particles ...
Eminent Domain and the Government's Right to Take Away Your Property
2011-10-06
Property rights are one of the essential tenets of our society. According to one California eminent domain attorney, property owners are entitled to use their property how they see fit within the bounds of the law. However, there are instances where the government is entitled to infringe upon one's property to support the greater good of the community. This is called eminent domain.
Under the principle of eminent domain, it is the government's right to "take" private property for public use. When a "taking" occurs, a municipality must pay fair market ...
Managing Medical Debt Through Bankruptcy
2011-10-06
The sluggish economy is not only affecting job growth in the United States, it is also spurring more debt due to medical expenses. According to study conducted by the Commonwealth Fund, 57 percent of workers who lost jobs that previously had health insurance have become uninsured. This creates two problems for those who become sick: Not only do they no longer have health insurance to defray medical expenses, they also lack the income to pay such costs out of pocket.
The Commonwealth Fund also found that debt collection companies contacted 30 million Americans in 2010 ...
MIT research: Career path closed, must take detour
2011-10-06
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- Technology firms frequently require workers to sign non-compete agreements, which typically bar their employees from joining rival companies for one to two years. For firms, the agreements keep workers from taking the knowledge and skills they have acquired and using them to help a rival.
But a new study of more than 1,000 engineers, conducted by an MIT professor, shows that non-compete agreements come with a high cost for employees: When those workers do shift jobs, roughly one-third of them end up leaving their chosen industry altogether, often ...
Spousal Support Reform Is Not As Good As It Looks on Paper
2011-10-06
Over the past few years, a movement to reform spousal support (called "alimony" and "spousal maintenance" in some states) has been making its way across the nation. Spousal support in its traditional form consists of the money-earning spouse providing financial support to the other spouse after a divorce. The amount of spousal support can be agreed upon or calculated based on the earning spouse's ability to pay and the needs of the non-earning spouse.
Because of changing times -- in which more and more wives and mothers work outside the home -- many ...
Report reveals economic, social costs of hunger in America
2011-10-06
The Great Recession and the currently tepid economic recovery swelled the ranks of American households confronting hunger and food insecurity by 30 percent. In 2010 48.8 million Americans lived in food insecure households, meaning they were hungry or faced food insecurity at some point during the year. That's 12 million more people than faced hunger in 2007, before the recession, and represents 16.1 percent of the U.S. population.
Yet hunger is not readily seen in America. We see neither newscasts showing small American children with distended bellies nor legions of thin, ...
Collectivism and bribery
2011-10-06
Why are some places more prone to bribery and corruption than others? Part of the answer seems to be the level of collective feeling in a society, according to research by Pankaj Aggarwal, University of Toronto Scarborough (UTSC) professor of marketing in the Department of Management, and Nina Mazar, University of Toronto professor of marketing.
Aggarwal and Mazar discovered that people in more collectivist cultures – in which individuals see themselves as interdependent and as part of a larger society – are more likely to offer bribes than people from more individualistic ...
Saving the Social Security Trust Fund from Washington Politicians
2011-10-06
Before Congress passed a budget deal in early August 2011, President Obama expressed concern in a televised speech that the federal government would be unable to pay Social Security benefits without a long-term agreement on the budget. Others in Washington, including President Obama's budget director Jack Lew and Senate majority leader Harry Reid, disputed the president's assertion, maintaining that Social Security is a self-funding program with a $2.6 trillion trust fund that is capable of funding benefit payments for the next 25 years. How could politicians deliver such ...
Zinc's role in the brain
2011-10-06
Zinc plays a critical role in regulating how neurons communicate with one another, and could affect how memories form and how we learn. The new research, in the current issue of Neuron, was authored by Xiao-an Zhang, now a chemistry professor at the University of Toronto Scarborough (UTSC), and colleagues at MIT and Duke University.
Researchers have been trying to pin down the role of zinc in the brain for more than fifty years, ever since scientists found high concentrations of the chemical in synaptic vesicles, a portion of the neuron that stores neurotransmitters. ...