(Press-News.org) AMHERST, Mass. -- New research based on post-hospital arrival data from U.S. trauma centers finds that even after adjusting for differences in injury severity, gun use, and other likely causes of race difference in death from assault, African-Americans have a significantly higher overall post-scene of injury mortality rate than whites. The study was conducted by Anthony R. Harris, emeritus professor of sociology at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, and colleagues and published in August by the Journal of Trauma, Injury, Infection and Critical Care.
The study, from a nationally representative sample of trauma centers, covered the period from 2005-08 and adjusted for types of weapons used, severity of injury, age, physiological condition, year, and trauma center differences. It concluded that, in addition to insurance status, among patients brought to the Level I and II trauma centers, race is a substantial independent predictor of who dies from assault. Blacks, especially the uninsured, have significantly worse outcomes overall, though there is some evidence that this pattern is minimized at higher levels of injury severity.
Black patients showed higher overall raw mortality rates from assault than whites (8.9 percent vs. 5.1 percent), but after statistical adjustment, the researchers found the black to white adjusted risk ratio for death from assault (homicide) dropped significantly. After adjustment, estimated black deaths were 29 percent in excess of white deaths for firearm injuries, 36 percent in excess for cutting/piercing injuries, and 61 percent in excess for blunt injuries. Uninsured blacks comprised 76 percent of all excess trauma center deaths from assault.
Harris says that the findings are consistent with the bulk of the medical research findings on race and insurance disparities in hospital outcomes from causes other than intentional assault. But he also notes that, as is the case with almost all of these studies, the causes of the disparities are not easily identified. He adds:
"The observed disparities raise questions about the social causes of the very large black/white difference in overall U.S. homicide victimization rates (about 7 to 1) and have important implications for individual lives, including whether or not a victim remains a victim in an assault case or becomes a victim in a homicide case. The victim's outcome is, in turn, likely to impact the chances the offender will be apprehended and, if so, faced with a charge of aggravated assault or of homicide. Unlike other medical outcomes, in the case of intentional assault, insurance and racial disparities in hospital mortality are thus likely to affect no less than two separate parties, and, often, two or more unrelated families."
###
The study, by Harris and Gene A. Fisher, both of UMass Amherst, and Dr. Stephen H. Thomas, of the University of Oklahoma School of Medicine, is based on data from the National Sample Program, the National Trauma Data Bank's representative sample of 100 Level I and Level II U.S. trauma centers.
The analysis represents an estimated 137,618 black and white assault cases aged 15 years and older. The sample includes 35 percent white, and 65 percent black patients, with 46 percent of the whites and 60 percent of the blacks identified as uninsured.
In 2009, Harris, received a two-year grant from the Harry Frank Guggenheim Foundation to research race differences in homicidal outcomes from criminal injury. The study was conducted in part by Harris as visiting scientist with the department of criminology and criminal justice at the University of Maryland, College Park.
Harris received national and international media attention in 2002 with a study, also co-authored with Fisher and Thomas, that found improvements in emergency medical services dramatically suppressed murder rates in the U.S. from 1960-99. The study noted that this 40-year trend held even though weapons became more lethal and available during the period, and overall criminal assault rates rose steeply.
Contact:
Anthony R. Harris, 413/296-8070, abobharris@verizon.net
Patrick J. Callahan, 413/545-0444, pjcall@admin.umass.edu
Researchers find race disparity in post-hospital arrival homicide deaths at trauma centers
2011-10-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
People without cars, financial assets less likely to marry: study
2011-10-10
A study published this week in the American Journal of Sociology finds that people who lack personal wealth in the form of a car or financial assets are significantly less likely to enter into a first marriage. The results, according to study author Daniel Schneider of Princeton University, shed light on recent changes in marriage patterns in the U.S.
For the past few decades, Americans have been getting married later in life and are becoming more likely forego marriage altogether. Between 1970 and 2000, the median age of first marriage in the U.S. rose by about four ...
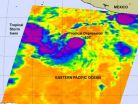
NASA's Aqua satellite sees birth of two tropical cyclones in Eastern Pacific
2011-10-10
The tropics in the eastern Pacific were quiet for a couple of days after Hurricane Hilary dissipated, and today gave birth to Tropical Depression 10 and Tropical Storm Irwin. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of both storms and saw the powerful convection in the center of Irwin that enabled the storm to go from a depression to a tropical storm in a short time.
The eleventh tropical depression quickly grew into Tropical Storm Irwin this morning, as strong convection surged around its center of circulation. That convection (rising air that creates the thunderstorms ...
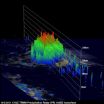
A 3-D look at Philippe provided clues of transition into a hurricane
2011-10-10
Tropical Storm Philippe took its time to strengthen into a hurricane because of wind shear problems. The wind shear lessened, and Philippe became a hurricane today, after 12 days of moving across the Atlantic Ocean. NASA's TRMM satellite saw towering thunderstorms and intense rainfall within Philippe yesterday, which provided forecasters with a clue that the storm was strengthening. Philippe reached hurricane status this morning, Oct. 6, 2011.
Over two days, the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite provided forecasters with cloud heights and rainfall rates ...
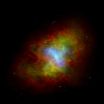
Astrophysicists spot pulsed radiation from Crab Nebula that wasn't supposed to be there
2011-10-10
An international collaboration of astrophysicists, including a group from the Department of Physics in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, has detected pulsed gamma rays from the neutron star at the heart of the Crab Nebula with energies far higher than the common theoretical models can explain.
The pulsed gamma rays had energies between 100 and 400 billion electronvolts (Gigaelectronvolts, or GeV), far higher than 25 GeV, the highest energy radiation from the neubla previously detected. A 400 GeV photon is 11 orders of magnitude – almost a trillion ...
Crab Pulsar emits light at highest energies ever detected in a pulsar system, scientists report
2011-10-10
An international team of scientists has detected the highest energy gamma rays ever observed from a pulsar, a highly magnetized and rapidly spinning neutron star.
The VERITAS experiment measured gamma rays coming from the Crab Pulsar at such large energies that they cannot be explained by current scientific models of how pulsars behave, the researchers said.
The results, published today in the journal Science, outline the first observation of photons from a pulsar system with energies greater than 100 billion electron volts -- more than 50 billion times higher than ...
Sniffing out the brain's predictive power
2011-10-10
CHICAGO --- In the moments before you "stop and smell the roses," it's likely your brain is already preparing your sensory system for that familiar floral smell. New research from Northwestern Medicine offers strong evidence that the brain uses predictive coding to generate "predictive templates" of specific smells -- setting up a mental expectation of a scent before it hits your nostrils.
Predictive coding is important because it provides animals -- in this case, humans -- with a behavioral advantage, in that they can react more quickly and more accurately to stimuli ...
Study uncovers why anti-rejection drugs for transplant patients cause hypertension
2011-10-10
PORTLAND, Ore. — Modern medicine's ability to save lives through organ transplantation has been revolutionized by the development of drugs that prevent the human body from rejecting the transplanted organ.
But those antirejection drugs have their own side effects — sometimes serious.
A group of researchers led by scientists at Oregon Health & Science University has discovered the process that may be causing many of those side effects. And the discovery means those side effects likely can be dealt with cheaply and easily — with a class of widely used drugs that are often ...
Bone marrow cells migrate to tumors and can slow their growth
2011-10-10
Philadelphia, PA, October 6, 2011 – Bone marrow-derived cells (BMDCs) participate in the growth and spread of tumors of the breast, brain, lung, and stomach. To examine the role of BMDCs, researchers developed a mouse model that could be used to track the migration of these cells while tumors formed and expanded. Their results, published in the November issue of The American Journal of Pathology, strongly suggest that more effective cancer treatments may be developed by exploiting the mechanism by which bone marrow cells migrate to tumors and retard their proliferation.
"Our ...
Raising 'good' cholesterol levels reduces heart attack and stroke risk in diabetes patients
2011-10-10
Increasing levels of high-density lipoproteins, better known as HDL or "good" cholesterol, reduced the risk for heart attack and stroke among patients with diabetes. That's according to a new study appearing online today in The American Journal of Cardiology.
The observational study, one of the largest of its kind, examined the medical records of more than 30,000 patients with diabetes and also found that patients whose HDL levels decreased had more heart attacks and strokes.
Researchers studied patients with diabetes because they are more prone to heart disease ...
'Non-invasive' cultivar? Buyer beware
2011-10-10
Cultivars of popular ornamental woody plants that are being sold in the United States as non-invasive are probably anything but, according to an analysis by botanical researchers published in the October issue of BioScience. Tiffany M. Knight of Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri, and her coauthors at the Chicago Botanic Garden write that the claims of environmental safety are in most cases based on misleading demographic evidence that greatly underestimates the plants' invasive potential. What is more, the offspring of cultivars do not usually "breed true" and ...