(Press-News.org) Volcanologists from the Universities of Leicester and Durham have forensically reconstructed the impact of a meteorite on Earth and how debris was hurled from the crater to devastate the surrounding region.
New research by Mike Branney, of the University of Leicester's Department of Geology, and Richard Brown, University of Durham, shows that some aspects of giant meteorite impacts onto Earth may mimic the behaviour of large volcanic eruptions.
Meteorite impacts are more common than is popularly appreciated – but what happens when the meteorite hits? Direct observation is understandably difficult, but researchers pick through impact debris that has been spared the ravages of erosion, to forensically reconstruct the catastrophic events.
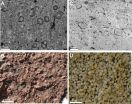
Mike Branney and Richard Brown analysed an ejecta layer derived from the impact of a huge meteorite and discovered that much of the ejected debris moved across the ground as rapid, dense, ground-hugging currents of gas and debris, remarkably similar to the awesome pyroclastic density currents that flow radially outwards from explosive volcanoes.
Dr Branney said: "In particular, the way that ash and dust stick together seems identical. Moist ash from explosive volcanoes sticks together in the atmosphere to fall out as mm-sized pellets. Where these drop back into a hot pyroclastic density current, they grow into larger layered structures, known as accretionary lapilli."
The researchers studied a finely preserved deposit in northwest Scotland from a huge impact that occurred a billion years ago. It shows both types of these 'volcanic' particles - pellets and lapilli - are produced.
Dr Brown added: "This reveals that that the 10 meter-thick layer, which has been traced for over 50 km along the Scottish coast, was almost entirely emplaced as a devastating density current that sped outwards from the point of impact - just like a density current from a volcano. Only the uppermost few centimetres actually fell out through the atmosphere. "
The Leicester and Durham scientists say that an improved understanding of what happens when large objects hits the Earth will help us understand how these catastrophic events may have affected life on the planet in the past ...and possibly in the future.
INFORMATION:
Note to editors
Publication: Branney, M.J. & Brown, R.J. 2011. Impactoclastic density current emplacement of terrestrial meteorite-impact ejecta and the formation of dust pellets and accretionary lapilli: evidence from Stac Fada, Scotland. Journal of Geology 119, 275-292.
Contact: Dr. Mike Branney, Department of Geology, University of Leicester. E-mail mjb26@le.ac.uk
CSI-style investigation of meteorite hits on Earth
Geologists assess deep impacts of near-Earth object strikes
2011-10-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Medicaid Planning: Establish a Framework to Protect Your Future Security
2011-10-19
Since 1990, health care expenditures in the United States have increased by more than 300 percent, reaching an annual total of approximately $2.5 trillion. This is more than eight times the $253 billion spent on health care in 1980.
Considering the aging American population, no one expects these costs to go anywhere but up. It is more important than ever to plan well for the possibility of a major health event later in life. With adequate forethought, and the proper help, Medicaid planning can help you hang on to the assets you have worked your whole life to collect.
Legal ...
New York's Scaffold Law Supports Work Place Safety
2011-10-19
On September 20, 2011, seventeen people were injured when a building scaffold collapsed onto a city bus in Harlem. Fortunately, the injuries of the scaffolding accident were minor, because the people waiting at the bus stop got on the bus moments before the collapse. The Department of Building had issued a stop-work order and will be issuing violations to the demolition contractor.
Not only can innocent bystanders be injured in scaffolding accidents, those who work in construction are also at risk. Construction is physically demanding and dangerous work. In 2009, 29 ...
Can we share vampires' appetite for synthetic blood?
2011-10-19
Vampires on the True Blood television series are already enjoying the advantages of synthetic blood. While this may seem to be only the imagination on the big screen, the true benefits of blood manufactured from embryonic stem cells may be less than a decade away.
It is unclear however whether society can develop an acceptance of cultured blood - or an appetite for synthetic meat produced by related technology. For this reason it is vital the public has every opportunity to get involved with the latest developments in stem cell research, say researchers from the Economic ...
Premature babies at risk of ill health in later life, research suggests
2011-10-19
Young adults who were born prematurely show multiple biological signs of risks to future health, research from Imperial College London has found. The scientists, reporting their findings tomorrow in the journal Pediatric Research, say that the research indicates that urgent work is now needed to monitor preterm babies into adulthood to improve the detection of early signs of disease.
The study of 48 volunteers aged 18-27 found that those who were born at 33 weeks of gestation or less had higher blood pressure, more fat tissue despite having a normal Body Mass Index, and ...
Light dependency underlies beneficial jetlag in racehorses
2011-10-19
A new study has shown that racehorses are extremely sensitive to changes in daily light and, contrary to humans, can adapt very quickly to sudden shifts in the 24-hour light-dark cycle, such as those resulting from a transmeridian flight, with unexpected benefits on their physical performance.
The research led by academics in the University of Bristol's Faculty of Medical and Veterinary Sciences is published in the Journal of Neuroendocrinology.
This is the first study of its kind to investigate the effects of jetlag on the physiology and performance of racehorses ...
Hospital heart attack death rates improving but very elderly still missing out
2011-10-19
Despite substantial reductions in the hospital death rates for heart attack patients across all age groups, there are still worrying inequalities in heart attack management for the elderly, a new study has shown.
The research, carried out by the University of Leeds, UK and funded by the British Heart Foundation, showed that the risk of a heart patient dying in hospital almost halved across all age groups between 2003 and 2010. Specialist treatments – such as coronary angioplasty – to open blocked or narrowed arteries that supply blood to the heart are also much more widely ...
Unknown species and larval stages of extremely long-legged beetles discovered by DNA test
2011-10-19
The research program AQUA Palawana has been exploring the unique freshwater biodiversity of the Philippine Island and biosphere reserve of Palawan for more than a decade. Scientists from the Senckenberg Museum of Zoology Dresden and the Bavarian State Collections of Zoology in Munich have now described larvae and a new species of the curious Spider Water Beetles (Ancyronyx) from this biodiversity hotspot. Their study was realized in cooperation with the Palawan Council for Sustainable Development and the De La Salle University Manila.
The scientists conducting this study, ...
Fellow-Servant Rule Bars Suit Against Injured Employer, Co-Worker in NJ
2011-10-19
The relationship between personal injury law and workers' compensation law requires careful explanation.
The New Jersey Superior Court, Appellate Division's decision in McDaniel v. Lee shows how the court applied the State's Workers' Compensation Act in a motor vehicle accident case to bar a third-party lawsuit against the plaintiff's co-worker. This is known as the fellow-servant rule, which provides an injured employee's co-workers with immunity from personal injury lawsuits. Although workers' compensation claims are handled differently than personal injury lawsuits, ...
Simple nerve cells regulate swimming depth of marine plankton
2011-10-19
As planktonic organisms the larvae of the marine annelid Platynereis swim freely in the open water. They move by activity of their cilia, thousands of tiny hair-like structures forming a band along the larval body and beating coordinately. With changing environmental conditions the larvae swim upward and downward to their appropriate water depth. Scientists of the Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology in Tübingen, Germany have now identified some signalling substances in the larval nervous system regulating swimming depth of the larvae. These substances influence ...
More poor kids in more poor places, Carsey Institute finds
2011-10-19
DURHAM, N.H. – Persistent high poverty is most prevalent among children, with those living in rural America disproportionally impacted, according to researchers from the Carsey Institute at the University of New Hampshire.
"Nearly 22 percent of America's children live in poverty, compared with 14 percent of the total population. Poverty is scattered and geographically concentrated, and it ebbs and flows with economic cycles. However, in some parts of the country, poverty has persisted for generations," the researchers said.
Areas with persistent high child poverty are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
[Press-News.org] CSI-style investigation of meteorite hits on EarthGeologists assess deep impacts of near-Earth object strikes