(Press-News.org) HOUSTON -- (Oct. 20, 2011) -- Giant flakes of graphene oxide in water aggregate like a stack of pancakes, but infinitely thinner, and in the process gain characteristics that materials scientists may find delicious.
A new paper by scientists at Rice University and the University of Colorado details how slices of graphene, the single-atom form of carbon, in a solution arrange themselves to form a nematic liquid crystal in which particles are free-floating but aligned.
That much was already known. The new twist is that if the flakes – in this case, graphene oxide – are big enough and concentrated enough, they retain their alignment as they form a gel. That gel is a handy precursor for manufacturing metamaterials or fibers with unique mechanical and electronic properties.
The team reported its discovery online this week in the Royal Society of Chemistry journal Soft Matter. Rice authors include Matteo Pasquali, a professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering and of chemistry; James Tour, the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of mechanical engineering and materials science and of computer science; postdoctoral research associate Dmitry Kosynkin; and graduate students Budhadipta Dan and Natnael Behabtu. Ivan Smalyukh, an assistant professor of physics at the University of Colorado at Boulder, led research for his group, in which Dan served as a visiting scientist.
"Graphene materials and fluid phases are a great research area," Pasquali said. "From the fundamental point of view, fluid phases comprising flakes are relatively unexplored, and certainly so when the flakes have important electronic properties.
"From the application standpoint, graphene and graphene oxide can be important building blocks in such areas as flexible electronics and conductive and high-strength materials, and can serve as templates for ordering plasmonic structures," he said.
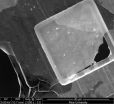
By "giant," the researchers referred to irregular flakes of graphene oxide up to 10,000 times as wide as they are high. (That's still impossibly small: on average, roughly 12 microns wide and less than a nanometer high.) Previous studies showed smaller bits of pristine graphene suspended in acid would form a liquid crystal and that graphene oxide would do likewise in other solutions, including water.
This time the team discovered that if the flakes are big enough and concentrated enough, the solution becomes semisolid. When they constrained the gel to a thin pipette and evaporated some of the water, the graphene oxide flakes got closer to each other and stacked up spontaneously, although imperfectly.
"The exciting part for me is the spontaneous ordering of graphene oxide into a liquid crystal, which nobody had observed before," said Behabtu, a member of Pasquali's lab. "It's still a liquid, but it's ordered. That's useful to make fibers, but it could also induce order on other particles like nanorods."
He said it would be a simple matter to heat the concentrated gel and extrude it into something like carbon fiber, with enhanced properties provided by "mix-ins."
Testing the possibilities, the researchers mixed gold microtriangles and glass microrods into the solution, and found both were effectively forced to line up with the pancaking flakes. Their inclusion also helped the team get visual confirmation of the flakes' orientation.
The process offers the possibility of the large-scale ordering and alignment of such plasmonic particles as gold, silver and palladium nanorods, important components in optoelectronic devices and metamaterials, they reported.
Behabtu added that heating the gel "crosslinks the flakes, and that's good for mechanical strength. You can even heat graphene oxide enough to reduce it, stripping out the oxygen and turning it back into graphite."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors of the paper are Angel Martinez and Julian Evans, graduate students of Smalyukh at the University of Colorado at Boulder.
The Institute for Complex Adaptive Matter, the Colorado Renewable and Sustainable Energy Initiative, the National Science Foundation, the Air Force Research Lab, the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the Welch Foundation, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Environmental Quality and Installation Program and M-I Swaco supported the research.
Read the abstract at http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2011/sm/c1sm06418e
Download images at
http://www.media.rice.edu/images/media/NEWSRELS/1020_Graphene1.jpg
http://www.media.rice.edu/images/media/NEWSRELS/1020_Graphene_drawing.jpg
CAPTIONS
(flake)
A single flake of graphene oxide roughly 40 microns wide, seen under an electron microscope, sits atop a copper support. Such "giant" flakes form into a gel-like liquid crystal in solution. (Credit Rice University/University of Colorado at Boulder)
(illustration)
Graphene oxide flakes in a solution align themselves with a director, a dimensionless vector that represents the preferred orientation of particles in a liquid crystal. (Credit Rice University/University of Colorado at Boulder)
Giant flakes make graphene oxide gel
Rice, Colorado discovery could boost metamaterials, high-strength fibers
2011-10-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA, NOAA data show significant Antarctic ozone hole remains
2011-10-22
WASHINGTON -- The Antarctic ozone hole, which yawns wide every Southern Hemisphere spring, reached its annual peak on Sept. 12. It stretched to 10.05 million square miles, the ninth largest ozone hole on record. Above the South Pole, the ozone hole reached its deepest point of the season on Oct. 9, tying this year for the 10th lowest in this 26-year record.
NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) use balloon-borne instruments, ground-based instruments and satellites to monitor the annual Antarctic ozone hole, global levels of ozone in the stratosphere ...
Nearby planet-forming disk holds water for thousands of oceans
2011-10-22
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---For the first time, astronomers have detected around a burgeoning solar system a sprawling cloud of water vapor that's cold enough to form comets, which could eventually deliver oceans to dry planets.
Water is an essential ingredient for life. Scientists have found thousands of Earth-oceans' worth of it within the planet-forming disk surrounding the star TW Hydrae. TW Hydrae is 176 light years away in the constellation Hydra and is the closest solar-system-to-be.
University of Michigan astronomy professor Ted Bergin is a co-author of a paper on the ...
'Trading places' most common pattern for couples dealing with male depression: UBC study
2011-10-22
University of British Columbia researchers have identified three major patterns that emerge among couples dealing with male depression. These can be described as "trading places," "business as usual" and "edgy tensions."
Published in the Social Science & Medicine journal and led by UBC researcher John Oliffe, the paper details how heterosexual couples' gender roles undergo radical shifts and strain when the male partner is depressed and the female partner seeks to help. Depression, a disorder often thought of as a women's health issue, is underreported in men, and little ...
Pitt/UPMC: Exceptional cognitive and physical health in old age leaves immunological fingerprint
2011-10-22
PITTSBURGH, Oct. 20 – Exceptional cognitive and physical function in old age leaves a tell-tale immunologic fingerprint, say researchers at the University of Pittsburgh and Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC. Likewise, older adults who have mild impairments bear a distinct immunologic pattern, too, according to findings published today in the Public Library of Science: One.
Old age is not synonymous with impairment and disability, noted lead investigator Abbe N. de Vallejo, Ph.D., associate professor of pediatrics and immunology, University of Pittsburgh School ...
Researchers at NYU Langone Medical Center review the microbiome and its possible role in cancers
2011-10-22
(New York City, October 20, 2011) In the October 20th edition of the journal Cell Host and Microbe, Drs. Claudia Plottel and Martin J. Blaser of the Departments of Medicine and Microbiology at NYU Langone Medical Center, and the Department of Biology at New York University, present a model for understanding how cancer evolves in humans based on an understanding of the bacteria living in our body, the microbiome.
The authors suggest that the bacteria that reside in us play a crucial role in maintaining our health. This starts early in our lives, when a newborn is "seeded" ...
Children with certain dopamine system gene variants respond better to ADHD drug
2011-10-22
CINCINNATI – Children with certain dopamine system gene variants have an improved response to methylphenidate - the most commonly prescribed medication for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder - in a finding that could help eliminate the guesswork from prescribing effective medications for children with ADHD.
Researchers reporting their results in the Oct. 21 Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry tested 89 children with ADHD between ages 7 and 11. They found that children with specific variants of the dopamine transporter (DAT) and dopamine ...
US residents say Hawaii's coral reef ecosystems worth $33.57 billion per year
2011-10-22
A peer-reviewed study commissioned by NOAA shows the American people assign an estimated total economic value of $33.57 billion for the coral reefs of the main Hawaiian Islands.
"The study shows that people from across the United States treasure Hawaii's coral reefs, even though many never get to visit them," said Jane Lubchenco, Ph.D., under secretary of commerce for oceans and atmosphere and NOAA administrator. "It illustrates the economic value of coral reefs to all Americans, and how important it is to conserve these ecosystems for future generations."
"We are ...
Study highlights issues faced by friends and family of the suicidal
2011-10-22
A study focusing on the family and friends of people who were suicidal has highlighted the main challenges they face when trying to judge whether a person is in danger and decide what they should do about it.
The research was carried out by Dr. Christabel Owens from the Peninsula College of Medicine and Dentistry, supported by Devon NHS Partnership Trust and funded by the UK Medical Research Council. The findings are published in the British Medical Journal on 22nd October 2011 (online 19th October 2011).
Researchers investigated 14 suicides aged 18-34 in London, the ...
NIPPV linked to increased hospital mortality rates in small group of patients
2011-10-22
Although increased use of noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation (NIPPV) nationwide has helped decrease mortality rates among patients hospitalized with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a small group of patients requiring subsequent treatment with invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) have a significantly higher risk of death than those placed directly on IMV, according to researchers in the United States who studied patterns of NIPPV use.
The findings were published online ahead of the print edition of the American Thoracic Society's American Journal of ...
Simple lifestyle changes can add a decade or more healthy years to the average lifespan
2011-10-22
Vancouver − Health prevention strategies to help Canadians achieve their optimal health potential could add a decade or more of healthy years to the average lifespan and save the economy billions of dollars as a result of reduced cardiovascular disease, says noted cardiologist Dr. Clyde Yancy.
Dr. Yancy, who will deliver the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada Lecture at the opening ceremonies of the Canadian Cardiovascular Congress in Vancouver this Sunday, will tell delegates that people who follow seven simple steps to a healthy life can expect to live an ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Visible light-driven deracemization of α-aryl ketones synergistically catalyzed by thiophenols and chiral phosphoric acid
Most AI bots lack basic safety disclosures, study finds
How competitive gaming on discord fosters social connections
CU Anschutz School of Medicine receives best ranking in NIH funding in 20 years
Mayo Clinic opens patient information office in Cayman Islands
Phonon lasers unlock ultrabroadband acoustic frequency combs
Babies with an increased likelihood of autism may struggle to settle into deep, restorative sleep, according to a new study from the University of East Anglia.
National Reactor Innovation Center opens Molten Salt Thermophysical Examination Capability at INL
International Progressive MS Alliance awards €6.9 million to three studies researching therapies to address common symptoms of progressive MS
Can your soil’s color predict its health?
Biochar nanomaterials could transform medicine, energy, and climate solutions
Turning waste into power: scientists convert discarded phone batteries and industrial lignin into high-performance sodium battery materials
PhD student maps mysterious upper atmosphere of Uranus for the first time
Idaho National Laboratory to accelerate nuclear energy deployment with NVIDIA AI through the Genesis Mission
Blood test could help guide treatment decisions in germ cell tumors
New ‘scimitar-crested’ Spinosaurus species discovered in the central Sahara
“Cyborg” pancreatic organoids can monitor the maturation of islet cells
Technique to extract concepts from AI models can help steer and monitor model outputs
Study clarifies the cancer genome in domestic cats
Crested Spinosaurus fossil was aquatic, but lived 1,000 kilometers from the Tethys Sea
MULTI-evolve: Rapid evolution of complex multi-mutant proteins
A new method to steer AI output uncovers vulnerabilities and potential improvements
Why some objects in space look like snowmen
Flickering glacial climate may have shaped early human evolution
First AHA/ACC acute pulmonary embolism guideline: prompt diagnosis and treatment are key
Could “cyborg” transplants replace pancreatic tissue damaged by diabetes?
Hearing a molecule’s solo performance
Justice after trauma? Race, red tape keep sexual assault victims from compensation
Columbia researchers awarded ARPA-H funding to speed diagnosis of lymphatic disorders
James R. Downing, MD, to step down as president and CEO of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in late 2026
[Press-News.org] Giant flakes make graphene oxide gelRice, Colorado discovery could boost metamaterials, high-strength fibers