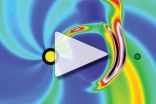
(Press-News.org) NOAA is now using a sophisticated forecast model that substantially improves predictions of space weather impacts on Earth. Better forecasts offer additional protection for people and the technology-based infrastructure we use daily.
Explosions in the sun's outer atmosphere – tracked and forecast by NOAA scientists – can cause geomagnetic and solar radiation storms at Earth that can impede the operation of electrical power grids, interfere with the normal function of Global Positioning Systems and temporarily hamper radio and satellite telecommunications. Grid and satellite operators and airlines can take protective measures when stormy conditions are forecast.
"This advanced model has strengthened forecasters' understanding of what happens in the 93 million miles between Earth and the sun following a solar disturbance," said Tom Bogdan, director of NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center in Boulder, Colo. "It will help power grid and communications technology managers know what to expect so they can protect infrastructure and the public."
Magnetic storms can occur on Earth 1 days after a coronal mass ejection – a burst of charged particles and magnetic field that streams out from the sun at more than one million miles an hour. Before development of this model, forecasters could predict timing of such impacts within a 30-hour window, on average. The new model allows forecasters to narrow that window to 12 hours.
That improvement gives airline operators more reliable information about when to reroute flights to avoid communications blackouts from storms. Satellite operators can avoid changing orbit or orientation when space weather threatens. Oil drilling, mining and other operations that rely on global positioning systems – which can be made unreliable by space weather – can avoid conditions that might put operators at risk. Power companies can work to prevent problems.
"The shorter prediction timeframe will enable the electric industry to better prepare for potential issues," said Gerry Cauley, president and chief executive officer of the North American Electric Reliability Corporation. "The continued improvement of forecasting through innovation and modernization of the existing satellite infrastructure is vital to support the reliability of North America's bulk electric system."
The new model, WSA-Enlil, combines two advanced models, the Wang-Sheeley-Arge (WSA) and Enlil (named for the Sumerian god of wind). These linked numerical forecast models simulate physical conditions and phenomena from the base of the sun's corona out into interplanetary space, to Earth and beyond. Space weather scientists "inject" solar events into the WSA-Enlil model to understand how the space weather storm system is likely to unfold.
INFORMATION:
Scientists with NOAA, NASA, the Air Force Research Laboratory, the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES) at the University of Colorado at Boulder, Boston University, the National Center for Atmospheric Research and George Mason University collaborated to develop the model.
The model has been used in experimental mode for several months and has accurately forecast the timing of recent space weather events. NOAA began running the new model on its supercomputers officially on September 30. Recent model run results are available online at www.swpc.noaa.gov/wsa-enlil/ambient.
NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center in Boulder, Colo. is the nation's official source of operational forecasts, warnings and alerts about space weather.
NOAA's mission is to understand and predict changes in the Earth's environment, from the depths of the ocean to the surface of the sun, and to conserve and manage our coastal and marine resources. Visit us online at www.noaa.gov or on Facebook at www.facebook.com/usnoaagov.
On the Web:
NOAA:
www.noaa.gov
NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC):
www.swpc.noaa.gov
WSA-Enlil model, current conditions:
www.swpc.noaa.gov/wsa-enlil/ambient
Space weather prediction model improves NOAA's forecast skill
2011-10-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Panera Bread Locations of the Bronx Celebrates Autumn with Seasonally-Inspired Flavors
2011-10-22
Autumn at Panera Bread is all about the best ingredients and flavors that warm from the inside out. To celebrate the transition into Fall, Panera is offering a variety of seasonally inspired flavors with the return of some favorite feel-good foods and the introduction of exciting new items.
New this Fall is the Roasted Turkey Artichoke Panini. Made with all-natural roasted turkey, artichoke-Parmesan spread, roasted red peppers, caramelized onions and fresh baby spinach, all expertly grilled on Asiago Cheese Focaccia, it can be savored alone or paired with Panera's Mac ...
Hudson Valley Panera Bread Locations Celebrate Autumn with Seasonally-Inspired Flavors
2011-10-22
Autumn at Panera Bread is all about the best ingredients and flavors that warm from the inside out. To celebrate the transition into Fall, Panera is offering a variety of seasonally inspired flavors with the return of some favorite feel-good foods and the introduction of exciting new items.
New this fall is the Roasted Turkey Artichoke Panini. Made with all-natural roasted turkey, artichoke-Parmesan spread, roasted red peppers, caramelized onions and fresh baby spinach, all expertly grilled on Asiago Cheese Focaccia, it can be savored alone or paired with Panera's Mac ...
Scientists determine family tree for most-endangered bird family in the world
2011-10-22
Using one of the largest DNA data sets for a group of birds and employing next-generation sequencing methods, Smithsonian scientists and collaborators have determined the evolutionary family tree for one of the most strikingly diverse and endangered bird families in the world, the Hawaiian honeycreepers.
Not only have the researchers determined the types of finches that the honeycreeper family originally evolved from, but they have also linked the timing of that rapid evolution to the formation of the four main Hawaiian Islands.
"There were once more than 55 species ...
Homicide, suicide outpace traditional causes of death in pregnant, postpartum women
2011-10-22
AUGUSTA, Ga. – Violent deaths are outpacing traditional causes of maternal mortality, such as hemorrhage and preeclampsia, and conflicts with intimate partner are often a factor, researchers report.
"We found that the mortality rate from homicide and suicide were more common than what we think of as traditional causes of maternal mortality," said Dr. Christie L. Palladino, an obstetrician-gynecologist and educational researcher at Georgia Health Sciences University. "It's not what you want to read, but it's the reality."
The analysis of the Centers for Disease Control ...
Panera Bread Celebrates Autumn with Seasonally-Inspired Flavors in Westchester County
2011-10-22
Autumn at Panera Bread is all about the best ingredients and flavors that warm from the inside out. To celebrate the transition into Fall, Panera is offering a variety of seasonally inspired flavors with the return of some favorite feel-good foods and the introduction of exciting new items.
New this Fall is the Roasted Turkey Artichoke Panini. Made with all-natural roasted turkey, artichoke-Parmesan spread, roasted red peppers, caramelized onions and fresh baby spinach, all expertly grilled on Asiago Cheese Focaccia, it can be savored alone or paired with Panera's Mac ...
New drug strategies for Alzheimer's, multiple sclerosis examined at UH
2011-10-22
HOUSTON, Oct. 20, 2011 – Researchers at the University of Houston (UH) are recommending a new strategy for developing drugs to treat cancer, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's and cardiovascular diseases.
In an invited review published in the October issue of Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, scientists at the Center for Nuclear Receptors and Cell Signaling (CNRCS) at UH outline the results of years of research following the team's 1996 discovery of the estrogen receptor beta (ERβ).
"We have known for some time that female sex hormones – estrogens – influence a number ...
West Nile virus transmission linked with land-use patterns and 'super-spreaders'
2011-10-22
After its initial appearance in New York in 1999, West Nile virus spread across the United States in just a few years and is now well established throughout North and South America.
Both the mosquitoes that transmit it and the birds that are important hosts for the virus are abundant in areas that have been modified by human activities.
As a result, transmission of West Nile virus is highest in urbanized and agricultural habitats.
"The virus has had an important impact on human health in the United States partly because it took advantage of species that do well around ...
Inconsistent evaluations may affect promotion of women in law firms
2011-10-22
Los Angeles, CA (October 20, 2011)- Partners in Wall Street law firms write equally nice things about the work of their male and female junior lawyers, but when they use hard numbers, they rate the men higher, according to a study in the current Social Psychological and Personality Science (published by SAGE).
The use of positive language may be to soften the blow of low evaluations or they may be based on lower expectations of female performance based on stereotypes, write Monica Biernat, of the University of Kansas, M.J. Tocci of Fulcrum Advisors and Joan Williams ...
Giant flakes make graphene oxide gel
2011-10-22
HOUSTON -- (Oct. 20, 2011) -- Giant flakes of graphene oxide in water aggregate like a stack of pancakes, but infinitely thinner, and in the process gain characteristics that materials scientists may find delicious.
A new paper by scientists at Rice University and the University of Colorado details how slices of graphene, the single-atom form of carbon, in a solution arrange themselves to form a nematic liquid crystal in which particles are free-floating but aligned.
That much was already known. The new twist is that if the flakes – in this case, graphene oxide – ...
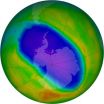
NASA, NOAA data show significant Antarctic ozone hole remains
2011-10-22
WASHINGTON -- The Antarctic ozone hole, which yawns wide every Southern Hemisphere spring, reached its annual peak on Sept. 12. It stretched to 10.05 million square miles, the ninth largest ozone hole on record. Above the South Pole, the ozone hole reached its deepest point of the season on Oct. 9, tying this year for the 10th lowest in this 26-year record.
NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) use balloon-borne instruments, ground-based instruments and satellites to monitor the annual Antarctic ozone hole, global levels of ozone in the stratosphere ...