(Press-News.org) UK doctors are willing to cite alcohol as a cause of death on death certificates, but not smoking, for fear of stigmatising the deceased, shows research published online in the Journal of Clinical Pathology.
This has implications for the true extent of the impact of smoking on health, say the researchers, who point out that the current statistical estimates of the death toll from smoking are potentially flawed.
They looked at just over 2,000 death certificates and 236 post mortem reports, issued at a large London teaching hospital between 2003 and 2009, to see what cause of death doctors had cited.
Doctors have been allowed to cite smoking and alcohol as a direct or underlying cause of death without the need to refer the case to a coroner since 1992.
Smoking was identified as the cause of death in only two certificates (0.1% of the total) and included in part II of the death certificate, which outlines other contributory conditions, in only 10 cases (0.5% of the total).
The two cases in which smoking was cited were lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Yet 279 deaths included these diagnoses, and in most cases the deceased was a current (over 45%) or former (over 23%) smoker. It is well known that smoking is the primary cause of both lung cancer and COPD.
In all, 407 deaths were caused by conditions in which smoking is thought to have a substantial role. Yet smoking was cited as the cause of death in only two of these certificates and as a contributory factor in six.
The post mortem reports were no better: not a single case cited smoking as causing or contributing to death, which the authors describe as "surprising."
Yet doctors willingly cited alcohol as a direct or contributory cause of death. This was cited in over half (57.4%) of the 54 death certificates, which included diagnoses linked to alcohol use.
"Death certification is an important source of mortality data and directly captures 99.79% of all deaths in the UK," say the authors, who point out that the doctors in this study are not unique in their reluctance to cite smoking as a cause of death.
"There are many reasons why smoking is not cited as a [cause of death] by doctors in the UK," they write. "The first and frequently debated reason relates to doctors' desire not to cause relatives distress by stigmatising the deceased and their smoking habit."
They continue: "While the results of this study would support this assumption, it is interesting that the same clinicians frequently cited alcohol use as an underlying cause of death."
This may be because alcohol use is generally more accepted culturally, suggest the authors, adding that the stigma associated with smoking is well documented, and may be worsening as a result of the recent legislation, banning smoking in public places.
"Given the overwhelming evidence showing a causal link between smoking and certain terminal conditions, more effort should be made to record smoking on the death certificate. It is clear that the current arrangements fail to achieve this," they conclude.
INFORMATION: END
Humans may have undergone a gradual rather than an abrupt transition from fishing, hunting and gathering to farming, according to a new study of ancient pottery.
Researchers at the University of York and the University of Bradford analysed cooking residues preserved in 133 ceramic vessels from the Western Baltic regions of Northern Europe to establish whether these residues were from terrestrial, marine or freshwater organisms.
The research led by Oliver Craig (York) and Carl Heron (Bradford) included an international team of archaeologists from The Heritage Agency ...
b-pack announces Rehmann recently chooses b-pack's Purchase-to-Pay Solution to implement their new Procurement and Asset Management strategy. The main objective is to quickly set up these functions with an Innovative On Demand solution.
One of the critical imperative of Rehmann was to bring visibility to their purchasing processes and also control their costs more efficiently. Selected in October 2011, b-pack was the best Purchase-to-Pay solution provider to implement Rehmann's new Procurement and Asset Management strategy.
Using b-pack, Rehmann is now able to track ...
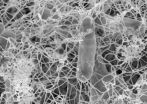
COLUMBUS, Ohio – New research suggests that some patients develop a potentially deadly blood infection from their implanted cardiac devices because bacterial cells in their bodies have gene mutations that allow them to stick to the devices.
Patients with implants can develop infections because of a biofilm of persistent bacterial bugs on the surfaces of their devices. Researchers found that some strains of the bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus, have just a few genetic variants in the proteins on their surfaces that make them more likely to form these biofilms.
The research ...
US Chemicals isn't your typical multi-million dollar chemical corporation. From a staff that's made up of roughly 80 percent women to corporate nutritionists to entryway waterfalls, the Darien, Conn. based company is really one-of-a-kind.
CEO Carol Piccaro, daughter of founder Howard T. Von Oehsen, wouldn't have it any other way.
"Corporate wellness is really important to me," Picarro explains. "Stress can kill you. We've tried to develop a different type of workplace here, and I think it really has a lot to do with wellness and performance and all ...
Originally founded as Blackman Field Services in 1989, Inter-Chillers has since seen its name change, but its commitment to excellence in the field of Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration (HVACR) continues to prosper throughout the reaches of Australia.
Based in Sydney and with an office in Melbourne, the company has extensive experience in the HVACR field, with over 800 years of accumulated knowledge in the industry. Graeme Blackman founded the company on the values of hard work and dedicated customer service, and those sentiments are clearly seen ...
Patients who take at least one blood pressure-lowering medication at bedtime have better control of their blood pressure and are less likely to experience heart problems than patients who take medications in the morning
Sleep-time blood pressure is a better measure of heart health than wake-time blood pressure
About one out of three U.S. adults has high blood pressure
Washington, DC (Monday, October 24, 2011) — It's better to take blood pressure-lowering medications before bed rather than first thing in the morning, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue ...
Patient characteristics affect whether dialysis clinics achieve treatment success and receive Medicare reimbursement
How well kidney disease patients follow their prescribed treatments has the greatest impact
Dialysis clinics in low-income urban areas provide care to more patients who don't follow their prescribed treatments; these clinics get unfairly penalized
Washington, DC (Monday, October 24, 2011) — Dialysis clinics that provide care to kidney disease patients who cannot or will not follow their prescribed treatments will be penalized under a new Medicare payment ...
Washington, DC -- Babies born with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) often develop kidney failure because they have very large kidneys filled with tiny cysts. Even with excellent medical care, about 30% die shortly after birth. New research now provides clues into how gene defects may cause this condition, which occurs in 1 out of 20,000 newborns. The findings appear in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society Nephrology (JASN), a publication of the American Society of Nephrology.
Mutations in a gene named PKHD1 cause ARPKD, but it's ...
DURHAM, N.C. -- Infectious films of Staph bacteria around an implanted cardiac device, such as a pacemaker, often force a second surgery to replace the device at a cost of up to $100,000. But not all implanted cardiac devices become infected.
Now researchers from Duke University Medical Center and Ohio State University (OSU) have discovered how and why certain strains of Staphylococcus aureus (SA) bacteria, the leading cause of these device infections, have infected thousands of implanted cardiac devices. About 4 percent of the 1 million annually implanted devices become ...
Rats exposed to an antidepressant just before and after birth showed substantial brain abnormalities and behaviors, in a study funded by the National Institutes of Health.
After receiving citalopram, a serotonin-selective reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), during this critical period, long-distance connections between the two hemispheres of the brain showed stunted growth and degeneration. The animals also became excessively fearful when faced with new situations and failed to play normally with peers – behaviors reminiscent of novelty avoidance and social impairments seen in ...