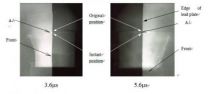
(Press-News.org) Athens, Ga. – Researchers at the University of Georgia have developed a "super strain" of yeast that can efficiently ferment ethanol from pretreated pine -- one of the most common species of trees in Georgia and the U.S. Their research could help biofuels replace gasoline as a transportation fuel.
"Companies are interested in producing ethanol from woody biomass such as pine, but it is a notoriously difficult material for fermentations," said Joy Doran-Peterson, associate professor of microbiology in the Franklin College of Arts and Sciences.
"The big plus for softwoods, including pine, is that they have a lot of sugar that yeast can use," she said. "Yeast are currently used in ethanol production from corn or sugarcane, which are much easier materials for fermentation; our process increases the amount of ethanol that can be obtained from pine."
Before the pinewood is fermented with yeast, however, it is pre-treated with heat and chemicals, which help open the wood for enzymes to break the cellulose down into sugars. Once sugars are released, the yeast will convert them to ethanol, but compounds produced during pretreatment tend to kill even the hardiest industrial strains of yeast, making ethanol production difficult.
Doran-Peterson, along with doctoral candidate G. Matt Hawkins, used directed evolution and adaptation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a species of yeast used commonly in industry for production of corn ethanol, to generate the "super" yeast.
Their research, published online in Biotechnology for Biofuels, shows that the pine fermented with the new yeast can successfully withstand the toxic compounds and produce ethanol from higher concentrations of pretreated pine than previously published.
"Others before us had suggested that Saccharomyces could adapt to harsh conditions. But no one had published softwood fermentation studies in which the yeast were pushed as hard as we pushed them," said Doran-Peterson.
During a two-year period, Doran-Peterson and Hawkins grew the yeast in increasingly inhospitable environments. The end result was a strain of yeast capable of producing ethanol in fermentations of pretreated wood containing as much as 17.5 percent solid biomass. Previously, researchers were only able to produce ethanol in the presence of 5 to 8 percent solids. Studies at 12 percent solids showed a substantial decrease in ethanol production.
This is important, said Doran-Peterson, because the greater the percentage of solids in wood, the more ethanol that can be produced. However, a high percentage of solids also places stress on the yeast.
"Couple that stress with the increase in toxic compounds, and the fermentation usually does not proceed very well," she said.
Pine is an ideal substrate for biofuels not only because of its high sugar content, but also because of its sustainability. While pine plantations account for only 15 percent of Georgia's trees, they provide 50 percent of harvested timber, according to Dale Greene, professor of forest operations in UGA's Warnell School of Forestry and Natural Resources. The loblolly pine that Doran-Peterson and Hawkins used for their research is among the fastest growing trees in the American South.
"We're talking about using forestry residues, waste and unsalable timber," said Peterson, "Alternatively, pine forests are managed for timber and paper manufacturing, so there is an existing infrastructure to handle tree-farming, harvest and transportation for processing.
"The basic idea is that we're trying to get the yeast to make as much ethanol as it can, as fast as it can, while minimizing costs associated with cleaning or washing the pretreated pine. With our process, no additional clean-up steps are required before the pine is fermented," she said.
###
The research was funded by grants from C2 Biofuels LLC and the U.S. Department of Energy. Their paper is available online at http://www.biotechnologyforbiofuels.com/content/4/1/49/.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain AJP50 is patent pending (PCT/US2009/043358) – University of Georgia Research Foundation.
For more information about bioenergy research at UGA, see http://bioenergy.uga.edu/ and http://bff.uga.edu/solutions/category/biofuels/.
UGA researchers develop 'super' yeast that turns pine into ethanol
From forest to fuel tank
2011-11-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Combo hormone therapy has increased breast cancer risk over estrogen alone
2011-11-21
The debate about using menopausal hormone therapies to relieve symptoms in post-menopausal women has been ongoing. Is the combination therapy of estrogen and progestin better or worse than just giving women estrogen alone? In women who still have a uterus (those who have not had a hysterectomy), progestin counteracts the increased risk of uterus cancer when estrogen is given alone, but at the expense of an increase in breast cancer risk compared to estrogen alone.
Now a study by researchers at UCLA's Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center has found that women taking the ...
Recent advance in detonation theory
2011-11-21
A detonation wave is a chemical reaction wave propagating at the velocity of a shock wave along the explosive charge. There is great demand for a detonation model that can accurately simulate the detonation process, which would provide a theoretical basis for highly efficient military destruction, the initiation of an atomic bomb, and calculations relating to the supernova SN Ia explosion. Detonation is complicated in that it involves mechanics, chemistry and thermodynamics simultaneously. The detonation product particles move multi-dimensionally, and there are transport ...
Corals can sense what's coming
2011-11-21
Australian scientists have thrown new light on the mechanism behind the mass death of corals worldwide as the Earth's climate warms.
Coral bleaching, one of the most devastating events affecting coral reefs around the planet, is triggered by rising water temperatures. It occurs when the corals and their symbiotic algae become heat-stressed, and the algae which feed the corals either die or are expelled by the coral.
There have been seven major bleaching events globally in the past 30 years, the most recent being in 2010 across the Indian Ocean and Coral Triangle. Australia's ...
Heart rate recovery predicts clinical worsening in pulmonary hypertension
2011-11-21
Heart rate recovery at one minute after a six-minute walking distance (6MWD) test is highly predictive of clinical worsening and time to clinical worsening in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH), according to a new study.
"Ours is the first study to show that heart rate recovery at one minute of rest (HRR1) following a 6MW test is a strong predictor of clinical worsening in IPAH patients," said Omar A. Minai, MD, staff physician in the Department of Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care Medicine at the Cleveland Clinic. "Predicting long-term ...
Metabolic syndrome biomarkers predict lung function impairment after exposure to WTC dust
2011-11-21
Metabolic syndrome biomarkers predict subsequent decline in lung function after particulate exposure, according to new research involving rescue personnel exposed to World Trade Center (WTC) dust.
In a nested case-control study of 327 non-smoking FDNY 9/11 rescue workers, metabolic syndrome biomarkers measured within six months of exposure to WTC dust predicted decline of forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) over the next six years.
"Study participants with dyslipidemia, elevated heart rate or elevated leptin levels had a significantly increased risk of developing ...
As probiotics use grows for gut health, VSL#3 has designations for specific GI issues
2011-11-21
GAITHERSBERG, MD, Nov. 18 – As clinical studies continue to validate the use of probiotics to help promote general gastrointestinal health, a growing U.S. market1 for probiotics indicates that the U.S. healthcare community and consumers alike are recognizing the value of these beneficial microorganisms. However, because most probiotics are classified as dietary supplements, directing patients to the best probiotic for their individual needs can be challenging. And, as the category matures, one probiotic preparation -- VSL#3 -- stands apart and ahead because it is not a ...
The protest vote prevails when a landslide victory is expected
2011-11-21
Researchers at the Juan March foundation and the Duke University (USA) have analysed the reason for casting a protest vote as a way of expressing unhappiness with a party during elections. Moderate voters are more likely to vote in this way than those at the extreme left or extreme right of the political spectrum.
Daniel Kselman, researcher at the Juan March Foundation and co-author of the study that analyses such behaviour states that "the protest vote is just a way of expressing discontent. In order for it to be effective, a lot more voters from your party need to vote ...
NRL Monterey develops more accurate tropical cyclone prediction model
2011-11-21
WASHINGTON -- Researchers at the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) Marine Meteorology Division (MMD), Monterey, Calif., have developed the Coupled Ocean/Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System Tropical Cyclone (COAMPS-TC™) model, achieving a significant research milestone in predictions of tropical cyclone intensity and structure.
While the predictions of the paths or tracks of hurricanes, more generally referred to as tropical cyclones (TC), have steadily improved over the last few decades, improvements in the predictions of storm intensity have proven much more difficult.
"Over ...
Protection from severe malaria explained
2011-11-21
Why do people with a hereditary mutation of the red blood pigment hemoglobin (as is the case with sickle-cell anemia prevalent in Africa) not contract severe malaria? Scientists in the group headed by Prof. Michael Lanzer of the Department of Infectious Diseases at Heidelberg University Hospital have now solved this mystery. A degradation product of the altered hemoglobin provides protection from severe malaria. Within the red blood cells infected by the malaria parasite, it blocks the establishment of a trafficking system used by the parasite's special adhesive proteins ...
Chalmers scientists create light from vacuum
2011-11-21
Scientists at Chalmers University of Technology have succeeded in creating light from vacuum – observing an effect first predicted over 40 years ago. The results is published tomorrow (Wednesday) in the journal Nature. In an innovative experiment, the scientists have managed to capture some of the photons that are constantly appearing and disappearing in the vacuum.
The experiment is based on one of the most counterintuitive, yet, one of the most important principles in quantum mechanics: that vacuum is by no means empty nothingness. In fact, the vacuum is full of various ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] UGA researchers develop 'super' yeast that turns pine into ethanolFrom forest to fuel tank