(Press-News.org) The structure of the corpus callosum, a thick band of nerve fibres that connects the two halves of the brain with each other and in this way enables the rapid exchange of information between the left and right hemispheres, plays an important role in the regaining of motor skills following a stroke. A study currently published in the journal Human Brain Mapping has shown that in stroke patients with particularly severely impaired hand movement, this communication channel between the two brain hemispheres in particular was badly damaged.
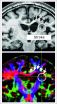
In order to relate brain function and anatomical structure with each other, in this study the scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Neurological Research and the Department of Neurology at the University Hospital of Cologne combined two imaging methods. They asked stroke patients to make a simple tapping movement using the hand affected by the stroke and recorded their brain activity using functional magnetic resonance imaging. The data obtained in this way were then compared with data from healthy subjects. As expected from previous test results, compared with the control group, the stroke patients recorded a lower tapping speed and increased brain activity on both sides of the brain. "The increased activity in the healthy brain hemisphere, in particular, points to the impaired processing of motor programs between the two brain hemispheres," explains Christian Grefkes, head of the research study.
In order to demonstrate the structural connection between brain areas, the Cologne researchers used diffusion-based magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI), which can be used to reconstruct longer stretches of nerve fibres. dMRI is based on the principle that cell elements, such as the membrane or extensions, inhibit the spread of water molecules thereby preventing them from diffusing randomly in all directions. Consequently, parallel nerve fibres can be clearly identified using dMRI. Compared to the healthy control group, the stroke patients had lower diffusion values in the corpus callosum region. This would indicate that this interhemispheric communications connection was damaged by the stroke. The most significant deviations from the values of the control group were observed in patients with more severe motor defects and increased activity in the healthy brain hemisphere.
Therefore, in addition to cell death in the actual stroke area, damage to a very distant connection structure plays a crucial role in the inability of stroke patients to fully regain their original motor capacities. "This is why, we are currently examining whether we can regenerate the communication between the brain hemispheres through early and regular stimulation treatment. Our long-term aim is to improve motor deficits in stroke patients," says Grefkes.
INFORMATION:
Original publication
Ling E. Wang, Marc Tittgemeyer, Davide Imperati, Svenja Diekhoff, Mitra Ameli, Gereon R. Fink und Christian Grefkes
Degeneration of corpus callosum and recovery of motor function after stroke: A multimodal magnetic resonance imaging study
Human Brain Mapping, online publication, 22, Oct. 2011 | DOI: 10.1002/hbm.21417
Regeneration after a stroke requires intact communication channels between brain hemispheres
Recovery depends on the exchange of information between the 2 halves of the brain
2011-11-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rainfall suspected culprit in leaf disease transmission
2011-11-22
Rainfalls are suspected to trigger the spread of a multitude of foliar (leaf) diseases, which could be devastating for agriculture and forestry. Instead of focusing on the large-scale, ecological impact of this problem, researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge and the University of Liege in Belgium are studying the phenomenon from a novel perspective: that of a single rain droplet.
"One may easily picture that a raindrop impacting a contaminated leaf grabs some of the pathogens there before being ejected and flying towards some healthy ...
Engineers devise shoe sampling system for detecting trace amounts of explosives
2011-11-22
The ability to efficiently and unobtrusively screen for trace amounts of explosives on airline passengers could improve travel safety – without invoking the ire of inconvenienced fliers. Toward that end, mechanical engineer and fluid dynamicist Matthew Staymates of the National Institute of Standards and Technology in Gaithersburg, Maryland, and colleagues have developed a prototype air sampling system that can quickly blow particles off the surfaces of shoes and suck them away for analysis.
The NIST engineers developed several different versions of the system. "One particular ...
Broward SCORE Creates 2012 Workshop Calendar to Fit Smart Phones and Tablets
2011-11-22
Broward SCORE will launch in December special digital editions of its upcoming winter workshops for 2012 designed for smart phones and tablets.
SCORE enlisted the expertise of Guni Bermudez of Reach MCS and Jeff Miller of Stallion Publishers, both based in Fort Lauderdale, to create the new platforms. The Broward chapter of SCORE, a resource partner with the SBA, tested its digital editions in the fall, working out the kinks and improving the user experience.
These new digital editions allow the nonprofit's workshop catalog to be easily viewed on smart phones, and ...
Mechanism of wine swirling explained
2011-11-22
Wine drinkers know that swirling a good vintage around in a glass aerates the wine and releases its bouquet. Just how the process – known as "orbital shaking" – works, however, has been something of a mystery.
Fluid dynamicists have long observed that orbital shaking generates a wave that propagates around the inner edge of the glass, churning the liquid as it travels. "The formation of this wave has probably been known since the introduction of glass or any other kind of cylindrical bowl, but what has been lacking is a description of the physics related to the mixing ...
Paleontologist describes large nest of juvenile dinosaurs, first of their genus ever found
2011-11-22
KINGSTON, R.I. – November 21, 2011 – A nest containing the fossilized remains of 15 juvenile Protoceratops andrewsi dinosaurs from Mongolia has been described by a University of Rhode Island paleontologist, revealing new information about postnatal development and parental care. It is the first nest of this genus ever found and the first indication that Protoceratops juveniles remained in the nest for an extended period.
The findings were reported in the most recent issue of the Journal of Paleontology.
David Fastovsky, URI professor of geosciences, said the bowl-shaped ...
Florida-Based Franchise Beats the 'Scramble' in Breakfast, Brunch and Lunch Category
2011-11-22
In the early '90s, a Department of Defense engineer at NASA assigned to work on the now defunct Super Conducting Super Collider project was sidetracked with a personal mission that had nothing to do with subatomic particles or electromagnetic fields. Instead, after federal budget cuts ended the project, Ron Green assigned himself an entirely new operation: hatching up the country's perfect breakfast, brunch and lunch restaurant concept.
Mission accomplished. Today, Another Broken Egg Cafe cracks more than 900,000 eggs a week at its 18 bustling locations in seven states, ...
EARTH: Highlights of 2011 -- energy and economics 2011-2012
2011-11-22
Alexandria, VA – Is the United States entering its "Lost Decade"? A crunch on natural resources coupled with a crippling economic crisis and an aging workforce threaten to hurl us into a decade—or more—of grudgingly slow development akin to that of the Japanese after their own real estate bust a few decades ago. Will the United States learn from past mistakes in order to reconcile economic growth with environmental safety? In the December issue of EARTH Magazine, learn how the facts and the fallacies measure up to the increasing challenges facing the United States in 2012 ...
Nursing home quality scorecards don't tell the whole score
2011-11-22
INDIANAPOLIS — The scoring system government agencies use to rate nursing home quality does not provide an adequate evaluation because they do not take into account the degree of cognitive impairment of their patient populations and whether facilities include a specialized dementia unit according to a new study.
Focusing on statistics from Minnesota, researchers from Indiana University School of Medicine and the Regenstrief Institute report on the inadequacy of quality of care indicators for nursing home residents with behavioral and psychological systems related to dementia ...
Le Meridien Amman Premieres Wine Tasting at Renowned 282 Steaks and Lounge
2011-11-22
Le Meridien Amman, a hotel dedicated to offering a chic experience, has recently hosted a "Culinary Wine Tasting" event, in the stylish setting of 282 Steaks and Lounge restaurant, in cooperation with Yousef M. Haddad & Partners Company and Kaylani Food Center.
Mr. Frederico Raviola from the Fontanafredda winery in Italy, the first in Piedmont to be awarded the official "Integrated Farm Management" Certification, briefed the audience on the different types of wines, in an informal market atmosphere. The invitees, amongst them many ambassadors, ...
IBD patients face increased skin cancer risk
2011-11-22
Certain patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) may have an increased risk of skin cancer, which is intensified by the use of immunosuppressant medications , according to two new studies in Gastroenterology, the official journal of the American Gastroenterological Association. Immunosuppressants are commonly used in the treatment of IBD.
In the first study, researchers found that both past and present exposure to thiopurines (a widely used class of immunosuppressants) significantly increased the risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC) in patients with IBD, even ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Regeneration after a stroke requires intact communication channels between brain hemispheresRecovery depends on the exchange of information between the 2 halves of the brain