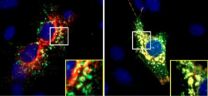
(Press-News.org) Sluggish recycling of a protein-slicing enzyme could promote Alzheimer's disease, according to a study published online on November 21 in The Journal of Cell Biology (www.jcb.org).
Abeta, the toxic protein that accumulates in the brains of Alzheimer's patients, is formed when enzymes cut up its parental protein, known as amyloid precursor protein. One of those enzymes is beta-secretase or BACE1. BACE1 cycles between the Golgi apparatus and the plasma membrane, traveling through endosomes on the way. A protein complex called the retromer helps transport proteins back from endosomes to the Golgi. Previous studies have found reduced levels of two retromer components, including the protein VPS35, in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease.
To find out whether VPS35 affects Alzheimer's disease progression, Wen-Cheng Xiong and colleagues crossed two mouse lines to create animals that are prone to many symptoms of the disease and generate half the normal amount of VPS35. The mice displayed Alzheimer's-like abnormalities earlier than their parental strains, and their brains accumulated more Abeta.
Cells lacking VPS35 carried extra BACE1 in their endosomes, consistent with a defect in retromer-mediated protein transport. BACE1 is more active in the acidic interior of endosomes than in the more basic surroundings of the Golgi apparatus. Thus, by leaving more BACE1 trapped in endosomes, the decline in VPS35 levels could enhance BACE1 activity and generate more Abeta. Although no VPS35 mutations have so far turned up in Alzheimer's patients, the protein's level in the brain dwindles in aging mice. The researchers suspect that certain Alzheimer's disease risk factors, such as oxidative stress, also diminish VPS35 levels in the brain.
INFORMATION:
About The Journal of Cell Biology
Founded in 1955, The Journal of Cell Biology (JCB) is published by The Rockefeller University Press. All editorial decisions on manuscripts submitted are made by active scientists in conjunction with our in-house scientific editors. JCB content is posted to PubMed Central, where it is available to the public for free six months after publication. Authors retain copyright of their published works and third parties may reuse the content for non-commercial purposes under a creative commons license. For more information, please visit www.jcb.org.
Wen, L., et al. 2011. J. Cell Biol. http://dx.doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201105109.
Poor recycling of BACE1 enzyme could promote Alzheimer's disease
2011-11-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
YourHomeSupply.com Introduces New Line Of Home Security Cabinet And Door Hardware
2011-11-22
Your Home Supply, a one stop shop for cabinet and door hardware needs, has recently introduced a new range of products that include First Watch Security, a premium line of home security hardware. The new selection of bolts, latches, strike plates, latch guards, drawer, cabinet, mailbox and window locks, door reinforcers as well as patio and replacement knobs is available at the lowest prices with an unmatched quality. The new First Watch Security product not only adds to the security of a home, but also lends a door a new style. Customers can even get custom designed products ...
Researchers shrink tumors and minimize side effects using tumor-homing peptide to deliver treatment
2011-11-22
LA JOLLA, Calif., November 21, 2011 – The trouble with most anti-cancer therapies is that they are lethal to most cells in the body, not just cancer cells. As a result, patients experience side effects like nausea, increased susceptibility to infection, and increased risk of developing secondary cancers later in life. Researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham) are developing techniques to deliver cancer drugs directly to tumors, increasing their effectiveness and decreasing collateral damage. In a study published the week of November 21 ...
New breast cancer screening guidelines released
2011-11-22
New breast cancer screening guidelines for women at average risk of breast cancer, published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) (pre-embargo link only) http://www.cmaj.ca/site/embargo/cmaj110334.pdf, recommend no routine mammography screening for women aged 40-49 and extend the screening interval from every 2 years, which is current clinical practice, to every 2 to 3 years for women aged 50-74. The guidelines also recommend against routine clinical breast exam and breast self-examination in asymptomatic women.
The guidelines, aimed at physicians and policy-makers, ...
DesignPractica Expands eCommerce and Custom CMS Services
2011-11-22
DesignPractica has been creating and maintaining custom websites for small businesses in Greater Vancouver area for several years. Now, in addition to offering WordPress, Django and Google Application Engine websites, DesignPractica will also provide support and development services with all top open-source and hosted eCommerce and CMS systems, such as Magento, Drupal, Volusion, Shopify, Satchmo and others, for small, medium and large businesses in the greater Vancouver region.
DesignPractica has a successful history of helping local manufacturers, farmers, restaurants ...
More than one-quarter of Canadian adults projected to have hypertension in 2012/13
2011-11-22
Hypertension in Canada is increasing, and it is projected that more than one-quarter of Canadian adults will be diagnosed with hypertension by 2012/13, according to a study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) (pre-embargo link only) http://www.cmaj.ca/site/embargo/cmaj101863.pdf. Older women were more likely to be diagnosed with high blood pressure compared with men, and people in the Atlantic provinces had the highest rates of hypertension.
Canadian researchers looked at data on 26 million adults aged 20 years and over between 1998 and 2007/08 to ...
Families report adverse events in hospitalized children not tracked by health-care providers
2011-11-22
Families of hospitalized children can provide valuable information about adverse events relating to their children's care that complements information documented by health care professionals, states a study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) (pre-embargo link only) http://www.cmaj.ca/site/embargo/cmaj110393.pdf.
Hospitals in Canada have instituted systems to encourage reporting of adverse events — things that may negatively affect the recovery or health of a patient — in patient care. In pediatrics, it is estimated that 1% of children in hospital ...
NIH researchers identify key proteins of inner ear transduction channel
2011-11-22
National Institutes of Health-funded researchers have identified two proteins that may be the key components of the long-sought after mechanotransduction channel in the inner ear—the place where the mechanical stimulation of sound waves is transformed into electrical signals that the brain recognizes as sound. The findings are published in the Nov. 21 online issue of The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The study used mice in which two genes, TMC1 and TMC2, have been deleted. The researchers revealed a specific functional deficit in the mechanotransduction channels ...
October Issue of Proceedings of the IEEE Presents Most Comprehensive Metamaterials Analysis Ever Assembled
2011-11-22
The future of the metamaterials field shows great promise for achieving exotic new functions according to October's Proceedings of the IEEE, the most highly-cited general-interest journal in electrical engineering and computer science, approaching its 100th year of publication in 2012. Entitled "Metamaterials: Fundamentals and Applications in the Microwave and Optical Regimes," the 16-article issue, written by internationally renowned leaders in the field is packed with innovative research reports on potential new functions and insights that could impact many ...
Implanted neurons, grown in the lab, take charge of brain circuitry
2011-11-22
MADISON -- Among the many hurdles to be cleared before human embryonic stem cells can achieve their therapeutic potential is determining whether or not transplanted cells can functionally integrate into target organs or tissues.
Writing today (Monday, Nov. 21) in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, a team of Wisconsin scientists reports that neurons, forged in the lab from blank slate human embryonic stem cells and implanted into the brains of mice, can successfully fuse with the brain's wiring and both send and receive signals.
Neurons are specialized, ...
Boosting the aged immune response to flu virus
2011-11-22
As people age, their immune system becomes less robust. This makes them more susceptible to serious and frequently life-threatening infections with viruses that affect the respiratory tract such as influenza A virus (IAV). Stanley Perlman and colleagues, at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, have now identified a new immune system defect in aged mice that makes them more susceptible than young mice to developing severe clinical disease upon infection with respiratory viruses such as IAV. Importantly, they were able to reverse the defect by inhibiting the immune molecule ...