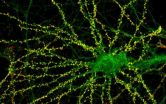
(Press-News.org) RICHMOND, Va. (Nov. 23, 2011) – Researchers interested in the treatment of schizophrenia and dementia have clarified how antipsychotic drugs that target a complex of two receptors at the surface of cells in the brain work, according to a new study published online Nov. 23 in the journal Cell.
The multidisciplinary team included researchers from the Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine, together with the Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York and the University of Maryland School of Pharmacy in Baltimore. In an earlier, but related study, the Mount Sinai School of Medicine team had shown that two brain receptors, which bind the critical neurotransmitter signals serotonin and glutamate at the outside of the cell, form a complex in the areas of the brain that malfunction in schizophrenic patients.
The team has now developed a metric that may help determine the effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs and advance drug design. The present work fills an important gap in knowledge as previously researchers did not understand how this receptor complex was connected to the phenotype of schizophrenia.
The current study findings show that the connection between the complex of the two receptors and the schizophrenic phenotype is a defect in how the serotonin and glutamate signals get interpreted at the inside of the cell, a process referred to as signaling. Moreover, it shows how antipsychotic drugs used to treat patients work to correct such a defect in the brain.
"Not only have we learned how antipsychotics drugs are effective, but we have also found that the signaling through this receptor complex is critical to how these anti-psychotics work," said the study's principal investigator Diomedes E. Logothetis, Ph.D., an internationally recognized leader in the study of ion channels and cell signaling mechanisms and chair of the VCU School of Medicine's Department of Physiology and Biophysics.
According to Logothetis, the most common cellular targets for drugs used in the clinic and by the pharmaceutical industry are G protein-coupled receptors, such as the ones that were examined in this study. Using cell and animal models, they found that the receptors signal very differently when they are together as a complex than when they are apart.
The metric developed by the team could be used to screen new drugs and determine their level of effectiveness, or be used to assess combination therapies - that is, putting two previously ineffective drugs together and making them more useful for some patients. Ultimately this work may translate to creating better antipsychotic drugs for patients.
"We can use the metric we developed to screen new drugs and determine their level of effectiveness," Logothetis said. "We can also use the metric to assess what combinations of existing drugs will give us the ideal balance between the signaling through the two receptors of the complex."
Logothetis said the hope is that by using this approach one day researchers will be able to develop a means by which high-throughput screening of drugs can be performed and they also will be able to develop more effective combinations of drugs that are able to help the third of schizophrenic patients who do not respond to current treatments.
Future studies will focus on further identifying the protein targets of the unique signaling pattern of this receptor complex and their link to schizophrenia.
The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health.
INFORMATION:
EDITOR'S NOTE: A copy of the study is available for reporters by email request from the journal by contacting elyons@cell.com.
About VCU and the VCU Medical Center: Virginia Commonwealth University is a major, urban public research university with national and international rankings in sponsored research. Located on two downtown campuses in Richmond, VCU enrolls more than 31,000 students in 216 certificate and degree programs in the arts, sciences and humanities. Sixty-nine of the programs are unique in Virginia, many of them crossing the disciplines of VCU's 13 schools and one college. MCV Hospitals and the health sciences schools of Virginia Commonwealth University compose the VCU Medical Center, one of the nation's leading academic medical centers. For more, see www.vcu.edu.
END
WALNUT CREEK, Calif. -- For a pest that isn't quite the size of a comma on a keyboard, the two-spotted spider mite can do a disproportionate amount of damage. These web-spinners extract the nutrients they need from leaves of more than a thousand different plant species, including bioenergy feedstocks and food staples. The cost of chemically controlling spider mites to counteract reduced harvest yields hovers around $1 billion annually, reflecting their significant economic impact.
With a 90-million nucleotide genome, the smallest of those that belong to the group of animals ...
PASADENA, Calif. -- Although many mental illnesses are uniquely human, animals sometimes exhibit abnormal behaviors similar to those seen in humans with psychological disorders. Such behaviors are called endophenotypes. Now, researchers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) have found that mice lacking a gene that encodes a particular protein found in the synapses of the brain display a number of endophenotypes associated with schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorders.
The new findings appear in a recent issue of the Journal of Neuroscience, with Mary ...
The elusive culprits that are killing countless coral reefs around the world can now be nabbed with technology normally used to diagnose human diseases, marine researchers say.
Coral researchers and reef managers will be able to identify coral infections using a new method that allows them to classify specific diseases based on the presence of microbes.
This could lead to more effective action to reduce the impact of disease on the world's imperilled coral reefs.
"Current classification of coral diseases is mostly based on a description of how the coral has deteriorated, ...
The Pennsylvania Workers' Compensation Act gives injured workers valuable rights. They include payment of medical bills, wage loss compensation, disfigurement awards for work-related facial and neck scars and awards for specific loss of use of a body part (ex. - leg, hand, finger, etc). The following are key points that workers should know about workers' compensation in Pennsylvania.
Workers' Compensation Benefits for Work-Related Injuries
According to the Pennsylvania Workers' Compensation Act, employers must give their full-time, part-time and seasonal employees ...
Blossom end rot on tomatoes and cucumbers, bitter-pit in apples – these unpleasant blemishes on fruits and vegetables not only compromises the flavor but also causes significant harvest losses every year. The characteristic blotches and spotting can be traced back to insufficient calcium uptake or faulty calcium transport within the plant. Consequently, the damage can occur even if the soil provides sufficient calcium. A team under the leadership of scientists from the University of Zurich and Pohang University of Science and Technology, Korea, has for the first time identified ...
The tiny two-spotted spider mite (Tetranychus urticae) causes much anxiety for farmers, and has been, to date, a scientific mystery. It feeds on over 1,100 species of plants, including 150 greenhouse plants and crops, such as maize, soy, tomatoes and citrus. The cost of chemically controlling damage caused by the spider mite exceeds USD 1 billion per year. In the latest issue of the journal Nature, a multinational consortium of scientists publish the sequenced genome of the spider mite, revealing how it is capable of such feeding frenzy, as well as other secrets of this ...
Glioblastoma is regarded as the most malignant form of brain tumor. In many cases, neurosurgeons are not able to remove such tumors completely because of the risk of destroying too much brain tissue in the process. Moreover, it is often impossible to identify all the fine extensions by which the tumor spreads into surrounding healthy tissue. To at least slow down the growth of tumor cells that have remained in the head, almost all glioblastoma patients are treated by radiotherapy after surgery.
"Unfortunately, we can only delay cancerous growth in this way, but we cannot ...
Countless people sustain injuries each year while on the property of another person or business. Some of these injuries could have been prevented if the owner, manager or occupier of the property had taken basic safety precautions or behaved as a reasonable person would have in the same situation.
Every slip and fall or trip and fall accident does not automatically result in a personal injury claim, but some of them do. It takes a skilled personal injury attorney to know the difference between a frivolous case and one that is likely to succeed. Slip and fall, trip and ...
Scientists have found that a strain of yeast implicated in inflammatory skin conditions, including eczema, can be killed by certain peptides and could potentially provide a new treatment for these debilitating skin conditions. This research is published today in the Society for Applied Microbiology's journal, Letters in Applied Microbiology.
20% of children in the UK suffer from atopic eczema and whilst this usually clears up in adolescence, 7% of adults will continue to suffer throughout their lifetime. Furthermore, this type of eczema, characterized by dry, itchy, flaking ...
How will the terrorist attacks in Norway on 22 July change the country? That question has been put to three social scientists at the University of Stavanger (UiS).
"Norwegians are still in a state of shock," says professor Odd Einar Olsen. "These incidents were so extensive and gruesome that people need time to come to terms with them."
He is very interested to see what content Norway will give to promises made about more openness and democracy after the car-bombing in Oslo and the massacre at Utøya north of the capital.
"While people have united in sorrow, a crippling ...