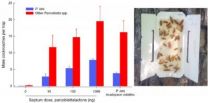
(Press-News.org) Drugs that enhance levels of small molecules derived naturally in the body from a major component of animal fats (small molecules known as epoxyeicosatrienoic acids [EETs]) are currently in clinical trials for the treatment of high blood pressure and diabetes. A team of researchers — led by Dipak Panigrahy and Mark Kieran, at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston; Sui Huang, at the Institute for Systems Biology, Seattle; and Darryl Zeldin, at the National Institute of Environmental Health Science, Research Triangle Park — has now generated data in mice that raise concern about the use of these drugs in humans.
The key observation of the team was that EETs promote primary tumor growth and spread to distant sites (metastasis) in a variety of mouse models of cancer. As noted by the authors and, in an accompanying commentary, Raymond DuBois and Dingzhi Wang, at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, the data generated suggest not only that raising levels of EETs in humans could have severe adverse effects but also that EET antagonists could provide a new approach to preventing and treating metastasis.
###
TITLE: Epoxyeicosanoids stimulate multiorgan metastasis and tumor dormancy escape in mice
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Dipak Panigrahy
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Massachusetts, USA.
Phone: 617-919-2198; Fax: 617-730-0231; E-mail:
dipak.panigrahy@childrens.harvard.edu.
Sui Huang
Institute for Systems Biology, Seattle, Washington, USA.
Phone: 206-354-3569; Fax: 206-732-1299; E-mail:
sui.huang@systemsbiology.org.
Mark W. Kieran
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Massachusetts, USA.
Phone: 617-632-4907; Fax: 617-632-4897; E-mail:
mark_kieran@dfci.harvard.edu.
Darryl C. Zeldin
National Institute of Environmental Health Science, NIH, Research
Triangle Park, North Carolina, USA.
Phone: 919-541-1169; Fax: 919-541-4214; E-mail:
zeldin@niehs.nih.gov.
ACCOMPANYING COMMENTARY
TITLE: Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids: a double-edged sword in cardiovascular diseases and cancer
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Raymond N. DuBois
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas, USA.
Phone: 713-745-4495; Fax: 713-792-6375; E-mail:
rdubois@mdanderson.org.
Potential concern about drugs in clinical trial
2011-12-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Blood pressure drug limits cigarette smoke-induced lung injury in mice
2011-12-19
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is among the most common causes of death in the US. It is a smoking-related disease for which there are currently no disease-altering therapies. However, hope that one could be developed is now provided by the work of Enid Neptune and colleagues, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, in a mouse model of lung disease caused by exposure to cigarette smoke.
Neptune and colleagues found that lostartan, a drug used widely in the clinic (e.g., to treat high blood pressure), reduced lung disease in mice caused by exposure to cigarette ...
JCI online early table of contents: Dec. 19, 2011
2011-12-19
EDITOR'S PICK: Potential concern about drugs in clinical trial
Drugs that enhance levels of small molecules derived naturally in the body from a major component of animal fats (small molecules known as epoxyeicosatrienoic acids [EETs]) are currently in clinical trials for the treatment of high blood pressure and diabetes. A team of researchers — led by Dipak Panigrahy and Mark Kieran, at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston; Sui Huang, at the Institute for Systems Biology, Seattle; and Darryl Zeldin, at the National Institute of Environmental Health Science, Research ...
Eating less keeps the brain young
2011-12-19
Overeating may cause brain aging while eating less turns on a molecule that helps the brain stay young.
A team of Italian researchers at the Catholic University of Sacred Heart in Rome have discovered that this molecule, called CREB1, is triggered by "caloric restriction" (low caloric diet) in the brain of mice. They found that CREB1 activates many genes linked to longevity and to the proper functioning of the brain.
This work was led by Giovambattista Pani, researcher at the Institute of General Pathology, Faculty of Medicine at the Catholic University of Sacred Heart ...
Brain function - A new way to measure the burden of aging across nations
2011-12-19
Cognitive function may be a better indicator of the impact of aging on an economy than age-distribution, with chronological age imposing less of a social and economic burden if the population is "functionally" younger, according to a study published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The study finds that one standardized indicator of cognitive ability - memory recall - is better in countries where education, nutrition, and health standards are generally higher. Aging populations are of concern to many countries as it is often assumed that ageing ...
Legumes give nitrogen-supplying bacteria special access pass
2011-12-19
A 125-year debate on how nitrogen-fixing bacteria are able to breach the cell walls of legumes has been settled. A paper to be published on Monday by John Innes Centre scientists reports that plants themselves allow bacteria in.
Once inside the right cells, these bacteria take nitrogen from the air and supply it to legumes in a form they can use, ammonia. Whether the bacteria breach the cell walls by producing enzymes that degrade it, or the plant does the work for them, has been contested since an 1887 paper in which the importance of the breach was first recognised.
"Our ...
Researchers find misinformation about emergency contraception common in low-income neighborhoods
2011-12-19
Boston – Researchers from Boston Medical Center (BMC) and Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have found that in low-income neighborhoods, misinformation about access to emergency contraception is a common occurrence. These findings appear as a research letter in the Dec. 19 on-line issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association.
In 2009, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration facilitated access to emergency contraception among adolescents by making it available over-the-counter to individuals age 17 years and older.
From September to December 2010, ...
Targeting EETs to treat cardiovascular disease may prove a double-edged sword
2011-12-19
Boston, Mass. – A group of small molecules called EETs – currently under scrutiny as possible treatment targets for a host of cardiovascular diseases – may also drive the growth and spread of cancer, according to researchers at the Dana-Farber/Children's Hospital Cancer Center (DF/CHCC) and other institutions. Their findings also raise the possibility that drugs that block EETs could serve as a new avenue for cancer treatment.
This study, led by Dipak Panigrahy, MD, of DF/CHCC and the Vascular Biology Program at Children's Hospital Boston, appeared online December 19 ...
Cockroach hookup signal could benefit endangered woodpecker
2011-12-19
A North Carolina State University discovery of the unique chemical composition of a cockroach signal – a "Let's hook up" sex pheromone emitted by certain female wood cockroaches to entice potential mates – could have far-ranging benefits, including improved conservation of an endangered woodpecker.
Dr. Coby Schal, Blanton J. Whitmire Professor of Entomology at NC State and the corresponding author of a paper describing the discovery, says that the study, published the week of Dec. 19 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, advances the knowledge of fundamental ...
Wayne State study finds soybean compounds enhances effects of cancer radiotherapy
2011-12-19
Detroit - A Wayne State University researcher has shown that compounds found in soybeans can make radiation treatment of lung cancer tumors more effective while helping to preserve normal tissue.
A team led by Gilda Hillman, Ph.D., professor of radiation oncology at Wayne State University's School of Medicine and the Barbara Ann Karmanos Cancer Institute, had shown previously that soy isoflavones, a natural, nontoxic component of soybeans, increase the ability of radiation to kill cancer cells in prostate tumors by blocking DNA repair mechanisms and molecular survival ...
Infrared technology for measuring the effect of fire on materials
2011-12-19
This press release is available in Spanish.
The main problem associated with measuring the effects of fire on materials lies in the temperature of the flames, which reaches over 1000 ºC and can obscure the actual temperature of the material. In addition, there is the problem of the high concentration of gasses (CO2, H2O and others), which makes it difficult to obtain clear images of the sample being subjected to fire. In order to solve this problem, the UC3M scientists who developed this method used a measurement that utilizes the infrared spectrum. "To do this, ...