(Press-News.org) The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has issued the world's first reference material for single-wall carbon nanotube soot. Distantly related to the soot in your fireplace or in a candle flame, nanotube-laden soot is the primary industrial source of single-wall carbon nanotubes, perhaps the archetype of all nanoscale materials. The new NIST material offers companies and researchers a badly needed source of uniform and well-characterized carbon nanotube soot for material comparisons, as well as chemical and toxicity analysis.
With walls of carbon only one atom thick and looking like a sheet of chicken wire curled into a cylinder, single-wall carbon nanotubes are one of several families of pure carbon materials that, because of their nanoscale size, have special properties. "Single-wall carbon nanotubes," says NIST chemical engineer Jeffery Fagan, "have exquisite optical, mechanical, thermal and electronic properties, and because of their small width but long lengths—think of something like a long piece of hair but 10,000 times thinner—full development of these materials should enable lighter, stronger materials, as well as improve many technologies from sensors to electronics and batteries."
Unfortunately, nanotubes are difficult to produce without significant impurities or in large quantities. Single-wall nanotubes, in particular, have been notorious for their relatively low quality and batch-to-batch variability. They typically are produced in complex processes using small particles of metal catalysts that promote the growth of the nanotubes. The resulting material—often a powder not unlike the soot you would find in your fireplace—has frequently contained large amounts of impurities, such as other forms of carbon, and sometimes significant levels of catalysts.
"One of the issues that this reference material addresses is that there's no homogeneous lot that people can buy to do comparative measurements," says Fagan. "Even batch-to-batch, raw carbon nanotube powder samples have varied so much that there is no interlaboratory consistency. And that's particularly a problem for comparisons such as toxicity measurements. If you bought carbon nanotubes, you were pretty much guaranteed that your sample could be so different from anyone else's samples that either your measurements could be specific to some flaw of your material, or that others might not be able to reproduce what you were doing."
To address these issues, a multidisciplinary research team at NIST has worked to develop the metrology necessary for quantitative single-wall carbon nanotube measurements through a three-prong approach: basic measurement and separation science, documentary protocols and standards through international standards organizations, and now certified reference materials.
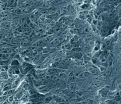
The new NIST product, Standard Reference Material (SRM) 2483, "Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes (Raw Soot)," will directly address the issue of comparability. It is possibly the world's single largest supply of homogeneous, chemically analyzed, carbon nanotube soot where the uniformity of the samples from unit to unit is assured. Each unit of SRM 2483, a glass vial containing 250 milligrams of soot, is certified by NIST for the mass fraction values of several common contaminants: barium, cerium, chlorine, cobalt, dysprosium, europium, gadolinium, lanthanum, molybdenum and samarium. Reference values (values believed to be accurate, but not rising to the level of confidence that NIST certifies) are provided for an additional seven elements.
NIST also provides additional reference data useful for nanotube analysis, including thermal gravimetric and Raman data, as well as informational values for ultraviolet-visible-near-infrared absorbance spectra, near-infrared fluorescence spectra, Raman scattering spectra and scanning electron microscopy images. With these sets of information, purchasers of the material should be able to compare their results against the NIST values and against those from suppliers or after processing, ensuring a consistent point of comparison.
INFORMATION:
Single units of SRM 2483, "Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes (Raw Soot)," are available from the NIST Standard Reference Materials Program at https://www.nist.gov/srm/. See https://www-s.nist.gov/srmors/view_detail.cfm?srm=2483 for details.
Standard Reference Materials are among the most widely distributed and used products from NIST. The agency prepares, analyzes and distributes more than a thousand different materials that are used throughout the world to check the accuracy of instruments and test procedures used in manufacturing, clinical chemistry, environmental monitoring, electronics, criminal forensics and dozens of other fields.
NIST releases first certified reference material for single-wall carbon nanotubes
2011-12-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Atlanta Dentist Joins Online Community for Increased Patient Communication
2011-12-22
Leading Atlanta dentist, Dr. Donald Rozema, shares important dental health care knowledge with patients via social media websites - Facebook and Twitter. In a society that continues to advance with online technology, Dr. Rozema takes advantage of these opportunities to further communicate and educate his patients about dental health care.
The practice's Facebook and Twitter pages were designed to improve patient-to-practice interaction. Functioning as an extension of the practice's professionally designed website, patients can now join Dr. Rozema's social network to ...
Study reveals how normal cells fuel tumor growth
2011-12-22
Research summary:
The study shows how normal cells in tumors can enhance the growth of the tumor's cancer cells after losing an important tumor suppressor gene called Pten.
The findings suggest a new strategy for treating breast cancer by interrupting signals between normal cells and cancer cells in tumors.
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study published in the journal Nature Cell Biology has discovered how normal cells in tumors can fuel tumor growth.
Led by researchers at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard ...
Protecting computers at start-up: New NIST guidelines
2011-12-22
A new draft computer security publication from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides guidance for vendors and security professionals as they work to protect personal computers as they start up.
The first software that runs when a computer is turned on is the "Basic Input/Output System" (BIOS). This fundamental system software initializes the hardware before the operating system starts. Since it works at such a low level, before other security protections are in place, unauthorized changes—malicious or accidental—to the BIOS can cause a significant ...
Cosmetic Dentist in Chicago Extends Office Hours
2011-12-22
Cosmetic dentist in Chicago, Dr. Carolyn Belke, invites patients to take advantage of Belke Dental's new extended office hours. Tuesdays and Thursdays, Dr. Belke is excited to offer patients later office hours.
Rather than closing at five on Tuesdays and Thursdays, Dr. Carolyn Belke, Chicago cosmetic dentist, has extended the office hours to 6:00 p.m. Patients can now enjoy the added hour to office hours for convenience and ease of receiving dental care. Additionally, patients can continue to visit the office during regular hours on Mondays and Wednesdays of 9:00 a.m. ...
NIST special publication expands government authentication options
2011-12-22
A newly revised publication from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) expands the options for government agencies that need to verify the identity of users of their Web-based services. Electronic Authentication Guideline (NIST Special Publication 800-63-1) is an extensive revision and update of the original document, released in 2006, and it recognizes that times, and technologies, have changed.
"Changes made to the document reflect changes in the state of the art," explains NIST computer security expert Tim Polk, Cryptographic Technology Group manager ...
Myths and truths of obesity and pregnancy
2011-12-22
Ironically, despite excessive caloric intake, many obese women are deficient in vitamins vital to a healthy pregnancy. This and other startling statistics abound when obesity and pregnancy collide. Together, they present a unique set of challenges that women and their doctors must tackle in order to achieve the best possible outcome for mom and baby.
In the December issue of the journal Seminars in Perinatology, maternal fetal medicine expert Loralei L. Thornburg, M.D., reviews many of the pregnancy-related changes and obstacles obese women may face before giving birth. ...
Supersized market economy, supersized belly: Wealthier nations have more fast food and more obesity
2011-12-22
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- New research from the University of Michigan suggests obesity can be seen as one of the unintended side effects of free market policies.
A study of 26 wealthy nations shows that countries with a higher density of fast food restaurants per capita had much higher obesity rates compared to countries with a lower density of fast food restaurants per capita.
"It's not by chance that countries with the highest obesity rates and fast food restaurants are those in the forefront of market liberalization, such as the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, ...
Dentist in Boulder Commits to Several Hours of Continuing Education Each Year
2011-12-22
Leading dentist in Boulder, Dr. Mark Barnes, has over 1100 hours of post-graduate training and commits to many hours each year for remaining up-to-date with dental advancements. Dr. Barnes maintains continuing education course, as well as lectures on subjects such as TMJ and sleep apnea treatment in Boulder and other areas.
Dr. Barnes, Boulder dentist, and his staff regularly participate in continuing education programs, while doing everything they can to offer patients the best care possible. Continuing education allows Dr. Barnes to help his patients achieve and maintain ...
Disease-causing strains of Fusarium prevalent in plumbing drains
2011-12-22
A study examining the prevalence of the fungus Fusarium in bathroom sink drains suggests that plumbing systems may be a common source of human infections.
In the first extensive survey of its kind, researchers in Penn State's College of Agricultural Sciences sampled nearly 500 sink drains from 131 buildings -- businesses, homes, university dormitories and public facilities -- in Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Florida and California.
They analyzed fungal DNA to compare the spectrum of Fusarium species and sequence types found ...
Vienna Dentist Encourages Patients to Leave Reviews of Practice
2011-12-22
Dr. Ardalan Sanati, Vienna dentist, invites patients to leave reviews of their experience via online search engines - Google, Yelp and Yahoo! The reviews are easily accessible via any of the available search engines and allow patients to view how other patients' experiences at Dr. Sanati's office were. Patients can visit Google, Yelp and Yahoo! to read reviews from previous patients who have received treatment from Dr. Sanati, cosmetic dentist in McLean.
"It is important for me to know what my patients' concerns are so that I know what I can do to make their time ...