(Press-News.org) A research team led by Glenn Rall at the Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia, PA developed a novel mouse model to show that a fatal central nervous system (CNS) disease can be caused by a pathogen that does not replicate in the CNS. The results of this new study are published December 22nd in the Open Access journal PLoS Pathogens.
The authors found that the immune response induced in response to a peripheral viral infection can be "mis-recruited" to the brain, where these activated immune cells can then lead to inflammation-induced neuropathology and disease. While "mis-recruitment" has been observed in other mouse models, this is the first study to show that this phenomenon can have pathogenic consequences.
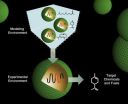
The novel model used two, tissue-restricted infections: lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), which, when injected intraperitoneally, is restricted to peripheral tissues such as the liver, spleen and kidney, and measles virus (MV), which is limited to CNS neurons. While infection with either virus alone resulted in no mortality, co-infection caused CNS symptoms in all mice, and death in approximately half. The authors show that this was due to migration of peripherally activated LCMV-specific T cells into the CNS, where they triggered edema leading to brain herniation, despite the apparent absence of LCMV antigens within the affected brain.
While the broader implications of this study await further investigation, this is a proof of principle study that addresses a key question: can a pathogen cause disease "at a distance"? Typically, we envision that diseases are manifested where infectious pathogens replicate: influenza causes respiratory infection because this is the primary site of replication. In contrast, this study suggests that infection can activate immune responses that can be deleterious in tissues that are not directly infected by the initiating pathogen. This may be of broader relevance to human CNS diseases of unknown etiology, including multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
The authors of this study point out, however, that "while making direct connections between this model system and human diseases would be premature, a similar phenomenon could account for both the reported increase in inflammatory cells found in the brain of patients, as well as the lack of consistent and convincing presence of any specific pathogen in the brains of affected individuals."
### END
Double trouble: Concomitant immune challenges result in CNS disease
2011-12-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
CAD for RNA
2011-12-23
The computer assisted design (CAD) tools that made it possible to fabricate integrated circuits with millions of transistors may soon be coming to the biological sciences. Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI) have developed CAD-type models and simulations for RNA molecules that make it possible to engineer biological components or "RNA devices" for controlling genetic expression in microbes. This holds enormous potential for microbial-based sustainable production of advanced biofuels, biodegradable plastics, therapeutic ...
For every road there is a tire
2011-12-23
KANSAS CITY, MO -- Life is complicated enough, so you can forgive the pioneers of DNA biology for glossing over transcriptional elongation control by RNA polymerase II, the quick and seemingly bulletproof penultimate step in the process that copies the information encoded in our DNA into protein-making instructions carried by messenger RNA.
In a new report appearing in the Dec. 23, 2011, issue of Molecular Cell, researchers at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research add not just a new layer, but a whole new dimension to transcriptional elongation control with evidence ...
Facebook Marketing Strategist Shows Chiropractors How to Get Endless New Patient Referrals from Social Media
2011-12-23
Chiropractic Internet marketing strategist and social media expert, Dr. Matthew Loop, has announced he'll continue to show DCs how to create an overwhelming presence on Facebook, which can easily net doctors an extra 20-30 new patients per month just from the social network. Dr. Loop's been helping fellow chiropractors master social media marketing since 2005-2006, which gives him an experience-based edge over other industry consultants.
He's garnered a well deserved reputation as the "go-to" guy for chiropractors that want to dramatically improve their new ...
Gene fusion in lung cancer afflicting never-smokers may be target for therapy
2011-12-23
December 22, 2011 – Smoking is a well-known risk factor for lung cancer, but nearly 25% of all lung cancer patients have never smoked. In a study published online today in Genome Research (www.genome.org), researchers have identified a previously unknown gene fusion event that could explain a significant proportion of lung cancer cases in never-smokers, and might serve as a target for new therapies.
Recent strides have been made to identify gene mutation events driving cases of lung adenocarcinoma in never-smokers, but the underlying genetic events leading to these lung ...
DNA mismatch repair happens only during a brief window of opportunity
2011-12-23
In eukaryotes – the group of organisms that include humans – a key to survival is the ability of certain proteins to quickly and accurately repair genetic errors that occur when DNA is replicated to make new cells.
In a paper published in the December 23, 2011 issue of the journal Science, researchers at the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research and the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have solved part of the mystery of how these proteins do their job, a process called DNA mismatch repair (MMR).
"One of the major questions in MMR is how MMR proteins ...
Biochemists develop promising new treatment direction for rare metabolic diseases
2011-12-23
AMHERST, Mass. – A research team led by biochemist Scott Garman at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has discovered a key interaction at the heart of a promising new treatment for a rare childhood metabolic disorder known as Fabry disease. The discovery will help understanding of other protein-folding disorders such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Huntington's diseases, as well. Findings are featured as the cover story in the current issue of Chemistry & Biology.
People born with Fabry disease have a faulty copy of a single gene that codes for the alpha-galactosidase ...
UT-ORNL research reveals aquatic bacteria more recent move to land
2011-12-23
Research by University of Tennessee, Knoxville, faculty has discovered that bacteria's move from sea to land may have occurred much later than thought. It also has revealed that the bacteria may be especially useful in bioenergy research.
Igor Jouline, UT-Oak Ridge National Laboratory joint faculty professor of microbiology and researcher at ORNL's Joint Institute for Computational Sciences, performed a genome sequence analysis of the soil bacteria Azospirillum, a species' whose forbearers made the sea-to-land move. The analysis indicates the shift may have occurred ...
Long intervening non-coding RNAs play pivotal roles in brain development
2011-12-23
FINDINGS: Whitehead Institute scientists have identified conserved, long intervening non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) that play key roles during brain development in zebrafish, and went on to show that the human versions of these RNAs can substitute for the zebrafish lincRNAs.
RELEVANCE: Despite their prevalence in the cell, lincRNAs have been referred to as the "dark matter" of all the transcribed RNAs because little is known of their functions or mechanisms. Until now, lincRNAs have been studied primarily in cell lines rather than at the organismal level, which has precluded ...
Unnatural disasters
2011-12-23
Global wildlife is facing an unprecedented threat from natural disasters exacerbated by climate change, warn scientists in a paper published in Trends in Ecology and Evolution.
Hurricanes, droughts, flooding and wildfires are predicted to increase in frequency and severity – but despite being able to spot human populations at risk, there is currently no mechanism for identifying vulnerable animal populations.
Now scientists from the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) have come up with a method to identify populations likely to experience drastic changes in their population ...
NIH researchers uncover clues related to metal-on-metal hip implants
2011-12-23
A new study, bringing together an interdisciplinary team of physicians and engineers from the United States and Germany, made a surprising finding about implants used in hip replacement surgery: Graphite carbon is a key element in the lubricating layer that forms on metal-on-metal hip implants. The lubricant has more in common with the lubrication of a combustion engine than that of a natural joint. The study was funded by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS), part of the National Institutes of Health.
Made possible by an ...