(Press-News.org) Damaged heart tissue is not known for having much inherent capacity for repair. But now, scientists are closing in on signals that may be able to coax the heart into producing replacement cardiac muscle cells. Using a zebrafish model system, researchers have identified a family of molecules that can stimulate stem cells to develop into beating heart muscle cells. The research, published by Cell Press in the December 21st issue of the journal Chemistry & Biology, may pave the way towards new therapeutic approaches for cardiac regeneration and repair.
"Despite advances in modern medicine, management of myocardial infarction and heart failure remains a major challenge," explains senior study author Dr. Tao P. Zhong from Fudan University in Shanghai, China. "There is intense interest in developing agents that can influence stem cells to differentiate into cardiac cells as well as enhance the inherent regenerative capacities of the heart. Developing therapies that can stimulate heart muscle regeneration in areas of infarction would have enormous medical impact."
To search for new molecules involved in heart development, Dr. Zhong and colleagues developed a robust small molecule screen using a zebrafish system. The zebrafish is an excellent model organism to study heart growth and development because there are established genetic approaches that permit visualization of fluorescent beating hearts within transparent embryos. After screening nearly 4,000 compounds, the researchers discovered three structurally related molecules that could selectively enlarge the size of the embryonic heart. The compounds, cardionogen-1, -2, and -3, could promote or inhibit heart formation, depending on when they were administered during development.
Cardionogen treatment enlarged the zebrafish heart by stimulating production of new cardiac muscle cells from stem cells. The researchers went on to show that cardionogen could stimulate mouse embryonic stem cells to differentiation into beating cardiac muscle cells. The effects of cardionogen were linked to Wnt signaling, a pathway best known for its role in embryonic and heart development. Cardionogen opposes Wnt signaling to induce cardiac muscle cell formation. Importantly, the interaction of cardionogen with Wnt seemed to be restricted to specific cell types.
Taken together, the results identify the cardionogen family members as important modulators of cardiac muscle cell development. "Evaluating the potential of cardionogen on human adult and embryonic stem cells is the next logical step," concludes Dr. Zhong. "This may ultimately aid in design of therapeutic approaches to enhance repopulation of damaged heart muscle and restore function in diseased hearts."
### END
How do you mend a broken heart?
2011-12-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists identify cell death pathway involved in lethal sepsis
2011-12-23
Sepsis, a form of systemic inflammation, is the leading cause of death in critically ill patients. Sepsis is linked with massive cell death; however, the specific mechanisms involved in the lethality of sepsis are unclear. Now, a new study published by Cell Press in the December 23rd issue of the journal Immunity finds that inhibition of a specific cell death pathway called "necroptosis" protected mice from lethal inflammation. The research may lead to new therapeutic interventions for fatal inflammatory conditions that are notoriously hard to control.
Systemic inflammatory ...
Web Design Company Bird and Co Creative Announce the Launch of New Website for Top Racehorse Trainer Kevin Ryan
2011-12-23
Kevin Ryan is the latest high profile racehorse trainer to have a website designed by Bird and Co Creative. Bird and Co are becoming well known in the horse racing and equestrian world for producing first class websites and marketing material for racehorse trainers and horse related businesses. Their knowledge and experience in these fields stands them in good stead for producing effective designs.
Kevin Ryan is one of the most respected trainers in the profession and has been training since 1998. The Yorkshire based racehorse trainer has a sizeable yard which is equipped ...
Fixing common blood disorder would make kidney transplants more successful
2011-12-23
Washington, DC (December 22, 2011) — Correcting anemia, a red blood cell deficiency, can preserve kidney function in many kidney transplant recipients, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society Nephrology (JASN). The results indicate that aggressively treating anemia may help save the kidneys—and possibly the lives—of many transplant recipients.
Anemia commonly arises in patients with kidney disease because the kidneys secrete most of the hormone erythropoietin that stimulates red blood cell production. Anemia is also a ...
Toddlers don't listen to their own voice like adults do
2011-12-23
When grown-ups and kids speak, they listen to the sound of their voice and make corrections based on that auditory feedback. But new evidence shows that toddlers don't respond to their own voice in quite the same way, according to a report published online on December 22 in Current Biology, a Cell Press publication.
The findings suggest that very young children must have some other strategy to control their speech production, the researchers say.
"As they play music, violinists will listen to the notes they produce to ensure they are in tune," explained Ewen MacDonald ...
How skin is wired for touch
2011-12-23
Compared to our other senses, scientists don't know much about how our skin is wired for the sensation of touch. Now, research reported in the December 23rd issue of the journal Cell, a Cell Press publication, provides the first picture of how specialized neurons feel light touches, like a brush of movement or a vibration, are organized in hairy skin.
Looking at these neurons in the hairy skin of mice, the researchers observed remarkably orderly patterns, suggesting that each type of hair follicle works like a distinct sensory organ, each tuned to register different ...
Science's breakthrough of the year: HIV treatment as prevention
2011-12-23
This press release is available in Arabic, French, Japanese, Spanish and Chinese on EurekAlert! Chinese.
The journal Science has lauded an eye-opening HIV study, known as HPTN 052, as the most important scientific breakthrough of 2011. This clinical trial demonstrated that people infected with HIV are 96 percent less likely to transmit the virus to their partners if they take antiretroviral drugs (ARVs).
The findings end a long-standing debate over whether ARVs could provide a double benefit by treating the virus in individual patients while simultaneously cutting ...
The Rise of In-House Strategy and Change Teams
2011-12-23
A little history...
In late 2009, as the economy started to pick up again, there was a surge in hiring activity from firms for consultancy jobs to bring on board the skills necessary to win, design and deliver new change programmes. There was the understanding that both government and private sector-led initiatives would guarantee medium-term revenue, and management consultancies and strategy houses were vying for a piece of the action after several lean years.
The top consultancies were getting involved in major transformation programmes (such as the Lloyds/HBOS ...
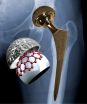
Hips that function better and last longer
2011-12-23
A team of engineers and physicians have made a surprising discovery that offers a target for designing new materials for hip implants that are less susceptible to the joint's normal wear and tear.
Researchers from Northwestern University, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, and the University of Duisburg-Essen Germany found that graphitic carbon is a key element in a lubricating layer that forms on metal-on-metal hip implants. The lubricant is more similar to the lubrication of a combustion engine than that of a natural joint.
The study will be published Dec. ...
Tackling Gender Inequality in the Boardroom
2011-12-23
Some signs are emerging that the executive-level diversity landscape is changing. Looking at individual cases paints a promising picture of women beginning to dominate the boardroom. Some of the world's largest technology companies are now led by women, Meg Whitman is president and chief exec at HP and Virginia Rometty is soon to assume the same role at IBM. Closer to home, Ruby McGregor-Smith is CEO of MITIE (and non-executive director at Michael Page) and Angela Ahrendts and Cynthia Carroll have led FTSE 100 listed Burberry and Anglo American respectively for several ...
MRI scan 'better' for heart patients
2011-12-23
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan for coronary heart disease is better than the most commonly-used alternative, a major UK trial of heart disease patients has shown.
The findings by University of Leeds researchers could change the way that people with suspected heart disease are assessed, potentially avoiding the need for tests that are invasive or use ionising radiation.
Full results of the study, which was funded by a £1.3 million grant from the British Heart Foundation (BHF), are published online today by the Lancet medical journal.
Coronary heart disease ...