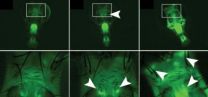
(Press-News.org) PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — To track what they can't see, pilots look to the green glow of the radar screen. Now biologists monitoring gene expression, individual variation, and disease have a glowing green indicator of their own: Brown University biologists have developed a "radar" for tracking ADAR, a crucial enzyme for editing RNA in the nervous system.
The advance gives scientists a way to view when and where ADAR is active in a living animal and how much of it is operating. In experiments in fruit flies described in the journal Nature Methods, the researchers show surprising degrees of individual variation in ADAR's RNA editing activity in the learning and memory centers of the brains of individual flies.
"We designed this molecular reporter to give us a fluorescent readout from living organisms," said Robert Reenan, professor of biology and senior author of the paper, which appears Dec. 25, 2011. "When it comes to gene expression and regulation, the devil is in the details."
Biologists already know that errors in transcribing RNA from DNA can lead to improper gene expression in the nervous system and might contribute to diseases such as epilepsy, suicidal depression, and schizophrenia. More recently they've gathered evidence that ADAR is associated with disease. For instance in a study in Nature Neuroscience two months ago, Reenan and colleagues at the University of Pennsylvania described profound connections between ADAR and a model of Fragile X mental retardation in fruit flies.
Reenan said that using the new "reporter" tool to look for correlations between ADAR activity levels and behavior or disease might yield new insights into how RNA editing errors lead to such variations. But he also speculated that the mechanics of how he and his research group created the fluorescent ADAR tracking system could be adapted to someday allow therapies based on targeted RNA repair. Their reporter works by requiring ADAR to fix a purposely broken individual letter of RNA on an engineered gene.
"We're actually repairing RNA at the level of a single informational bit, or nucleotide," Reenan said. "Here we've shown we can take a mutant version of a gene and restore its function, but at the level of RNA rather than DNA."
A reporter of an editor
Reenan and third author Kyle Jay began working to create the reporter in 2006 when Jay was an undergraduate student just embarking on what would become a celebrated senior thesis at Brown. They started with a well-known tool of molecular biology: a jellyfish gene that produces a protein that glows green upon exposure to ultraviolet light. The strategy was to intentionally break the gene in a way that ADAR is uniquely suited to fix.
First they engineered the gene to include necessary "intron" code that requires a specific splicing operation to take place. Then they inserted the "stop codon" T-A-G in place of T-G-G, which causes transcription to cease, effectively preventing production of the green fluorescent protein. But before splicing occurs and when ADAR finds the stop codon U-A-G in the RNA transcript, it edits the A to an I, which restores the correct information, and translation of the whole gene proceeds as if there were no stop mutation in the DNA. So when splicing and ADAR editing occurs, neurons with the gene reporter glow green.
To see where ADAR editing and splicing were occurring, compared to just splicing alone, they also rigged up an engineered gene with the splicing requirement, but not the T-A-G codon. That would produce yellow fluorescent protein when splicing alone occurred.
Armed with their new ADAR reporter, Reenan and lead author James Jepson set out to make some biological observations in flies. One was that ADAR activity is more pronounced in certain parts of the brains of developing larvae than it is in the brains of adults. The team also found wide variation in ADAR activity in the brains of flies of similar ages from individual to individual. This was a surprise, Reenan said, because all the flies were essentially genetically identical.
A versatile new tool?
Reenan said he is confident that the ADAR reporter could be useful in more organisms than the fruit fly. The idea of creating the reporter grew out of his lab's studies of comparative genomics in a number of species. ADAR, meanwhile, is found in both invertebrates and vertebrates. In fact, in the paper the researchers describe testing the flexibility of their engineering by inserting into their engineered jellyfish gene — destined as it was for a fruit fly — the splicing intron of a moth.
"Thus it was, a jellyfish-moth gene chimera was crippled by mutation, and repaired by a fruit fly enzyme," Reenan said. "Rube Goldberg would be proud."
Reenan said he plans to use the ADAR reporter in flies to continue the investigation of the genes associated with Fragile X and is eager for someone who works on the disorder in mice to give it a try.
The idea of adapting this method to direct ADAR to fix mistranscribed RNA or reverse DNA damage at the RNA level in a therapeutic fashion is farther into the future. But in a sense, at least ADAR is now on the radar.
INFORMATION:
In addition to Reenan, Jepson, and Jay, the paper's other author is Yannis A. Savva. Jepson is also affiliated with Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia and Jay now works at the University of California–San Francisco.
An Ellison Medical Foundation Senior Scholar award funded the research.
A radar for ADAR: Altered gene tracks RNA editing in neurons
Biologists use technology to observe individual differences in fruit flies
2011-12-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New synthetic molecules treat autoimmune disease in mice
2011-12-27
A team of Weizmann Institute scientists has turned the tables on an autoimmune disease. In such diseases, including Crohn's and rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's tissues. But the scientists managed to trick the immune systems of mice into targeting one of the body's players in autoimmune processes, an enzyme known as MMP9. The results of their research appear today in Nature Medicine.
Prof. Irit Sagi of the Biological Regulation Department and her research group have spent years looking for ways to home in on and block members of the ...
Faster, more accurate, more sensitive
2011-12-27
Lightning fast and yet highly sensitive: HHblits is a new software tool for protein research which promises to significantly improve the functional analysis of proteins. A team of computational biologists led by Dr. Johannes Söding of LMU's Genzentrum has developed a new sequence search method to identify proteins with similar sequences in databases that is faster and can discover twice as many evolutionarily related proteins as previous methods. From the functional and structural properties of the identified proteins conclusions can then be drawn on the properties of ...
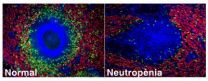
Discovered the existence of neutrophils in the spleen
2011-12-27
This release is available in Spanish.
Barcelona, 23rd of December 2011.- For the first time, it has been discovered that neutrophils exist in the spleen without there being an infection. This important finding made by the research group on the Biology of B Cells of IMIM (Hospital del Mar Research Institute) in collaboration with researchers from Mount Sinai in New York, has also made it possible to determine that these neutrophils have an immunoregulating role.
Neutrophils are the so-called cleaning cells, since they are the first cells to migrate to a place ...
Study links quality of mother-toddler relationship to teen obesity
2011-12-27
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The quality of the emotional relationship between a mother and her young child could affect the potential for that child to be obese during adolescence, a new study suggests.
Researchers analyzed national data detailing relationship characteristics between mothers and their children during their toddler years. The lower the quality of the relationship in terms of the child's emotional security and the mother's sensitivity, the higher the risk that a child would be obese at age 15 years, according to the analysis.
Among those toddlers who had the lowest-quality ...
Memo to pediatricians: Allergy tests are no magic bullets for diagnosis
2011-12-27
An advisory from two leading allergists, Robert Wood of the Johns Hopkins Children's Center and Scott Sicherer of Mt. Sinai Hospital in New York, urges clinicians to use caution when ordering allergy tests and to avoid making a diagnosis based solely on test results.
In an article, published in the January issue of Pediatrics, the researchers warn that blood tests, an increasingly popular diagnostic tool in recent years, and skin-prick testing, an older weapon in the allergist's arsenal, should never be used as standalone diagnostic strategies. These tests, Sicherer ...
Study uncovers a molecular 'maturation clock' that modulates branching architecture in tomato plants
2011-12-27
Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y. – The secret to pushing tomato plants to produce more fruit might not lie in an extra dose of Miracle-Gro. Instead, new research from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) suggests that an increase in fruit yield might be achieved by manipulating a molecular timer or so-called "maturation clock" that determines the number of branches that make flowers, called inflorescences.
"We have found that a delay in this clock causes more branching to occur in the inflorescences, which in turn results in more flowers and ultimately, more fruits," says CSHL ...
Over 65 million years North American mammal evolution has tracked with climate change
2011-12-27
PROVIDENCE, R.I. -- History often seems to happen in waves – fashion and musical tastes turn over every decade and empires give way to new ones over centuries. A similar pattern characterizes the last 65 million years of natural history in North America, where a novel quantitative analysis has identified six distinct, consecutive waves of mammal species diversity, or "evolutionary faunas." What force of history determined the destiny of these groupings? The numbers say it was typically climate change.
"Although we've always known in a general way that mammals respond ...
Sunlight and bunker oil a fatal combination for Pacific herring
2011-12-27
The 2007 Cosco Busan disaster, which spilled 54,000 gallons of oil into the San Francisco Bay, had an unexpectedly lethal impact on embryonic fish, devastating a commercially and ecologically important species for nearly two years, reports a new study by the University of California, Davis, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
The study, to be published the week of Dec. 26 in the early edition of the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggests that even small oil spills can have a large impact on marine life, and that common chemical ...
Avital Web, Los Angeles SEO Company, is Offering Free Dental SEO Services
2011-12-27
Internet marketing is an important component in the marketing strategy of every business, including dentists. Having a top ranking website is quite essential for bringing in new customers. That is why Avital Web, a top SEO company in Los Angeles, is now offering free dental SEO packages to qualified dentists to help them improve the ranking of their websites.
Competition Fierce for Dental Practices
The family dentistry office barely exists anymore. Between teeth whitening and dental implants, impressive new Invisalign technology and other cosmetic dental practices, ...
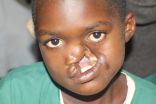
Dr. Leon Klempner, an Orthodontist in Medford and Port Jefferson, NY, Founder of The Smile Rescue Fund for Kids, Funds Facial Surgery for Kenyan Girl Infected With NOMA Disease
2011-12-27
Saline, an 11 year old Kenyan girl received the first of three surgeries last week. Saline had been rejected from all major charities due to the complexity of her facial deformity. She was born with a cleft lip and palate and then infected with NOMA disease. NOMA is a flesh eating disease caused by malnutrition, poor sanitation and dehydration. Estimates show 80-90% die from the disease. Click here to see YouTube video.
Dr. Leon Klempner founded Coolsmiles Orthodontics in 1978 with offices in Medford and Port Jefferson, NY. In addition to treating local patients with ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
[Press-News.org] A radar for ADAR: Altered gene tracks RNA editing in neuronsBiologists use technology to observe individual differences in fruit flies