(Press-News.org) Scientists have determined the structure of the enzyme endomannosidase, significantly advancing our understanding of how a group of devastating human viruses including HIV and Hepatitis C hijack human enzymes to reproduce and cause disease.
The findings open the door to the development of new drugs to combat these deadly viruses that infect more than 180 million people worldwide.
The team of international scientists led by and Professor Gideon Davies from the University of York and Associate Professor Spencer Williams from the University of Melbourne, studied bacterial endomannosidase as a model for the same human enzyme and successfully determined the three dimensional structure of the enzyme using state of the art synchrotron technology.
Professor Davies, of the Department of Chemistry at York, said that knowing the structure of the enzyme revealed details on how viruses play biological "piggy-back", borrowing our cellular machinery to replicate and cause disease
"If we understand how the viruses use our enzymes, we can develop inhibitors that block the pathway they require, opening the door to drug developments," he said.
In the past the problem has been that this group of viruses including HIV, Hepatitis C, Dengue Fever and West Nile virus, are able to bypass the main pathway if inhibited and replicate via a second pathway using this enzyme. Thus for a treatment to be effective, both pathways need to be blocked.
"It was already known how to block the main pathway for these viruses but until now, this endomannosidase bypass pathway has proved a considerable challenge to study," Professor Davies said.
Dr Williams said: "Combining international resources and expertise, we were able to determine the endomannosidase structure and this has revealed how we can block the bypass route, stopping the viruses from hijacking human enzymes."
Professor Davies added: "We hope that the work will lead beyond viruses and will point the way towards similar treatments for other diseases including cancer."
###The research received funding support from the Biotechnology and Biosciences Research Council and the Australian Research Council.
The study is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) this week.
No more free rides for 'piggy-backing' viruses
2012-01-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Russian river water unexpected culprit behind Arctic freshening near US, Canada
2012-01-05
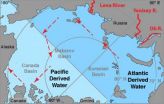
A hemispherewide phenomenon – and not just regional forces – has caused record-breaking amounts of freshwater to accumulate in the Arctic's Beaufort Sea.
Frigid freshwater flowing into the Arctic Ocean from three of Russia's mighty rivers was diverted hundreds of miles to a completely different part of the ocean in response to a decades-long shift in atmospheric pressure associated with the phenomenon called the Arctic Oscillation, according to findings published in the Jan. 5 issue of Nature.
The new findings show that a low pressure pattern created by the Arctic Oscillation ...
One in Four Brits Spend 40% of Take-Home Pay on Debt Payments, Reveals Debt Solutions Company, Debt Relief Orders
2012-01-05
The report from Moneysupermarket.com revealed that the average amount of non-mortgage debt paid off each month is GBP322 a month, around 25% of the average monthly net salary for a UK adult, while a shocking 8% claim to have spent over 80% of their wages repaying debt. And despite women having the reputation for being prolific shoppers, it is men that appear to have 15% more personal unsecured debt compared to their female counterparts - on average GBP7,944 compared to GBP6,739.
MoneySupermarket.com's head of loans and debt, Tim Moss, said: "With the cost of living ...
New fermented soy ingredient containing S-equol significantly reduced hot flash frequency
2012-01-05
Northridge, CALIF (Jan 4, 2012) – Daily doses of a soy germ-based nutritional supplement containing S-equol significantly improved menopausal symptoms, including significantly reducing hot flash frequency after 12 weeks according to a placebo-controlled study in postmenopausal Japanese women published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Women's Health.
"It is believed that S-equol, produced from the isoflavone daidzein during the fermentation of soy germ, interacts with specific estrogen receptors to promote the improvement in menopausal symptoms. Data from this study and ...
Results, Long-Term Breast Implants
2012-01-05
In 2006, the Food & Drug Administration approved two new models of silicone implants: one model was made by Mentor and the other by Allergan. This approval by the FDA proved controversial as many critics claimed there wasn't enough evidence of silicone implants being safe for the long term.
To study how the implants held up over long-term, the FDA required both Mentor and Allergan to perform a variety of follow-up studies--some studies won't even end until 2016. The study involved 40,000 participants for each model, totaling 80,000 in all.
Some studies included ...
Seriously, we're poisonous: Coloration is an honest signal of toxicity in poison frogs
2012-01-05
January article highlights:
Seriously, we're poisonous: Coloration is an honest signal of toxicity in poison frogs
Bright Eyes: How butterflies recognize their compatriots in a world of mimics
Researchers show how a nest parasite can be a good thing for an ant colony
A rough start for a hatchling could mean duller plumage for life
For a complete list of articles in the January issue, go to www.journals.uchicago.edu/an
Seriously, we're poisonous: Coloration is an honest signal of toxicity in poison frogs
The conspicuous colors of poisonous frogs serve as a warning ...
Non-Surgical Facelifts
2012-01-05
If you are looking to reduce the signs of facial aging that make you look prematurely aged, but you are not ready for a surgical facelift, you may be considering nonsurgical treatments. Nonsurgical facelifts are not an alternative to traditional facelifts, but they can be an interim treatment for some people. However, if you are considering using nonsurgical treatments for your facial rejuvenation, you should make sure that your choice of plastic surgeon is capable of combining treatments successfully.
Here are some of the elements that go into a nonsurgical facelift.
BOTOX ...
Kaiser Permanente study finds continuous health coverage essential for patients managing diabetes
2012-01-05
January 04, 2012-PORTLAND, Ore. — When patients with diabetes experience interruptions in health - insurance coverage, they are less likely to receive the screening tests and vaccines they need to protect their health. A new study finds that this is true even when patients receive free or reduced-cost medical care at federally funded safety net clinics.
The study was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health and findings published online in the Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine.
“Our study shows that patients need continuous health insurance ...
Tampa Bay Sinkhole Attorney Ted Corless Gives Florida Homeowners' Side on Sinkhole Insurance
2012-01-05
With more than a decade of experience helping Tampa-area homeowners recover for sinkhole damage to their homes, Attorney Ted Corless, of Corless Associates, wants to clear the air related to recent coverage of sinkhole claims and insurance 'abuse' by policyholders. In the first of three articles to be run by the Tampa Bay Times, sinkhole insurance is characterized as the "Great Florida Sinkhole Lottery;" examples of Florida homeowners receiving payment for losses due to sinkhole damage and using the money for other purposes than repairing the damaged home are ...
How can Lyme disease be prevented and controlled?
2012-01-05
Lyme disease is the most commonly reported vector-borne disease in the United States, with the majority of cases occurring in the Northeast. It has been three decades since the agent of the disease, the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi, and the ticks that vector it were identified. However, the number of Lyme disease cases have steadily increased.
In a new article appearing in the forthcoming issuue of the Journal of Medical Entomology called "What Do We Need to Know About Disease Ecology to Prevent Lyme Disease in the Northeastern United States?" authors from Colorado ...
Research shows progress toward a genital herpes vaccine
2012-01-05
ST. LOUIS -- An investigational vaccine protected some women against infection from one of the two types of herpes simplex viruses that cause genital herpes, according to findings in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The vaccine was partially effective at preventing herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), but did not protect women from herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2). There were less than half of the cases of genital herpes caused by HSV-1 – 58 percent fewer -- in women who received the investigational vaccine compared to women who received the control vaccine.
"There ...