(Press-News.org) A team of geneticists and computational biologists in the UK today reveal how an ancient mechanism is involved in gene control and continues to drive genome evolution. The new study is published in the journal Cell.
To function properly, mammalian tissues require the protein CTCF, which has several key activities including the regulation of genes and interaction with proteins in the cell's nucleus to alter gene activity. CTCF acts by binding to DNA and plays a role in diseases such as HIV infection and cancer. However, very little is known about the origin of the DNA sequences that are bound by CTCF.
In this study, the researchers used samples from six mammals (human, macaque, mouse, rat, dog, and short-tailed opossum) to pinpoint where CTCF binds to each genome. They discovered around 5000 sites that are present in most cell types and tissues, and that have not changed over hundreds of millions of years of mammalian evolution. Because these CTCF binding sites are conserved throughout evolution, the researchers believe that many might play an important role in gene regulation.
The team found an even larger number of locations where CTCF binds DNA in only one lineage or a single species. These additional sites represent a signature of important evolutionary changes since our last common ancestor – legacies, in some cases, of the evolutionary path to humans. These newer CTCF sites are embedded inside virus-like stretches of DNA called 'retro-transposons'. Retro-transposons use a copy-paste mechanism to spread copies of themselves throughout the genome.
"We developed a new, integrated model of CTCF evolution, which explains the origin of these 5000 highly conserved CTCF binding events in mammals," said Paul Flicek of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory-European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) and the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute. "Taken together, our findings provide fascinating insight into an ancient mechanism of evolution that is still actively changing our genome."
"CTCF is a key regulator involved in chromatin and gene expression remodelling, both of which are perturbed in the development of cancer. The gene expression and chromatin changes in cancer have also recently been relied on to predict the outcome of specific cancer treatments, which is why it is so important to have a detailed understanding of how particular parts of the genome are resistant or plastic to changes," said Duncan Odom of Cancer Research UK and the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute.
The retro-transposon's copy-and-paste behaviour has long been considered totally self-serving. However, the study showed that when a retro-transposon containing a CTCF-binding sequence spreads around a mammal's genome, it can deposit functional CTCF binding sites in novel locations, altering the activity of distant genes.
"We looked at six mammalian species representing primates, marsupials, rodents and carnivores, and discovered a simple mechanism that they all use to remodel their DNA," explained Petra Schwalie of EMBL-EBI. "We also found that our distant ancestors also experienced the same complicated relationship between CTCF and retro-transposons."
Using molecular palaeontology techniques, the researchers were able to identify fossil traces of older retro-transposon expansions in the DNA around the shared CTCF binding locations, and showed that this process has been active for hundreds of millions of years.
INFORMATION:
The study combined the efforts of researchers at EMBL-EBI, the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Cancer Research UK, and the Cambridge Hepatobiliary Service at Addenbrooke's Hospital in Cambridge, UK.
END
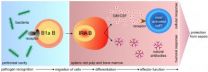
Investigators in the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) Center for Systems Biology have discovered a previously unknown type of immune cell, a B cell that can produce the important growth factor GM-CSF, which stimulates many other immune cells. They also found that these novel cells may help protect against the overwhelming, life-threatening immune reaction known as sepsis.
"B cells are a family of white blood cells that secrete antibodies, and GM-CSF induces the production or activation of granulocytes and macrophages, other white blood cells that have specific ...
DURHAM, N.C. -- While physicists at the Large Hadron Collider smash together thousands of protons and other particles to see what matter is made of, they're never going to hurl electrons at each other. No matter how high the energy, the little negative particles won't break apart. But that doesn't mean they are indestructible.
Using several massive supercomputers, a team of physicists has split a simulated electron perfectly in half. The results, which were published in the Jan. 13 issue of Science, are another example of how tabletop experiments on ultra-cold atoms and ...
More than half of all cases of dementia in the elderly can be attributed to Alzheimer's disease. Despite vast research efforts, an effective therapy has not been developed, and treatment consists of dealing with the symptoms. Changes in brain tissues are a hallmark of Alzheimer's. In affected individuals, small protein fragments known as amyloid beta peptides accumulate and are deposited in the gray brain matter. Researchers recently identified a series of synthetic compounds (inhibitors) that interfere with the self-assembly of the amyloid beta peptide in vitro; they influence ...
PASADENA, Calif.—Astronomers from the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and the University of Arizona have released the largest data set ever collected that documents the brightening and dimming of stars and other celestial objects—two hundred million in total.
The night sky is filled with objects like asteroids that dash across the sky and others—like exploding stars and variable stars—that flash, dim, and brighten. Studying such phenomena can help astronomers better understand the evolution of stars, massive black holes in the centers of galaxies, and the ...
PASADENA, Calif. -- A team of researchers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) has devised a new method for making complex molecules. The reaction they have come up with should enable chemists to synthesize new varieties of a whole subclass of organic compounds called nitrogen-containing heterocycles, thus opening up new avenues for the development of novel pharmaceuticals and natural products ranging from chemotherapeutic compounds to bioactive plant materials such as morphine.
The team—led by Brian Stoltz, the Ethel Wilson Bowles and Robert Bowles Professor ...
SAN DIEGO – (January 12, 2012) Researchers at the La Jolla Institute for Allergy & Immunology have proven – for the first time in human tissues -- the specific immune system T cells which trigger the destruction of type 1 diabetes in the pancreas. The finding is an important advance that verifies in humans several important disease characteristics shown in mouse studies and provides a key focal point for interrupting the disease process.
"This study marks the first time that the presence of beta cell-reactive T cells has been directly proven in pancreas tissues from ...
EVANSTON, Ill. --- By putting 18 million cracks in the proverbial glass ceiling, Hillary Clinton changed the way Americans think about women in politics, and new Northwestern University research suggests that an affirmative action law in India is doing the same for Indian women.
The research, to be published Jan. 12 in the journal Science, focused on the long-term outcomes of a law that reserved leadership positions for women in randomly selected village councils in India.
The law has led to a direct role model effect and is changing the way the girls as well as their ...
No less than one third of a car's fuel consumption is spent in overcoming friction, and this friction loss has a direct impact on both fuel consumption and emissions. However, new technology can reduce friction by anything from 10% to 80% in various components of a car, according to a joint study by VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland and Argonne National Laboratory (ANL) in USA. It should thus be possible to reduce car's fuel consumption and emissions by 18% within the next 5 to 10 years and up to 61% within 15 to 25 years.
There are 612 million cars in the world ...
Mothers who take anti-depressants during pregnancy are more likely to give birth to children with persistent pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the lungs) finds a study published today on bmj.com.
Persistent pulmonary hypertension is an increase in blood pressure in the lungs leading to shortness of breath and difficulty breathing. It is a rare, but severe disease with strong links to heart failure.
The study, carried out by researchers at the Centre for Pharmacoepidemiology at Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm Sweden, reviewed 1.6 million births in total ...
It is time to leave apart the belief that mass media are always a source of bad habits. Television, newspaper and the Internet, when used to get information, may turn out to be of help for health.
It is the conclusion of a study conducted by the Research Laboratories at the Fondazione di Ricerca e Cura "Giovanni Paolo II" in Campobasso which analyzed data from a sample of more than 1,000 people from the largest Moli-sani Project, the epidemiological study that recruited 25,000 subjects in Molise, a southern region of Italy.
The report, published on line in the International ...