(Press-News.org) In a breakthrough paper published in Science, researchers from The University of Manchester, The University of Bristol and Sandia National Laboratories report the potentially revolutionary effects of Criegee biradicals.
These invisible chemical intermediates are powerful oxidisers of pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide, produced by combustion, and can naturally clean up the atmosphere.
Although these chemical intermediates were hypothesised in the 1950s, it is only now that they have been detected.
Scientists now believe that, with further research, these species could play a major role in off-setting climate change.
The detection of the Criegee biradical and measurement of how fast it reacts was made possible by a unique apparatus, designed by Sandia researchers, that uses light from a third-generation synchrotron facility, at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory's Advanced Light Source.
The intense, tunable light from the synchrotron allowed researchers to discern the formation and removal of different isomeric species – molecules that contain the same atoms but arranged in different combinations.
The researchers found that the Criegee biradicals react more rapidly than first thought and will accelerate the formation of sulphate and nitrate in the atmosphere. These compounds will lead to aerosol formation and ultimately to cloud formation with the potential to cool the planet.
The formation of Criegee biradicals was first postulated by Rudolf Criegee in the 1950s. However, despite their importance, it has not been possible to directly study these important species in the laboratory.
In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about 0.8 °C with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades.
Most countries have agreed that drastic cuts in greenhouse gas emissions are required, and that future global warming should be limited to below 2.0 °C (3.6 °F).
Dr Carl Percival, Reader in Atmospheric Chemistry at The University of Manchester and one of the authors of the paper, believes there could be significant research possibilities arising from the discovery of the Criegee biradicals.
He said: "Criegee radicals have been impossible to measure until this work carried out at the Advanced Light Source. We have been able to quantify how fast Criegee radicals react for the first time.
"Our results will have a significant impact on our understanding of the oxidising capacity of the atmosphere and have wide ranging implications for pollution and climate change.
"The main source of these Criegee biradicals does not depend on sunlight and so these processes take place throughout the day and night."
Professor Dudley Shallcross, Professor in Atmospheric Chemistry at The University of Bristol, added: "A significant ingredient required for the production of these Criegee biradicals comes from chemicals released quite naturally by plants, so natural ecosystems could be playing a significant role in off-setting warming.'
INFORMATION: END
Boston, MA — Dozens of studies, many from Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH) researchers, have shown that low-fat diets are no better for health than moderate- or high-fat diets—and for many people, may be worse.
To combat this "low fat is best" myth, nutrition experts at HSPH and chefs and registered dietitians at The Culinary Institute of America (CIA) have developed five new muffin recipes that incorporate healthy fats and whole grains, and use a lighter hand on the salt and sugar. Their goal? To "make over" the ubiquitous low-fat muffin, touted as a "better-for-you" ...
The level of HIV-1 in the blood of an HIV-infected partner is the single most important factor influencing risk of sexual transmission to an uninfected partner, according to a multinational study of heterosexual couples in sub-Saharan Africa. The study, published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases, calculated the risk of HIV-1 transmission per act of sexual intercourse and found the average rate of infection to be about 1 per 900 coital acts. The findings also confirmed that condoms are highly protective and reduce HIV infectivity by 78 percent.
James P. Hughes, PhD, ...
Scientists have offered up a convincing explanation for the harsh winters recently experienced in the Northern Hemisphere; increasing temperatures and melting ice in the Arctic regions creating more snowfall in the autumn months at lower latitudes.
Their findings may throw light on specific weather incidents such as the extremely harsh Florida winter of 2010 which ended up killing a host of tropical creatures, as well as the chaos-causing snow that fell on the UK in December 2010.
Published today, Friday 13 January, in IOP Publishing's journal Environmental Research ...
The world population is estimated to be seven billion and all these mouths need feeding. With fears about overfishing and the sustainability of fish stocks in our seas fish farming is becoming big business. As with all farming there are issues about maintaining the health of stock and how to prevent bacterial infection. New research published in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Microbiology demonstrates that a prototype water purification reactor containing a thin film of titanium dioxide (TiO2) is able to enhance the sun's natural disinfection properties This device ...
Furring of the arteries, atherosclerosis, is a leading cause of death across the world. Atherosclerosis leads to peripheral arterial disease, coronary heart disease, stroke and heart attacks. However, atherosclerosis is a sneaky killer - most people do not realize they have it until they have cardiovascular disease (CV). New research published in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Medical Genomics has identified a set of biomarkers which can be used to test for early stage atherosclerosis.
Researchers from the University of Virginia compared biomarkers isolated ...
A team of geneticists and computational biologists in the UK today reveal how an ancient mechanism is involved in gene control and continues to drive genome evolution. The new study is published in the journal Cell.
To function properly, mammalian tissues require the protein CTCF, which has several key activities including the regulation of genes and interaction with proteins in the cell's nucleus to alter gene activity. CTCF acts by binding to DNA and plays a role in diseases such as HIV infection and cancer. However, very little is known about the origin of the DNA sequences ...
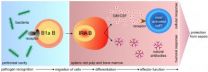
Investigators in the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) Center for Systems Biology have discovered a previously unknown type of immune cell, a B cell that can produce the important growth factor GM-CSF, which stimulates many other immune cells. They also found that these novel cells may help protect against the overwhelming, life-threatening immune reaction known as sepsis.
"B cells are a family of white blood cells that secrete antibodies, and GM-CSF induces the production or activation of granulocytes and macrophages, other white blood cells that have specific ...
DURHAM, N.C. -- While physicists at the Large Hadron Collider smash together thousands of protons and other particles to see what matter is made of, they're never going to hurl electrons at each other. No matter how high the energy, the little negative particles won't break apart. But that doesn't mean they are indestructible.
Using several massive supercomputers, a team of physicists has split a simulated electron perfectly in half. The results, which were published in the Jan. 13 issue of Science, are another example of how tabletop experiments on ultra-cold atoms and ...
More than half of all cases of dementia in the elderly can be attributed to Alzheimer's disease. Despite vast research efforts, an effective therapy has not been developed, and treatment consists of dealing with the symptoms. Changes in brain tissues are a hallmark of Alzheimer's. In affected individuals, small protein fragments known as amyloid beta peptides accumulate and are deposited in the gray brain matter. Researchers recently identified a series of synthetic compounds (inhibitors) that interfere with the self-assembly of the amyloid beta peptide in vitro; they influence ...
PASADENA, Calif.—Astronomers from the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and the University of Arizona have released the largest data set ever collected that documents the brightening and dimming of stars and other celestial objects—two hundred million in total.
The night sky is filled with objects like asteroids that dash across the sky and others—like exploding stars and variable stars—that flash, dim, and brighten. Studying such phenomena can help astronomers better understand the evolution of stars, massive black holes in the centers of galaxies, and the ...