(Press-News.org) Two independent groups of researchers — one led by Adrian Clark, at Queen Mary University of London, United Kingdom; and the other led by Jean-Laurent Casanova, at The Rockefeller University, New York — have now identified the disease-causing gene in patients with a complex inherited syndrome most commonly observed in the Irish Traveller community. As noted by Jordan Orange, at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia, in an accompanying commentary, the new data provide deep mechanistic insight into a complex human condition and expand our understanding of the human immune and endocrine systems, both of which are disrupted in patients.
Within the Irish Traveller community, several families have been found to suffer from an inherited condition characterized by failure of the adrenal glands to produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones, abnormal development (in particular, retarded growth), and a deficiency in immune cells known as NK cells. Both groups of researchers found that mutations in the MCM4 gene are responsible for this complex inherited condition. The MCM4 gene is responsible for templating a protein that is required for DNA to replicate itself, something that happens every time a cell divides. Consistent with this, both groups of researchers found that the MCM4 mutations associated with disease caused genomic instability, something that they suggest might possibly put affected individuals at increased risk for cancer.
INFORMATION:
TITLE: MCM4 mutation causes adrenal failure, short stature, and natural killer cell deficiency in humans
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Adrian J.L. Clark
Queen Mary University of London, Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry, London, United Kingdom.
Phone: 44.20.7882.6202; Fax: 44.20.7882.6197; E-mail: a.j.clark@qmul.ac.uk.
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/60224?key=cb4664b3464dffe5841c
ACCOMPANYING ARTICLE
TITLE: Partial MCM4 deficiency in patients with growth retardation, adrenal insufficiency, and natural killer cell deficiency
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Jean-Laurent Casanova
The Rockefeller University, New York, New York, USA.
Phone: 212.327.7331; Fax: 212.327.7330; E-mail: jean-laurent.casanova@rockefeller.edu.
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/61014?key=9c3e63bab008bc523ccd
ACCOMPANYING COMMENTARY
TITLE: Unraveling human natural killer cell deficiency
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Jordan S. Orange
University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA.
Phone: 267.426.5622; Fax 267.426.0947; E-mail: orange@upenn.edu.
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/62620?key=7b2cf2771a25813f75d8
END
Children with Down syndrome (DS) have an increased risk of developing leukemia, in particular acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Through their studies in a mouse model of DS, a team of researchers led by John Crispino, at Northwestern University, Chicago, has now identified a potential explanation as to why children with DS are at increased risk of AMKL. In doing so, they have also identified a candidate therapeutic target.
DS is a genetic condition in which a person has an extra copy of chromosome 21 (they have 3 copies rather ...
EDITOR'S PICK: Unraveling why children with Down syndrome have increased leukemia risk
Children with Down syndrome (DS) have an increased risk of developing leukemia, in particular acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Through their studies in a mouse model of DS, a team of researchers led by John Crispino, at Northwestern University, Chicago, has now identified a potential explanation as to why children with DS are at increased risk of AMKL. In doing so, they have also identified a candidate therapeutic target.
DS is a genetic ...
Researchers from UCLA's Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, together with scientists from 12 other sites in the United States and Australia, report for the first time that a newly approved drug for patients with metastatic melanoma nearly doubles median survival times, a finding that will change the way this deadly form of skin cancer is treated.
The data comes from an international Phase II study of Zelboraf that included 132 patients followed for at least one year.
Patients with this advanced form of melanoma that has spread to other organs typically survive about ...
The Virginia Tech – Wake Forest University School of Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (SBES) announces the first ever publication with data on head impacts from youth football players. The paper is published in the Annals of Biomedical Engineering and is available online for free download. The manuscript includes the details of over 700 head impacts measured on 7 and 8 year old youth football players.
Based on the importance of this initial publication, the School of Biomedical Engineering and Sciences is also announcing today a new study to instrument and map the ...
Nursing homes are supposed to provide quality care, but recent studies raise concerns that some of these homes put our elderly population at increased risk of injury and death. The studies, conducted by both the Government Accountability Office and Health Services Research, found well-known nursing home chains often violate federal regulations in ways that can lead to increased risk of nursing home injuries.
Connection Between For-Profit Facilities and Poor Care
The Government Accountability Office published a study in July of 2011, reviewing complaints that for-profit ...
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (February 22, 2012) – If you were to discover that a fundamental component of human biology has survived virtually intact for the past 25 million years, you'd be quite confident in saying that it is here to stay.
Such is the case for a team of Whitehead Institute scientists, whose latest research on the evolution of the human Y chromosome confirms that the Y—despite arguments to the contrary—has a long, healthy future ahead of it.
Proponents of the so-called rotting Y theory have been predicting the eventual extinction of the Y chromosome since it was ...
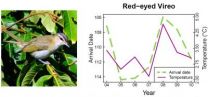
Bird migration timing across North America has been affected by climate change, according to a study published Feb. 22 in the open access journal PLoS ONE. The results are based on a systematic analysis of observations from amateur birdwatchers. This citizen science approach provided access to data for 18 common North American bird species, including orioles, house wrens, and barn swallows, across an unprecedented geographical region.
The researchers, led by Allen Hurlbert of University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, found that the average arrival time for all species ...
Workers face many dangers on construction sites, including falls from heights and unsafe scaffolds or ladders. At any busy worksite, construction workers are also at risk of being struck by falling objects.
A recent New York Court of Appeals opinion, Wilinski v. 334 East 92nd Housing Development Fund, considered a worker's remedies for a Manhattan construction accident that occurred during demolition of a brick wall in a vacant warehouse. The worker suffered serious and lasting injuries when he was struck on the head, shoulder and arm by two ten-foot long, four-inch ...
Stress is known to lead to short-term escape behavior, and new research on elephants in South Africa shows that it can also cause long-term escape behavior, affecting the extent that elephants use their habitat. The work is published Feb. 22 in the open access journal PLoS ONE.
The researchers, led by David Jachowski of the University of Missouri, measured levels of FGM (fecal glucocorticoid metabolite), a proxy of physiological stress, and land use patterns for three different elephant populations, and found that higher FGM was associated with 20-43% lower land usage. ...
Like drivers in every other state, South Carolina motorists face their share of hazards that lead to car, truck and motorcycle accidents. From drunk drivers to dangerous roadways and defective tires or brakes, there are often several reasons why an accident occurred and people suffered injuries.
One common factor from coast to coast: inexperienced drivers pose more than their share of risks to themselves and other motorists and passengers as they learn to drive in various types of weather and traffic. A recent study published by the AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety ...