(Press-News.org) If people see news coverage of alcohol's role in violent crime and fatal injuries, they may give more support to alcohol-control laws, according to a study in the March issue of the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
It's estimated that drinking is involved in almost one third of deaths from accidents and violent crime. But the news reports on those deaths often make no mention of alcohol.
"People have some awareness of the social cost that alcohol can have," said the study's lead author, Michael D. Slater, Ph.D., of Ohio State University in Columbus. "But only a small fraction of news stories on violent crime and non–motor vehicle accidents acknowledge the contributing role of alcohol."
As a result, many people may not realize how often drinking contributes to accidents off the roadways, as well as to violence, Slater noted.
And that lack of awareness might dampen the public's support for alcohol-control laws, such as the strict enforcement of underage-drinking laws or prohibitions on serving alcohol to intoxicated customers.
To see how media coverage affects people's views on alcohol control, Slater's team sent online surveys to a national sample of 789 U.S. adults. The surveys contained stories on violent crime, car crashes and other accidents taken from local U.S. newspapers; each story was manipulated into one version that mentioned alcohol involvement and a second that did not.
After reading the media accounts, participants were asked about their support for existing alcohol-control laws, as well as proposed restrictions—such as limits on the number of bars and liquor stores that can exist in a given area.
Overall, Slater's team found that when people read stories that mentioned alcohol, they were more likely to throw their support to existing alcohol-control laws.
"I think this buttresses the idea that media coverage does matter," Slater said. "Alcohol, as a public health issue, is not as front and center as it might be if there were more news coverage."
Even if alcohol-control laws are already on the books, public support matters because local resources are needed to enforce those laws, Slater noted.
He said that local authorities can help by mentioning any role of alcohol when discussing crimes and accidents with the media. And reporters, Slater noted, can also ask about any alcohol involvement—not just in car crashes but in other accidents and crimes as well.
### Slater, M. D., Hayes, A. F., Goodall, C. E., & Ewoldsen, D. R. (March 2012). Increasing support for alcohol-control enforcement through news coverage of alcohol's role in injuries and crime. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 73(2), 311.
Available at: http://www.jsad.com/jsad/link/73/311
To arrange an interview with Michael D. Slater, Ph.D., please contact Jeff Grabmeier at 614-292-8457 or grabmeier.1@osu.edu.
The Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs (http://www.jsad.com) is published by the Center
of Alcohol Studies, Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey. It is the oldest
substance-abuse journal published in the United States.
News coverage of alcohol's harm may sway support for liquor-control laws
2012-02-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Restoring reality: Training improves brain activation and behavior in schizophrenia
2012-02-23
A pioneering new study finds that a specific type of computerized cognitive training can lead to significant neural and behavioral improvements in individuals with schizophrenia. The research, published by Cell Press in the February 23 issue of the journal Neuron, reveals that 16 weeks of intensive cognitive training is also associated with improved social functioning several months later and may have far-reaching implications for improving the quality of life for patients suffering from neuropsychiatric illness.
Schizophrenia is a debilitating psychiatric illness that ...
NIH-funded science on hearing research at annual ARO meeting
2012-02-23
What: NIH-supported scientists will be presenting their latest research findings at the 2012 Midwinter Meeting of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology (ARO).
When: February 25-29, 2012
Where: The Manchester Grand Hyatt Hotel, San Diego, California, USA
Additional Information: Research topics to be presented by NIDCD-funded scientists will include:
Bilateral ≠ Binaural: Can the Ability to Localize Sounds Be Regained After Bilateral Cochlear Implantation?
Ruth Litovsky, Ph.D., University of Wisconsin-Madison
Bilateral cochlear implants—one implant ...
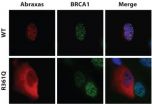
New member of the breast-cancer gene network found by Penn-led team
2012-02-23
PHILADELPHIA - The infamous BRCA genes do not act alone in causing cancer; there is a molecular syndicate at work preventing the way cells normally repair breaks in DNA that is at the root of breast cancer. But finding all of the BRCA molecular collaborators has been elusive.
Researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and the University of Oulu, Finland, published their discovery of a mutation in the Abraxas gene, which interacts with the well-known breast-cancer gene BRCA1, in Science Translational Medicine this week.
The mutation ...
Mini molecules could help fight battle of aortic bulge, Stanford study shows
2012-02-23
STANFORD, Calif. — When aortic walls buckle, the body's main blood pipe forms an ever-growing bulge. To thwart a deadly rupture, a team of Stanford University School of Medicine researchers has found two tiny molecules that may be able to orchestrate an aortic defense.
A team led by cardiovascular scientists Philip Tsao, PhD, and Joshua Spin, MD, PhD, identified two microRNAs — small molecules that usually block proteins from being made — that work to strengthen the aorta during bulge growth. By tweaking the activity of each molecule, they could reduce abdominal aortic ...
NTSB Recommends Cellphone Ban: Will Ohio Heed the Advice?
2012-02-23
Recently, the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) called for every state in the nation and Washington, D.C., to ban all non-emergency cellphone use while driving a motor vehicle. This recommendation follows various studies that have concluded cellphone use while driving can be extremely distracting - often leading to severe or even deadly accidents.
One tragic trucking accident illustrating the NTSB's concerns was an accident in which a truck driver, while using his cellphone, crossed the median and hit a van, killing 11 people in the process. It remains to be ...
Uncovered: Genetic cause of complex disease seen in Irish Traveller community
2012-02-23
Two independent groups of researchers — one led by Adrian Clark, at Queen Mary University of London, United Kingdom; and the other led by Jean-Laurent Casanova, at The Rockefeller University, New York — have now identified the disease-causing gene in patients with a complex inherited syndrome most commonly observed in the Irish Traveller community. As noted by Jordan Orange, at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia, in an accompanying commentary, the new data provide deep mechanistic insight into a complex human condition and expand our understanding ...
Unraveling why children with Down syndrome have increased leukemia risk
2012-02-23
Children with Down syndrome (DS) have an increased risk of developing leukemia, in particular acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Through their studies in a mouse model of DS, a team of researchers led by John Crispino, at Northwestern University, Chicago, has now identified a potential explanation as to why children with DS are at increased risk of AMKL. In doing so, they have also identified a candidate therapeutic target.
DS is a genetic condition in which a person has an extra copy of chromosome 21 (they have 3 copies rather ...
JCI online early table of contents: Feb. 22, 2012
2012-02-23
EDITOR'S PICK: Unraveling why children with Down syndrome have increased leukemia risk
Children with Down syndrome (DS) have an increased risk of developing leukemia, in particular acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Through their studies in a mouse model of DS, a team of researchers led by John Crispino, at Northwestern University, Chicago, has now identified a potential explanation as to why children with DS are at increased risk of AMKL. In doing so, they have also identified a candidate therapeutic target.
DS is a genetic ...
Newly approved drug for metastatic melanoma nearly doubles median survival
2012-02-23
Researchers from UCLA's Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, together with scientists from 12 other sites in the United States and Australia, report for the first time that a newly approved drug for patients with metastatic melanoma nearly doubles median survival times, a finding that will change the way this deadly form of skin cancer is treated.
The data comes from an international Phase II study of Zelboraf that included 132 patients followed for at least one year.
Patients with this advanced form of melanoma that has spread to other organs typically survive about ...
Virginia Tech, Wake Forest University announce youth football publication, new head impact study
2012-02-23
The Virginia Tech – Wake Forest University School of Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (SBES) announces the first ever publication with data on head impacts from youth football players. The paper is published in the Annals of Biomedical Engineering and is available online for free download. The manuscript includes the details of over 700 head impacts measured on 7 and 8 year old youth football players.
Based on the importance of this initial publication, the School of Biomedical Engineering and Sciences is also announcing today a new study to instrument and map the ...