(Press-News.org) A team led by a North Carolina State University researcher has shown that water-gel-based solar devices – "artificial leaves" – can act like solar cells to produce electricity. The findings prove the concept for making solar cells that more closely mimic nature. They also have the potential to be less expensive and more environmentally friendly than the current standard-bearer: silicon-based solar cells.
The bendable devices are composed of water-based gel infused with light-sensitive molecules – the researchers used plant chlorophyll in one of the experiments – coupled with electrodes coated by carbon materials, such as carbon nanotubes or graphite. The light-sensitive molecules get "excited" by the sun's rays to produce electricity, similar to plant molecules that get excited to synthesize sugars in order to grow, says NC State's Dr. Orlin Velev, Invista Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the lead author of a paper published online in the Journal of Materials Chemistry describing this new generation of solar cells.
Velev says that the research team hopes to "learn how to mimic the materials by which nature harnesses solar energy." Although synthetic light-sensitive molecules can be used, Velev says naturally derived products – like chlorophyll – are also easily integrated in these devices because of their water-gel matrix.
Now that they've proven the concept, Velev says the researchers will work to fine-tune the water-based photovoltaic devices, making them even more like real leaves.
"The next step is to mimic the self-regenerating mechanisms found in plants," Velev says. "The other challenge is to change the water-based gel and light-sensitive molecules to improve the efficiency of the solar cells."
Velev even imagines a future where roofs could be covered with soft sheets of similar electricity-generating artificial-leaf solar cells.
"We do not want to overpromise at this stage, as the devices are still of relatively low efficiency and there is a long way to go before this can become a practical technology," Velev says. "However, we believe that the concept of biologically inspired 'soft' devices for generating electricity may in the future provide an alternative for the present-day solid-state technologies."
###
Researchers from the Air Force Research Laboratory and Chung-Ang University in Korea co-authored the study. The study was funded by the Air Force Research Laboratory and the U.S. Department of Energy. The work is part of NC State's universitywide nanotechnology program, Nano@NC State.
NC State's Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering is part of the university's College of Engineering.
Note to editors: The abstract of the paper follows. Velev is currently in Europe on academic leave; please consider the time difference when attempting to contact him.
"Aqueous soft matter based photovoltaic devices"
Authors: Hyung-Jun Koo and Dr. Orlin D. Velev, NC State University; Suk Tai Chang, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea; Joseph M. Slocik and Rajesh R. Naik, Air Force Research Laboratory
Published: Online Sept. 21, 2010, in Journal of Materials Chemistry
Abstract: We present a new type of photovoltaic system based on aqueous soft gel materials. Two photosensitive ions, DAS and [Ru(bpy)3]2+, were used as photoactive molecules embedded in aqueous gel. The hydrogel photovoltaic devices (HGPVs) showed performance comparable with or higher than those of other biomimetic or ionic photovoltaic systems reported recently. We suggest a provisional mechanism, which is based on a synergetic effect of the two dye molecules in photocurrent generation. We found an efficient replacement of the expensive Pt counter-electrode with copper coated with carbon materials, such as carbon nanotubes, carbon black or graphite. These Cu electrodes coated with carbon layers could drastically reduce the cost of such hydrogel devices without efficiency loss. Thus, a new class of low cost and flexible photovoltaic cells made of biocompatible matrix was demonstrated. Biologically derived photoactive molecules, such as Chlorophyll and Photosystem II, were successfully operated in aqueous gel media of such HGPVs.
END
London, UK (September 24, 2010) – Prison numbers in England and Wales have risen sharply in the last decade, and are set to rise further. A study out today in the Probation Journal published by SAGE suggests that economists have a unique opportunity to help solve the prison crisis by bringing sophisticated economic modelling techniques to bear on the problem.
Chris Fox and Kevin Albertson from Manchester Metropolitan University contend that during the last decade, penal policy allowed many opportunities to harness the latest analytical research to optimise public spending ...
Sept. 24, 2010 — Biometric systems -- designed to automatically recognize individuals based on biological and behavioral traits such as fingerprints, palm prints, or voice or face recognition -- are "inherently fallible," says a new report by the National Research Council, and no single trait has been identified that is stable and distinctive across all groups. To strengthen the science and improve system effectiveness, additional research is needed at virtually all levels of design and operation.
"For nearly 50 years, the promise of biometrics has outpaced the application ...
Basic physical limitations following breast cancer treatment can have far-reaching consequences that substantially affect how long a patient lives.
According to a new study published online in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, breast cancer survivors with functional limitations – an inability to perform normal daily activities – caused by the disease or its treatment are more likely to die because of overall poorer health.
The scientists found that survivors who reported physical limitations after breast cancer treatment have the same risk of dying from ...
The first cultivar of 'ōhelo berry, a popular native Hawaiian fruit, has been released by U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists and their university and industry cooperators.
'Ōhelo (Vaccinium reticulatum Smith) is a small, native Hawaiian shrub in the cranberry family, commonly found at high elevations on the islands of Maui and Hawaii. As people scour the landscape to harvest this delectable berry for use in jam, jelly and pie filling, they unfortunately disrupt the fragile habitats where this plant grows.
In an effort to reduce damage to the ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A new study has determined that teenagers who have abortions are no more likely to become depressed or have low self-esteem than their peers whose pregnancies do not end in abortion.
The study conducted by researchers from Oregon State University and University of California, San Francisco, is the first to use both depression and low self-esteem as outcomes with a nationally representative sample of adolescents.
The researchers found that young women in the study who had an abortion were no more likely to become depressed or have low self-esteem within ...
You'd think that people choosing to live near to outdoor recreation amenities would have a lower body mass index or BMI thanks to an increase in all that healthy outdoor activity right on one's doorstep. Yet a new University of Alberta study looking at the relationship between reasons for choosing a neighbourhood to live in, physical activity and BMI, shows that's simply not the case.
In fact researchers found that those who said they'd moved to be closer to outdoor recreation opportunities actually showed a marked increase in BMI over the six years of a longitudinal ...
BOSTON—In the quest to arrest the growth and spread of tumors, there have been many attempts to get cancer genes to ignore their internal instruction manual. In a new study, a team led by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute scientists has created the first molecule able to prevent cancer genes from "hearing" those instructions, stifling the cancer process at its root.
The study, published online by the journal Nature, demonstrates that proteins issuing stop and start commands to a cancer gene – known as epigenetic "reader" proteins – can be targeted for future cancer therapies. ...
With several advanced warfare vehicles and a lineup of exciting technologies, the Office of Naval Research (ONR) will showcase its latest expeditionary equipment at the 2010 Modern Day Marine Exposition scheduled Sept. 28-30 at Quantico Marine Corps Base, Quantico, Va.
Modern Day Marine is one of the world's largest trade shows featuring expeditionary warfare equipment. More than 400 exhibitors and 8,000 attendees are expected to attend the event—now in its 30th year—for an up-close look at equipment and systems that support the U.S. Marine Corps and other allied forces' ...
An instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite noticed increasing colder cloud top temperatures of tropical depression 15 in the south-central Caribbean just before it strengthened into Tropical Storm Matthew late on Sept. 23. The TRMM satellite also spotted heavy rainfall within the system. Matthew is now headed to the western Caribbean and watches and warnings are in place as Matthew may continue to strengthen.
Cloud top temperatures indicate the strength of the storm to forecasters. The colder the cloud top temperatures, the stronger the convection and uplift. When cloud top ...
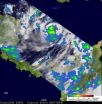
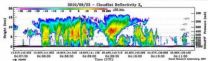
Towering thunderstorms and heavy rainfall are two things that NASA's CloudSat satellite saw as it passed over Typhoon Malakas, and those two factors confirm a strong storm. NASA's CloudSat satellite's Cloud Profiling Radar can basically slice a tropical cyclone in half and take a look at its clouds and rainfall, and that's what it did when it passed over Typhoon Malakas on Sept. 23.
CloudSat flew over Typhoon Malakas during the daytime on Sept. 23. At that time, Malakas had a minimum central pressure of 965 millibars, maximum winds of around 115 mph (100 knots), and ...