(Press-News.org) Washington, D.C. -- Plant science is key to addressing the major challenges facing humanity in the 21st Century, according to Carnegie's David Ehrhardt and Wolf Frommer. In a Perspective published in The Plant Cell, the two researchers argue that the development of new technology is key to transforming plant biology in order to meet human needs.
Plants serve as the conduit of energy into the biosphere, provide food and materials used by humans, and they shape our environment. According to Ehrhardt and Frommer, the three major challenges facing humanity in our time are food, energy, and environmental degradation. All three are plant related.
All of our food is produced by plants, either directly or indirectly via animals that eat them. Plants are a source of energy production. And they are intimately involved in climate change and a major factor in a variety of environmental concerns, including agricultural expansion and its impact on habitat destruction and waterway pollution.
What's more, none of these issues are independent of each other. Climate change places additional stresses on the food supply and on various habitats. So plant research is instrumental in addressing all of these problems and moving into the future.
For plant research to move significantly forward, Ehrhardt and Frommer say technological development is critical, both to test existing hypotheses and to gain new information and generate fresh hypotheses. If we are to make headway in understanding how these essential organisms function and build the foundation for a sustainable future, then we need to apply the most advanced technologies available to the study of plant life, they say.
They divide the technology into three categories: existing technology that isn't being applied for all of its potential uses, new readily envisioned technology, and technology we'd like to have but don't know how to create.
The technological overview includes expanding existing technologies such as DNA sequencing, RNA cataloguing, mass spectroscopy, fluorescence-based microscopy, and electron microscopy, among many others. A key focus is on the advances possible through advanced imaging technologies.
Ehrhardt and Frommer point out that many of the most often-cited academic papers related to the development new technology, demonstrating the interest of the scientific community.
"We certainly expect that new technologies will continue to revolutionize biological research," they say. "Plant science has not often been the driver of innovation but often enough has profited from developments made in other areas."
###
The Carnegie Institution for Science (carnegiescience.edu) is a private, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with six research departments throughout the U.S. Since its founding in 1902, the Carnegie Institution has been a pioneering force in basic scientific research. Carnegie scientists are leaders in plant biology, developmental biology, astronomy, materials science, global ecology, and Earth and planetary science.
The future of plant science – a technology perspective
2012-03-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
When your ship comes in
2012-03-05
Every day, thousands of cargo containers from around the world pass through our nation's sea ports carrying items we need, and possibly some that are not so welcome: drugs, explosives, chemical, biological, or radiological weapons – even human cargo.
The possible concealment of such items in containers led lawmakers to call for the screening of all ocean cargo containers—thousands per port per day. The Department of Homeland Security's (DHS) U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) is charged with the critical task of securing the country from terrorists and their ...
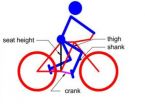
A new optimum design method of bicycle parameters for a specified person
2012-03-05
The optimum design of bicycle parameters has been explored by many scholars and institutes since bicycles were first invented. Professor Xin-Jun Liu and his group at Tsinghua University established a new way to design bicycle parameters according to the dimensions of the rider's body. They introduced a new perspective of the rider–bicycle system by considering the complete system as a mechanism. The group then established a new method for the optimum design of bicycle parameters from a completely theoretical basis, which may result in a new field of optimum design of bicycle ...
National Sleep Foundation poll explores transportation workers' sleep
2012-03-05
WASHINGTON, DC, March 3, 2012 – The people we trust to take us or our loved ones from place to place struggle with sleep, according to the National Sleep Foundation's (NSF) 2012 Sleep in America® poll. It is the first poll to ask transportation professionals, including pilots, train operators,* truck, bus, taxi and limo drivers about their sleep habits and work performance.
Pilots and train operators are most likely to report sleep-related job performance and safety problems.
The results of the poll are striking. About one-fourth of train operators (26%) and pilots (23%) ...
Ice hockey feels the heat in Canada
2012-03-05
The future of Canadian outdoor ice hockey – a sport synonymous with the country's culture – is being threatened by anthropogenic climate change, new research suggests.
As warmer winter temperatures restrict ice from freezing over, researchers believe the ice hockey stars of the future will have limited access to the frozen lakes and backyard rinks that have helped shape the careers of some of the greatest professional players, such as Wayne Gretzky; the Canadian considered to be the greatest of all time who started skating as a child on a rink in his backyard.
Evidence ...
Study shows brain flexibility, gives hope for natural-feeling neuroprosthetics
2012-03-05
Berkeley – Opening the door to the development of thought-controlled prosthetic devices to help people with spinal cord injuries, amputations and other impairments, neuroscientists at the University of California, Berkeley, and the Champalimaud Center for the Unknown in Portugal have demonstrated that the brain is more flexible and trainable than previously thought.
Their new study, to be published Sunday, March 4, in the advanced online publication of the journal Nature, shows that through a process called plasticity, parts of the brain can be trained to do something ...
Boosting cell production could help treat liver disease
2012-03-05
Scientists have shed light on how the liver repairs itself with research that could help develop drugs to treat liver disease.
Researchers at the Medical Research Council (MRC) Centre for Regenerative Medicine at the University of Edinburgh have discovered how to enhance the production of key cells needed to repair damaged liver tissue.
The study, published in the journal Nature Medicine, could help heal livers affected by diseases such as cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis.
Scientists were able to unpick the process of how different cells in the liver are formed.
When ...
Keep smiling: Collagen matrix promotes gum healing around exposed roots
2012-03-05
Receding gums often result in tooth sensitivity and can lead to decay of the root and persistent inflammation of the gum. New research published in BioMed Central's open access journal Head & Face Medicine demonstrates that a novel method using bovine collagen is able to enhance gum healing. This resulted in thicker margins around the tooth and, in over half the cases, complete coverage of exposed roots.
Researchers across Germany and Switzerland led by Dr Shahram Ghanaati and the dentist Dr Markus Schlee investigated the possibility of using collagen, extracted from ...
Seeing without eyes: Hydra stinging cells respond to light
2012-03-05
In the absence of eyes, the fresh water polyp, Hydra magnipapillata, nevertheless reacts to light. They are diurnal, hunting during the day, and are known to move, looping end over end, or contract, in response to light. New research published in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Biology shows that stinging cells (cnidocytes) in hydra tentacles, which the animals use for self protection and to catch prey, are linked via a simple nervous system to primitive light responsive cells that co-ordinate the animals' feeding behavior.
Hydra are members of a family of radially ...
Does your mother know?
2012-03-05
Do your parents know where you are at night? According to 36 per cent of 15 year old boys and nearly a quarter of 15 year old girls the answer to that question, at least once a month, is no.
This is the finding from Understanding Society, a long term study of 40,000 UK households, which asked more than 2,000 10-15 year olds how frequently they stayed out past 9.00pm without their parents knowing where they were. The study, which is funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC), also found that staying out late without telling your parents is unrelated to ...
Escaping parasites and pathogens
2012-03-05
In nature, how do host species survive parasite attacks? This has not been well understood, until now. A new mathematical model shows that when a host and its parasite each have multiple traits governing their interaction, the host has a unique evolutionary advantage that helps it survive.
The results are important because they might help explain how humans as well as plants and animals evolve to withstand parasite onslaught.
The research, reported in the March 4 online edition of Nature, was supported by the National Institute for Mathematical and Biological Synthesis ...