(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR, Mich.—A new power scheme for cardiac pacemakers turns to an unlikely source: vibrations from heartbeats themselves.
Engineering researchers at the University of Michigan designed a device that harvests energy from the reverberation of heartbeats through the chest and converts it to electricity to run a pacemaker or an implanted defibrillator. These mini-medical machines send electrical signals to the heart to keep it beating in a healthy rhythm. By taking the place of the batteries that power them today, the new energy harvester could save patients from repeated surgeries. That's the only way today to replace the batteries, which last five to 10 years.
"The idea is to use ambient vibrations that are typically wasted and convert them to electrical energy," said Amin Karami, a research fellow in the U-M Department of Aerospace Engineering. "If you put your hand on top of your heart, you can feel these vibrations all over your torso."
The researchers haven't built a prototype yet, but they've made detailed blueprints and run simulations demonstrating that the concept would work. Here's how: A hundredth-of-an-inch thin slice of a special "piezoelectric" ceramic material would essentially catch heartbeat vibrations and briefly expand in response. Piezoelectric materials' claim to fame is that they can convert mechanical stress (which causes them to expand) into an electric voltage.
Karami and his colleague Daniel Inman, chair of Aerospace Engineering at U-M, have precisely engineered the ceramic layer to a shape that can harvest vibrations across a broad range of frequencies. They also incorporated magnets, whose additional force field can drastically boost the electric signal that results from the vibrations.
The new device could generate 10 microwatts of power, which is about eight times the amount a pacemaker needs to operate, Karami said. It always generates more energy than the pacemaker requires, and it performs at heart rates from 7 to 700 beats per minute. That's well below and above the normal range.
Karami and Inman originally designed the harvester for light unmanned airplanes, where it could generate power from wing vibrations.
### A paper on the research, titled "Powering pacemakers from heartbeat vibrations using linear and nonlinear energy harvesters," is published in the current print edition of Applied Physics Letters.
The research is funded by the National Institute of Standards and Technology and the Institute for Critical Technology and Applied Science at Virginia Tech.
Daniel Inman: http://aerospace.engin.umich.edu/people/faculty/Inman/index.html
Paper: http://apl.aip.org/resource/1/applab/v100/i4/p042901_s1?bypassSSO=1 END
Heart-powered pacemaker could one day eliminate battery-replacement surgery
2012-03-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Another severe weather system seen on satellite movie from NASA
2012-03-05
VIDEO:
This movie was created using GOES-13 visible and infrared satellite imagery. The 25 second movie runs from Feb. 29 at 1718 UTC (12:18 pm EST) through March 2 at 1740...
Click here for more information.
Another powerful weather system is moving through the central and eastern U.S., generating more severe weather. NASA created an animation of data from NOAA's GOES-13 satellite that shows the frontal system pushing east as it generated severe weather in Ohio, Kentucky, ...
Dark matter core defies explanation in NASA Hubble image
2012-03-05
Astronomers using data from NASA's Hubble Telescope have observed what appears to be a clump of dark matter left behind from a wreck between massive clusters of galaxies. The result could challenge current theories about dark matter that predict galaxies should be anchored to the invisible substance even during the shock of a collision.
Abell 520 is a gigantic merger of galaxy clusters located 2.4 billion light-years away. Dark matter is not visible, although its presence and distribution is found indirectly through its effects. Dark matter can act like a magnifying glass, ...
HollywoodSportsbook.eu Announces Its Own Unique March Madness Contest
2012-03-05
Hollywood Sportsbook (www.hollywoodsportsbook.eu) a leading online entertainment gaming site since 1997, today announced it will offer a month long promotion allowing players to pick the winners of certain NBA and college basketball games all month long.
Robert Evans, Hollywood's Director of Operations says, "Well here we are... the most exciting month for basketball. In addition to all the cool stuff we will have going on this month for the NCAA tournament, we hope this contest will float our players' boats as well..."
For each coming weekend in March, ...
NASA sees tropical storm Irina hit by wind shear, headed for Mozambique
2012-03-05
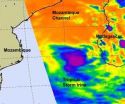
The AIRS instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite provided forecasters with an infrared look at what was happening "under the hood" of Tropical Storm Irina's clouds and saw two reasons why it temporarily weakened before moving into the Mozambique Channel and heading for landfall in Mozambique in a couple of days.
WHY DID IT WEAKEN?
NASA's Aqua satellite's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of Tropical Cyclone Irina over the Mozambique Channel on March 1, 2012 at 0130 UTC (8:30 p.m. EST, Feb. 29). At that time, the strongest thunderstorms ...
NASA's TRMM satellite sees remnants of Tropical Cyclone 15S's 'difficult childhood'
2012-03-05
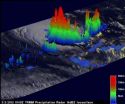
Tropical Cyclone 15S has had a difficult "childhood." It was born on March 1 and immediately dealt with a harsh environment. The cyclone weakened within 24 hours to a remnant low pressure area, and NASA's TRMM satellite revealed there was still some strength remaining in the storm.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed over the remnants of Tropical Cyclone 15S in the South Indian Ocean on March 2, 2012 at 0140 UTC (8:40 p.m. EST, March 1). A rainfall analysis from TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) instruments showed very ...
The future of plant science – a technology perspective
2012-03-05
Washington, D.C. -- Plant science is key to addressing the major challenges facing humanity in the 21st Century, according to Carnegie's David Ehrhardt and Wolf Frommer. In a Perspective published in The Plant Cell, the two researchers argue that the development of new technology is key to transforming plant biology in order to meet human needs.
Plants serve as the conduit of energy into the biosphere, provide food and materials used by humans, and they shape our environment. According to Ehrhardt and Frommer, the three major challenges facing humanity in our time are ...
When your ship comes in
2012-03-05
Every day, thousands of cargo containers from around the world pass through our nation's sea ports carrying items we need, and possibly some that are not so welcome: drugs, explosives, chemical, biological, or radiological weapons – even human cargo.
The possible concealment of such items in containers led lawmakers to call for the screening of all ocean cargo containers—thousands per port per day. The Department of Homeland Security's (DHS) U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) is charged with the critical task of securing the country from terrorists and their ...
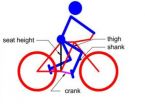
A new optimum design method of bicycle parameters for a specified person
2012-03-05
The optimum design of bicycle parameters has been explored by many scholars and institutes since bicycles were first invented. Professor Xin-Jun Liu and his group at Tsinghua University established a new way to design bicycle parameters according to the dimensions of the rider's body. They introduced a new perspective of the rider–bicycle system by considering the complete system as a mechanism. The group then established a new method for the optimum design of bicycle parameters from a completely theoretical basis, which may result in a new field of optimum design of bicycle ...
National Sleep Foundation poll explores transportation workers' sleep
2012-03-05
WASHINGTON, DC, March 3, 2012 – The people we trust to take us or our loved ones from place to place struggle with sleep, according to the National Sleep Foundation's (NSF) 2012 Sleep in America® poll. It is the first poll to ask transportation professionals, including pilots, train operators,* truck, bus, taxi and limo drivers about their sleep habits and work performance.
Pilots and train operators are most likely to report sleep-related job performance and safety problems.
The results of the poll are striking. About one-fourth of train operators (26%) and pilots (23%) ...
Ice hockey feels the heat in Canada
2012-03-05
The future of Canadian outdoor ice hockey – a sport synonymous with the country's culture – is being threatened by anthropogenic climate change, new research suggests.
As warmer winter temperatures restrict ice from freezing over, researchers believe the ice hockey stars of the future will have limited access to the frozen lakes and backyard rinks that have helped shape the careers of some of the greatest professional players, such as Wayne Gretzky; the Canadian considered to be the greatest of all time who started skating as a child on a rink in his backyard.
Evidence ...