(Press-News.org) Emotion-sensing computer software that models and responds to students' cognitive and emotional states – including frustration and boredom – has been developed by University of Notre Dame Assistant Professor of Psychology Sidney D'Mello and colleagues from the University of Memphis and Massachusetts Institute of Technology. D'Mello also is a concurrent assistant professor of computer science and engineering.
The new technology, which matches the interaction of human tutors, not only offers tremendous learning possibilities for students, but also redefines human-computer interaction.
"AutoTutor" and "Affective AutoTutor" can gauge the student's level of knowledge by asking probing questions, analyzing the student's responses to those questions; proactively identifying and correcting misconceptions; responding to the student's own questions, gripes, and comments; and even sensing a student's frustration or boredom through facial expression and body posture and dynamically changing its strategies to help the student conquer those negative emotions.
"Most of the 20th-century systems required humans to communicate with computers through windows, icons, menus, and pointing devices," says D'Mello, who specializes in human-computer interaction and artificial intelligence in education.
"But humans have always communicated with each other through speech and a host of non-verbal cues such as facial expressions, eye contact, posture, and gesture. In addition to enhancing the content of the message, the new technology provides information regarding the cognitive states, motivation levels, and social dynamics of the students."
AutoTutor is an Intelligent Tutoring System (ITS) that helps students learn complex technical content in Newtonian physics, computer literacy, and critical thinking by holding a conversation in natural language; simulating teaching and motivational strategies of human tutors; modeling students' cognitive states; using its student model to dynamically tailor the interaction to individual students; answering students' questions; identifying and correcting misconceptions; and keeping students engaged with images, animations, and simulations. In addition to these capabilities, Affective AutoTutor adds emotion-sensitive capabilities by monitoring facial features, body language, and conversational cues; regulating negative states such as frustration and boredom; and synthesizing emotions via the content of its verbal responses, speech intonation, and facial expressions of an animated teacher.
The study, titled "AutoTutor and Affective AutoTutor: Learning by Talking with Cognitively and Emotionally Intelligent Computers that Talk Back" that details
this new technology will be published in a special edition of ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems that highlights innovative technology of the last decade.
"Much like a gifted human tutor, AutoTutor and Affective AutoTutor attempt to keep the student balanced between the extremes of boredom and bewilderment by subtly modulating the pace, direction, and complexity of the learning task," D'Mello says.
Considerable empirical evidence has shown that one-on-one human tutoring is extremely effective when compared to typical classroom environments, and AutoTutor and Affective AutoTutor closely model the pedagogical styles, dialogue patterns, language, and gestures of human tutors. They are also one of the few ITSs that help learning by engaging students in natural language dialogues that closely mirror human-human tutorial dialogues.
Tested on more than one thousand students, AutoTutor produces learning gains of approximately one letter grade – gains which have proven to outperform novice human tutors and almost reach the bar of expert human tutors.
INFORMATION:
END
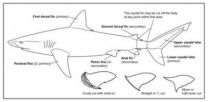
Shark fins are worth more than other parts of the shark and are often removed from the body, which gets thrown back into the sea. To curtail this wasteful practice, many countries allow the fins to be landed detached from shark bodies, as long as their weight does not exceed five per cent of the total shark catch. New University of British Columbia research shows that this kind of legislation is too liberal.
A study published this week in the journal Fish Biology analyzes the fin to body weight ratios for 50 different shark species. The authors find the average fin ...
DestinationPro.com is a solution allowing independent execution of events and incentive programs. If anyone needed to organize a corporate meeting, business trip, training, bonus (incentive) trip for employees, conference, etc., he/she usually took advantage of services provided by one of the specialized agencies (DMCs - Destination Management Company). Based on the client's specification, such agency proposed agenda and individual suppliers (accommodation, restaurants, venues, transportation, logistic, etc.), subsequently ensuring and executing the whole event.
We ...
Philadelphia, PA, March 2, 2012 – Impaired social function is a cardinal symptom of autism spectrum disorders (ASDs). One of the brain circuits that enable us to relate to other people is the "mirror neuron" system. This brain circuit is activated when we watch other people, and allows our brains to represent the actions of others, influencing our ability to learn new tasks and to understand the intentions and experiences of other people.
This mirror neuron system is impaired in individuals with ASD and better understanding the neurobiology of this system could help ...
WASHINGTON, D.C., March 2, 2012 – Newly proposed asthma outcome measures will help standardize and improve results from the hundreds of millions of dollars the National Institutes of Health (NIH) spends annually to study asthma, according to the Merck Childhood Asthma Network, Inc. (MCAN), the nation's only organization focused solely on childhood asthma. Even though years of research have led to groundbreaking improvements in better understanding and managing asthma, MCAN noted that the inability to compare results across many studies has hindered the nation's efforts ...
MAYWOOD, Ill. -- A scientific method paper and video by Loyola researchers has gone viral. The video demonstrates a laboratory technique used to study some aspects of mitochondrial dysfunctions in Alzheimer's disease and many other disorders.
It has been accessed by more than 14,000 scientists around the world since it was published in the Journal of Visualized Experiments, a peer-reviewed, PubMed-indexed journal that publishes biological and other scientific research in a video format.
Senior author is Joanna C. Bakowska, DVM, PhD, an assistant professor in the Department ...
A consortium of federal agencies and nongovernmental organizations has published a report proposing a set of common measures and data-collection methods for use in asthma clinical research. Asthma Outcomes in Clinical Research: Report of the Asthma Outcomes Workshop, which appears as a supplement to the March 2012 issue of the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, resulted from a meeting organized by the National Institutes of Health, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the Merck Childhood Asthma Network, Inc., with additional support for the publication ...
As more organizations look for ways to manage the cost of employee healthcare, what better way to bring this message to your organization than to have your CEO enter a fitness challenge. Nancy Munro, CEO of KnowledgeShift was willing to take on this challenge offered to members of the Illinois Technology Association starting in November of 2011. The contest was sponsored by InerTrain, an online fitness company.
Contestants had to evaluate their fit age before and after the contest. Each contestant worked with one of InerTrain's online virtual trainers with personalized ...
Scientists from PRBO Conservation Science and the Department of Fish and Game have completed an innovative study on the effects of climate change on bird species of greatest concern. This first-of-its-kind study prioritizes which species are most at risk and will help guide conservation measures in California. The study was published this week in the journal PLoS ONE.
"What's most exciting about the study is that our unique approach is one that other scientists and resource managers can duplicate to help them conserve wildlife in the face of climate change," said PRBO ...
A University of Alberta research team has discovered that technology commonly used to decontaminate food industry equipment can also rid meat processing plants of lethal microbial material responsible for the human version of the ailment Mad Cow disease.
U of A microbiology professors Mike Belosevic and Norm Neumann and engineering professor Mohamed Gamal El-Din demonstrated that infectious proteins found in the brain matter of cattle can be eradicated from water treated with ozone.
The discovery could have applications in decontaminating wastewater in settings such ...
Athens, Ga. – In an emergency, minutes matter. With this knowledge, University of Georgia researchers developed a new method for determining where emergency vehicle stations should be located. The results of their work could improve ambulance response time for the 200 million Americans who dial 911 each year, according to the Federal Communications Commission.
"If we can meet this critical time window [of 8 minutes], we can maximize benefits," said Ping Yin, a UGA graduate student studying geography who co-authored the paper.
The model uses geographical information ...