EAST PROVIDENCE, RI, March 12, 2012 (Press-News.org) Rhode Island Attorney, David Slepkow, was honored to be sworn into the Exclusive United States Supreme Court Bar. This honor is a culmination of 15 years of Legal excellence by RI Auto Accident and Family Law Lawyer, David Slepkow.
David is also honored to receive a Superb rating by AVVO, an industry leading Legal Information provider. This is the highest rating that AVVO awards to attorneys.
Rhode Island Personal Injury Attorney David also was rated 4.9 out of 5, Preeminent by Martindale-Hubbell Client Review Rating. Martindale-Hubbell states the following on its website "The Martindale-Hubbell Ratings provide the most comprehensive and compelling view of lawyers and firms from a trusted source to aid buyers of legal services."
David has an extensive legal background in Family Law, RI Personal Injury, Auto Accidents, Criminal Law & Child Custody. This experience includes a meaningful win at the Rhode Island Supreme Court in 2011. David challenged a decision of a Rhode Island Judge in the case of Rogers V. Rogers and was able to convince 5 Supreme Court Justices to vacate the incorrect decision in a unanimous 5-0 decision. This precedential decision helped determine the Jurisdiction of the Rhode Island Family Court to determine divorce matters.
On February 22nd, 2012 David Slepkow Travelled to Washington DC for the swearing in ceremony prior to the Courts scheduled Oral Argument calendar. A small contingent of distinguished and accomplished Lawyers was sworn into this exclusive Bar. David was honored to be selected by a Major United States Law School for inclusion in this bar. David is also a member of the Rhode Island Bar, the Massachusetts Bar and the Bar for the Federal Court First Circuit District of Rhode Island.
David is a Partner and Owner of Slepkow Slepkow & Associates, Inc. which was established by David's Grandfather in 1932. SS&A is currently celebrating its 80th birthday
Rhode Island Personal Injury Lawyer, David Slepkow has authored hundreds of legal articles and blog posts concerning RI Law including: RI Car Accidents, RI Child Custody, RI Criminal law, Rhode Island Divorce, and Rhode Island Personal Injury.
RI Car accident Attorney David Slepkow has also written hundreds of posts concerning Truck, Motorcycle, Auto, Bus, Bike, Swimming Pool, Slip and Fall and Premises Liability Accidents. These articles can be found at David's numerous Rhode Island Law Blogs.
The RI Supreme Court licenses all lawyers and attorneys in the general practice of law, but does not license or certify any lawyer / attorney as an expert or specialist in any field of practice. While this firm maintains joint responsibility, most cases of this type are referred to other attorneys for principle responsibility.
Please contact David Slepkow at (401)-437-1100.
Website: http://www.slepkowlaw.com
After RI Supreme Court Win, Attorney Sworn into US Supreme Court Bar
After RI Supreme Court win, accomplished Rhode Island Personal Injury Attorney, David Slepkow, sworn in as a member of the US Supreme Court bar.
2012-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study by UC Santa Barbara researchers suggests that bacteria communicate by touch
2012-03-05
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– What if bacteria could talk to each other? What if they had a sense of touch? A new study by researchers at UC Santa Barbara suggests both, and theorizes that such cells may, in fact, need to communicate in order to perform certain functions. The findings appear today in the journal Genes & Development.
Christopher Hayes, UCSB associate professor of molecular, cellular, and development biology, teamed with graduate students Elie Diner, Christina Beck, and Julia Webb to study uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC), which causes urinary tract infections ...
IU biologists offer clearer picture of how protein machine systems tweak gene expression
2012-03-05
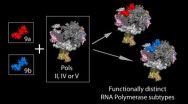
Indiana University biologists have found that specific types of RNA polymerase enzymes, the molecular machines that convert DNA into RNA, can differ in function based on variation in the parts -- in this case protein subunits -- used to assemble those machines.
The new findings on the synthesis and function of different RNA polymerases (Pols), including two RNA polymerases that lead author Craig Pikaard discovered over a decade ago -- the plant-specific enzymes Pol IV and Pol V -- indicate that subunit composition of the polymerases plays a role in selecting how some ...
Vitamin D shrinks fibroid tumors in rats
2012-03-05
Treatment with vitamin D reduced the size of uterine fibroids in laboratory rats predisposed to developing the benign tumors, reported researchers funded by the National Institutes of Health.
Uterine fibroids are the most common noncancerous tumors in women of childbearing age. Fibroids grow within and around the wall of the uterus. Thirty percent of women 25 to 44 years of age report fibroid-related symptoms, such as lower back pain, heavy vaginal bleeding or painful menstrual periods. Uterine fibroids also are associated with infertility and such pregnancy complications ...
Turning off small RNA
2012-03-05
For the last dozen years, scientists have known that minuscule strings of genetic material called small RNA are critically important to our genetic makeup. But finding out what they do hasn't been easy. Now a scientist from Michigan Technological University and his team have developed a way to turn off small RNAs and find out just how important they can be.
When it comes to inheritance, DNA is just the half of it. What we are is also driven by the epigenetic world of RNA: the countless, twisting molecules that DNA churns out. RNA in turn transforms the amino acid soup ...
New pathway found for regulation of blood vessel growth in cancer
2012-03-05
Researchers at Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University have identified a new function for a gene that normally prevents the development of cancer.
Scientists had known that the gene, which encodes a protein called p14 ARF, works inside the cell to control proliferation and division. A team led by Erwin Van Meir, PhD, discovered that p14 ARF also regulates tumor-induced angiogenesis, the process by which growing cancers attract new blood vessels.
The findings, published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, provide insight into how cancers form and progress, ...
Simulator computes evacuation scenarios for major events
2012-03-05
VIDEO:
The new simulation program represents every individual in a ten-thousand crowd and shows color-coded crowd densities.
Click here for more information.
At twenty past five on Saturday evening in the German city of Kaiserslautern, 40,000 rival soccer fans pour out of the Fritz-Walter stadium after the final whistle has been blown on a league game. All of the fans are either heading to the parking lots or train stations. Even without any incidents, this is a difficult ...
March 2012 story tips
2012-03-05
ENERGY -- Designing tomorrow's water heater . . .
Consumers and the environment could ultimately be the beneficiaries of a high-efficiency CO2 heat pump water heater concept being researched by General Electric and Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Through a cooperative research and development agreement, GE and ORNL are designing a prototype residential water heater that will feature an energy factor of greater than 2.0 with a first hour rating of more than 50 gallons. If the design proves to be technically and economically viable, it could ultimately result in a commercial ...
Mobile mayhem
2012-03-05
First, the bad news: all across America, trucks and tractor-trailers are transporting industrial explosives on nearly every artery of the country's interstate and highway system. That's right, volatile explosives, including munitions, rocket motors, and dynamite, are moving at a high rate of speed down a roadway not too far from you.
Now, the good news: America's track record in transporting these materials is about as safe as they come. Very rarely, almost never in fact, are the potential dangers of these transports realized, largely due to instituted safeguards that ...
Research reveals first evidence of hunting by prehistoric Ohioans
2012-03-05
Cleveland . . . Cut marks found on Ice Age bones indicate that humans in Ohio hunted or scavenged animal meat earlier than previously known. Dr. Brian Redmond, curator of archaeology at The Cleveland Museum of Natural History, was lead author on research published in the Feb. 22, 2012 online issue of the journal World Archaeology.
Redmond and researchers analyzed 10 animal bones found in 1998 in the collections of the Firelands Historical Society Museum in Norwalk, Ohio. Found by society member and co-author Matthew Burr, the bones were from a Jefferson's Ground Sloth. ...
Solving mystery of how sulfa drugs kill bacteria yields 21st century drug development target
2012-03-05
MEMPHIS, Tenn. -- More than 70 years after the first sulfa drugs helped to revolutionize medical care and save millions of lives, St. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists have determined at an atomic level the mechanism these medications use to kill bacteria. The discovery provides the basis for a new generation of antibiotics that would likely be harder for bacteria to resist and cause fewer side effects.
The work focused on sulfa drugs and their target enzyme, dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS). Most disease-causing microorganisms need DHPS to help make the molecule ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
[Press-News.org] After RI Supreme Court Win, Attorney Sworn into US Supreme Court BarAfter RI Supreme Court win, accomplished Rhode Island Personal Injury Attorney, David Slepkow, sworn in as a member of the US Supreme Court bar.