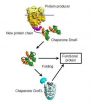
(Press-News.org) Proteins are the molecular building blocks and machinery of cells and involved in practically all biological processes. To fulfil their tasks, they need to be folded into a complicated three-dimensional structure. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry (MPIB) in Martinsried near Munich, Germany, have now analysed one of the key players of this folding process: the molecular chaperone DnaK. "The understanding of these mechanisms is of great interest in the light of the many diseases in which folding goes awry, such as Alzheimer's or Parkinson's," says Ulrich Hartl, MPIB director. The work of the researchers has now been published in Cell Reports.
Proteins are responsible for almost all biological functions. The cells of the human body continuously synthesize thousands of different proteins in the form of amino acid chains. In order to be biologically useful, these chains must fold into a complex three-dimensional pattern. When this difficult process goes wrong, it can lead to useless or even dangerous protein clumps. All cells, from bacteria to human, have therefore developed a network of molecular chaperones, proteins themselves, which help other proteins to fold properly.
MPIB scientists have now investigated the organisation of this network in the bacterium Escherichia coli. Using proteomic analyses they show how different chaperones cooperate during the folding process. "We identified the Hsp70 protein DnaK as the central player of the network," explains Ulrich Hartl. "It functions as a kind of turntable." DnaK binds to about 700 different protein chains as they are synthesised. Furthermore, DnaK mediates the folding of most of these protein chains. Those it cannot fold are transferred to yet another chaperone, the barrel-shaped GroEL. GroEL is a highly specialised folding machine. It forms a nano-cage in which a single protein chain is temporarily enclosed and allowed to fold while protected from external influences.
Disruptions in the Chaperone Network
The researchers also investigated what happens when the chaperone network is disturbed. For example, when GroEL is removed from the cells, its client proteins accumulate on DnaK, which then shuttles them to proteases to be decomposed. "Apparently, DnaK realises that the attached protein chains will never be able to mature into useful molecules," says the biochemist. Similar but even more complicated chaperone networks control the proteome of human cells. Understanding these reactions is of great interest in the light of the many neurodegenerative diseases in which folding goes awry.
INFORMATION:
Original Publication:
G. Calloni, T. Chen, S.M. Schermann, H. Chang, P. Genevaux, F. Agostini, G.G. Tartaglia, M. Hayer-Hartl and F.U. Hartl: DnaK Functions as a Central Hub in the E. coli Chaperone Network. Cell Reports, March 8, 2012
DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2011.12.007
The dance of the chaperones
Max Planck scientists identify key player of protein folding
2012-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ultrafast sonograms shed new light on rapid phase transitions
2012-03-12
An international team of physicists has developed a method for taking ultrafast 'sonograms' that can track the structural changes that take place within solid materials in trillionth-of-a-second intervals as they go through an important physical process called a phase transition.
Common phase transitions include the melting of candle wax before it burns and dissolving sugar in water. They are purely structural changes that produce dramatic changes in a material's physical properties and they play a critical role both in nature and in industrial processes ranging from ...
Double Text Wedding Signs and Family Name Signs Now Featured by Arttowngifts.com
2012-03-12
Arttowngifts.com, a popular online retailer of whimsical signs and personalized gifts announced the addition of wedding name signs to its line of custom wood signs. These personalized signs, which feature the couple's names and wedding date, often feature popular romantic quotes and sayings. These handcrafted custom wedding signs are as unique and charming as the newlyweds they represent.
Made from recycled wood and hand painted by the artist, these custom wood signs contain two layers of vinyl lettering, allowing the customer to include their family's last name overlaid ...
Vaccination may be key for true elimination of HIV-1
2012-03-12
In what may prove to be a major step forward for the treatment of HIV-1 infection, scientists have discovered an effective way to eliminate a notoriously persistent form of the virus that does not respond to current therapies. The research, published online by Cell Press on March 8th from the journal Immunity, describes a vaccination strategy that may be essential for successful eradication efforts and should therefore be considered for future clinical trials.
Current antiretroviral therapies suppress the ability of HIV-1 to copy itself, but they cannot completely eliminate ...
Could a NOSH-aspirin-a-day keep cancer away?
2012-03-12
The humble aspirin may soon have a new role. Scientists from The City College of New York have developed a new aspirin compound that has great promise to be, not only an extremely potent cancer-fighter, but even safer than the classic medicine cabinet staple.
The new designer aspirin curbed the growth of 11 different types of human cancer cells in culture without harming normal cells, reported a team from the Sophie Davis School of Biomedical Education of The City College of New York in a paper published this month in the journal ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. The cancers ...
The work-life integration overload: Thousands of researchers weigh in on outmoded work environments
2012-03-12
NEW YORK – Attracting workers into science and technology fields could be hampered by work-life integration issues according to a new international survey. Drawing data from 4,225 publishing scientists and researchers worldwide, the Association for Women in Science (AWIS) finds that lack of flexibility in the workplace, dissatisfaction with career development opportunities and low salaries are driving both men and women to re-consider their profession.
More than half (54%) of all scientists and researchers said that work demands conflict with their personal lives at ...
Do you hear what I hear?
2012-03-12
PASADENA, Calif.—In both animals and humans, vocal signals used for communication contain a wide array of different sounds that are determined by the vibrational frequencies of vocal cords. For example, the pitch of someone's voice, and how it changes as they are speaking, depends on a complex series of varying frequencies. Knowing how the brain sorts out these different frequencies—which are called frequency-modulated (FM) sweeps—is believed to be essential to understanding many hearing-related behaviors, like speech. Now, a pair of biologists at the California Institute ...
Dr Jill, Former Health Care Professional, Promoted
2012-03-12
Dr Jill, formerly a health care professional, joined ProU this fall to learn skills and to grow her online business, working from home. Things are going well and she has moved up within ProU. In February 2012, Dr Jill has advanced twice. Dr Jill upgraded to Master Affiliate and is now eligible and looking forward to attending and learning even more at the next ProU Master Marketing Event. Dr Jill also upgraded to Ascent Level of ProU program. At this new, higher level she is eligible to attend the BREAKTHROUGH Mastery Workshop and have access to the recorded 12 month BREAKTHROUGH ...
Gravitational lens reveals details of distant, ancient galaxy
2012-03-12
Thanks to the presence of a natural "zoom lens" in space, University of Chicago scientists working with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope have obtained a uniquely close-up look at the brightest gravitationally magnified galaxy yet discovered.
The imagery offers a visually striking example of gravitational lensing, in which one massive object's gravitational field can magnify and distort the light coming from another object behind it.
Such optical tricks stem from Einstein's theory of general relativity, which describes how gravity can warp space and time, including bending ...
Minority administrators, school personnel key to engaging immigrant parents
2012-03-12
Minority principals and other administrative personnel at elementary and high schools play a key role in implementing policies and practices aimed at engaging immigrant parents of students, according to new research from Rice University, the University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee and Vanderbilt University.
The researchers examined how schools in districts with immigrant populations are addressing low levels of parent involvement in their children's education and providing opportunities for engagement and support. The study, which will be published in the March edition of ...
Experiment observes elusive neutrino transformation
2012-03-12
PASADENA, Calif.—An international team of physicists—including several from the California Institute of Technology (Caltech)—has detected and measured, for the first time, a transformation of one particular type of neutrino into another type. The finding, physicists say, may help solve some of the biggest mysteries about the universe, such as why the universe contains more matter than antimatter—a phenomenon that explains why stars, planets, and people exist at all.
The results, released online on March 8, come from the Daya Bay Reactor Neutrino Experiment, which consists ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
New approach to qualifying nuclear reactor components rolling out this year
U.S. medical care is improving, but cost and health differ depending on disease
AI challenges lithography and provides solutions
Can AI make society less selfish?
UC Irvine researchers expose critical security vulnerability in autonomous drones
Changes in smoking status and their associations with risk of Parkinson’s, death
In football players with repeated head impacts, inflammation related to brain changes
Being an early bird, getting more physical activity linked to lower risk of ALS
The Lancet: Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Black Americans face increasingly higher risk of gun homicide death than White Americans
Flagging claims about cancer treatment on social media as potentially false might help reduce spreading of misinformation, per online experiment with 1,051 US adults
Yawns in healthy fetuses might indicate mild distress
Conservation agriculture, including no-dig, crop-rotation and mulching methods, reduces water runoff and soil loss and boosts crop yield by as much as 122%, in Ethiopian trial
Tropical flowers are blooming weeks later than they used to through climate change
Risk of whale entanglement in fishing gear tied to size of cool-water habitat
Climate change could fragment habitat for monarch butterflies, disrupting mass migration
Neurosurgeons are really good at removing brain tumors, and they’re about to get even better
Almost 1-in-3 American adolescents has diabetes or prediabetes, with waist-to-height ratio the strongest independent predictor of prediabetes/diabetes, reveals survey of 1,998 adolescents (10-19 years
Researchers sharpen understanding of how the body responds to energy demands from exercise
[Press-News.org] The dance of the chaperonesMax Planck scientists identify key player of protein folding