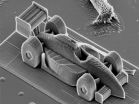
(Press-News.org) Printing three dimensional objects with incredibly fine details is now possible using "two-photon lithography". With this technology, tiny structures on a nanometer scale can be fabricated. Researchers at the Vienna University of Technology (TU Vienna) have now made a major breakthrough in speeding up this printing technique: The high-precision-3D-printer at TU Vienna is orders of magnitude faster than similar devices (see video). This opens up completely new areas of application, such as in medicine.
Setting a New World Record
The 3D printer uses a liquid resin, which is hardened at precisely the correct spots by a focused laser beam. The focal point of the laser beam is guided through the resin by movable mirrors and leaves behind a polymerized line of solid polymer, just a few hundred nanometers wide. This high resolution enables the creation of intricately structured sculptures as tiny as a grain of sand. "Until now, this technique used to be quite slow", says Professor Jürgen Stampfl from the Institute of Materials Science and Technology at the TU Vienna. "The printing speed used to be measured in millimeters per second – our device can do five meters in one second." In two-photon lithography, this is a world record.
This amazing progress was made possible by combining several new ideas. "It was crucial to improve the control mechanism of the mirrors", says Jan Torgersen (TU Vienna). The mirrors are continuously in motion during the printing process. The acceleration and deceleration-periods have to be tuned very precisely to achieve high-resolution results at a record-breaking speed.
Photoactive Molecules Harden the Resin
3D-printing is not all about mechanics – chemists had a crucial role to play in this project too. "The resin contains molecules, which are activated by the laser light. They induce a chain reaction in other components of the resin, so-called monomers, and turn them into a solid", says Jan Torgersen. These initiator molecules are only activated if they absorb two photons of the laser beam at once – and this only happens in the very center of the laser beam, where the intensity is highest. In contrast to conventional 3D-printing techniques, solid material can be created anywhere within the liquid resin rather than on top of the previously created layer only. Therefore, the working surface does not have to be specially prepared before the next layer can be produced (see Video), which saves a lot of time. A team of chemists led by Professor Robert Liska (TU Vienna) developed the suitable initiators for this special resin.
VIDEO:
The video shows the 3-D printing process in real time. Due to the very fast guiding of the laser beam, 100 layers, consisting of approximately 200 single lines each, are...
Click here for more information.
Researchers all over the world are working on 3D printers today – at universities as well as in industry. "Our competitive edge here at the Vienna University of Technology comes from the fact that we have experts from very different fields, working on different parts of the problem, at one single university", Jürgen Stampfl emphasizes. In materials science, process engineering or the optimization of light sources, there are experts working together and coming up with mutually stimulating ideas.
Because of the dramatically increased speed, much larger objects can now be created in a given period of time. This makes two-photon-lithography an interesting technique for industry. At the TU Vienna, scientists are now developing bio-compatible resins for medical applications. They can be used to create scaffolds to which living cells can attach themselves facilitating the systematic creation of biological tissues. The 3d printer could also be used to create tailor made construction parts for biomedical technology or nanotechnology.
INFORMATION:
Picture download: http://www.tuwien.ac.at/dle/pr/aktuelles/downloads/2012/3d_nanodrucker/
Youtube-Version: http://youtu.be/5y0j191H0kY
Further Information:
Jan Torgersen
Additive Manufacturing Technologies
Vienna University of Technology
T.: 0043-1-58801-30869
jan.torgersen@tuwien.ac.at
Prof. Jürgen Stampfl
Additive Manufacturing Technologies
Vienna University of Technology
T.: 0043-1-58801-30862
jstampfl@pop.tuwien.ac.at
3-D printer with nano precision
Ultra-high-resolution 3-D printer breaks speed records at Vienna University of Technology
2012-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
JoVE shows how researchers open the brain to new treatments
2012-03-14
One of the trickiest parts of treating brain conditions is the blood brain barrier, a blockade of cells that prevent both harmful toxins and helpful pharmaceuticals from getting to the body's control center. But, a technique published in JoVE, uses an MRI machine to guide the use of microbubbles and focused ultrasound to help drugs enter the brain, which may open new treatment avenues for devastating conditions like Alzheimer's and brain cancers.
"It's getting close to the point where this could be done safely in humans," said paper-author Meaghan O'Reilly, "there is ...
Scientists tap the cognitive genius of tots to make computers smarter
2012-03-14
People often wonder if computers make children smarter. Scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, are asking the reverse question: Can children make computers smarter? And the answer appears to be 'yes.'
UC Berkeley researchers are tapping the cognitive smarts of babies, toddlers and preschoolers to program computers to think more like humans.
If replicated in machines, the computational models based on baby brainpower could give a major boost to artificial intelligence, which historically has had difficulty handling nuances and uncertainty, researchers ...
Reduced baby risk from another cesarean
2012-03-14
A major study led by the University of Adelaide has found that women who have had one prior cesarean can lower the risk of death and serious complications for their next baby - and themselves - by electing to have another cesarean.
The study, known as the Birth After Caesarean (BAC) study, is the first of its kind in the world. It involves more than 2300 women and their babies and 14 Australian maternity hospitals. The results are published this week in the international journal, PLoS Medicine.
The study shows that infants born to women who had a planned elective ...
St. Michael's doctor uses wiki to empower patients and help them to develop asthma action plans
2012-03-14
TORONTO, Ont., March 13, 2012—Imagine that you have asthma, and rather than give you a set of instructions about what to do if you have an attack, your doctor invites you to help write them?
Would that make patients feel more engaged and empowered in managing their health care, and would that ultimately make them happier if not healthier?
These questions are being raised by Dr. Samir Gupta, a respirologist at St. Michael's Hospital.
His research has found that a wiki – a website developed collaboratively by a community of users, allowing any user to add and edit content ...
Get me out of this slump! Visual illusions improve sports performance
2012-03-14
With the NCAA men's college basketball tournament set to begin, college basketball fans around the United States are in the throes of March Madness. Anyone who has seen a game knows that the fans are like extra players on the court, and this is especially true during critical free throws. Fans of the opposing team will wave anything they can, from giant inflatable noodles to big heads, to make it difficult for players to focus on the basket.
But one way a player might be able to improve his chances at making that free throw is by tricking himself into thinking the basket ...
Post-exposure antibody treatment protects primates from Ebola, Marburg viruses
2012-03-14
Army scientists have demonstrated, for the first time, that antibody-based therapies can successfully protect monkeys from the deadly Ebola and Marburg viruses. In addition, the animals were fully protected even when treatment was administered two days post-infection, an accomplishment unmatched by any experimental therapy for these viruses to date. The work appears in this week's electronic edition of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The filoviruses, Ebola and Marburg, cause hemorrhagic fever with human case fatality rates as high as 90 percent. They ...
Global warming skepticism climbs during tough economic times
2012-03-14
STORRS, Conn. – The American public's growing skepticism in recent years about the existence of man-made global warming is rooted in apprehension about the troubled economy, a University of Connecticut study suggests.
Lyle Scruggs, associate professor of political science in UConn's College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, says the public's belief in climate change dropped significantly as the economy dipped and unemployment climbed in the late 2000s.
His research with UConn political science graduate student Salil Benegal found that popular alternative explanations -- ...
Data support theory on location of lost Leonardo da Vinci painting
2012-03-14
Evidence uncovered during research conducted in Florence's Palazzo Vecchio late last year appears to support the theory that a lost Leonardo da Vinci painting existed on the east wall of the Hall of the 500, behind Giorgio Vasari's mural "The Battle of Marciano." The data supporting the theoretical location of the da Vinci painting "The Battle of Anghiari" was obtained through the use of an endoscopic probe that was inserted through the wall on which the Vasari fresco was painted. The probe was fitted with a camera and allowed a team of researchers, led by scientist Maurizio ...
Santorini: The ground is moving again in paradise
2012-03-14
Do a Google image search for "Greece." Before you find pictures of the Parthenon or Acropolis, you'll see several beautiful photos of Santorini, the picturesque island in the Aegean Sea. The British Broadcasting Company named it the world's best island in 2011. Santorini is a tourist magnet, famous for its breathtaking, cliff side views and sunsets.
It's also a volcanic island that has been relatively calm since its last eruption in 1950. Until now. The Santorini caldera is awake again and rapidly deforming at levels never seen before. Georgia Tech Associate Professor ...
South Dennis Dentist Raises Money for Cancer Research
2012-03-14
South Dennis dentist Dr. Michael Bittrich's service to the community does not stop with his dental practice. For the fifth year in a row, he is riding his bike in the Pan Massachusetts Challenge to raise money for cancer research and treatment on Aug. 4 and 5th, 2012.
Last year the event raised $35 million and the Dennis dentist and his "Miles for Mary" team were able to raise more than 55 thousand dollars. The money raised from the event is donated to the Jimmy Fund and the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. Both organizations strive to both provide expert cancer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
New approach to qualifying nuclear reactor components rolling out this year
[Press-News.org] 3-D printer with nano precisionUltra-high-resolution 3-D printer breaks speed records at Vienna University of Technology