(Press-News.org) A study by researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and The University of Minnesota indicates that a parent's weight change is a key contributor to the success of a child's weight loss in family-based treatment of childhood obesity. The results were published today in the advanced online edition of the journal Obesity.
"We looked at things such as parenting skills and styles, or changing the home food environment, and how they impacted a child's weight," said Kerri N. Boutelle, PhD, associate professor of pediatrics and psychiatry at UC San Diego and Rady Children's Hospital-San Diego. "The number one way in which parents can help an obese child lose weight? Lose weight themselves. In this study, it was the most important predictor of child weight loss."
Recent data suggests that 31 percent of children in the United States are overweight or obese, or between four and five million children. Current treatment programs generally require participation by both parents and children in a plan that combines nutrition education and exercise with behavior therapy techniques.
"Parents are the most significant people in a child's environment, serving as the first and most important teachers," said Boutelle "They play a significant role in any weight-loss program for children, and this study confirms the importance of their example in establishing healthy eating and exercise behaviors for their kids."
The researchers looked at eighty parent-child groups with an 8 to 12-year-old overweight or obese child, who participated in a parent-only or parent + child treatment program for five months.
The study focused on evaluating the impact of three types of parenting skills taught in family-based behavioral treatment for childhood obesity, and the impact of each on the child's body weight: the parent modeling behaviors to promote their own weight loss, changes in home food environment, and parenting style and techniques (for example, a parent's ability to help limit the child's eating behavior, encouraging the child and participating in program activities).
Consistent with previously published research, parent BMI change was the only significant predictor of child's weight loss.
The researchers concluded that clinicians should focus on encouraging parents to lose weight to help their overweight or obese child in weight management.
###For more information about weight loss programs for children and adolescents at UC San Diego, visit www.obesitytreatment.ucsd.edu or email Kidsweight@ucsd.edu.
Additional contributors to the study include Guy Cafri, UCSD Child and Adolescent Services Research Center, and Scott J. Crown, University of Minnesota.
How to best help your child lose weight: Lose weight yourself
2012-03-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
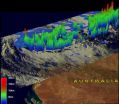
NASA's TRMM satellite sees tropical storm Lua's rainfall
2012-03-15
A tropical storm called Lua formed in the Indian Ocean off Australia's northwestern coast on March 13, 2012. NASA's TRMM satellite passed over Lua and observed moderate rainfall and strong towering thunderstorms within on March 13. By March 14, it was turning back toward Australia and storm warnings had been posted.
The area of Australia where Cyclone Lua is located is sparsely populated, but Lua caused the shutdown of over one quarter of the country's crude oil production.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite flew over that area on March 13, 2012 ...
Silicon-carbon electrodes snap, swell, don't pop
2012-03-15
RICHLAND, Wash. -- A study that examines a new type of silicon-carbon nanocomposite electrode reveals details of how they function and how repeated use could wear them down. The study also provides clues to why this material performs better than silicon alone. With an electrical capacity five times higher than conventional lithium battery electrodes, silicon-carbon nanocomposite electrodes could lead to longer-lasting, cheaper rechargeable batteries for electric vehicles.
Published online in the journal Nano Letters last week, the study includes videos of the electrodes ...
A Troubling Confluence of Events is Affecting Sales and Marketing Executives in 2012
2012-03-15
The Kathy Freeman Company, a retained executive search firm focused exclusively on assignments within the investment industry, has concluded its latest proprietary research designed to identify current trends among senior sales and marketing executives.
Based on that research the firm has just published its most recent annual whitepaper: "Should I Stay or Should I Go Now?"
The trends identified in the paper can be leveraged by CEOs, their human resources partners, or line executives to design a more effective and relevant approach to retaining or attracting ...
New drug now available for actinic keratosis
2012-03-15
A new topical gel now available by prescription significantly decreases the amount of time needed to treat actinic keratosis, a skin condition that is a common precursor to skin cancer, according to a multi-center trial led by researchers at Mount Sinai School of Medicine. The gel, called ingenol mebutate, is applied to the skin for just a few days, making it quicker and even more effective as current therapies require weeks to months to apply. The Phase III study results of the trial are published in the March 15, 2012 issue of the The New England Journal of Medicine.
Actinic ...
Some NHS trusts consistently outperform others on patient experience
2012-03-15
Some NHS trusts consistently outperform others on a range of measures of patient experience, finds research published online in BMJ Quality & Safety.
Furthermore, the top performers tend to be Foundation Trusts and teaching hospitals, the study shows.
Patient experience is one of the five domains for assessing NHS performance (NHS Outcomes Framework) and is recognised internationally as a key dimension of healthcare quality.
But it is one of the more difficult areas to measure because of the many contributory factors involved, say the authors.
The authors, from ...
Heavy rucksacks storing up back problems for many school-kids
2012-03-15
Significant numbers of teens regularly carry rucksacks for school which top 10 to 15 per cent of their body weight and risk back pain and other related disorders, finds research published online in the Archives of Disease in Childhood.
The problem is compounded by a predominantly sedentary lifestyle, say the researchers.
They assessed the back health of 1403 pupils between the ages of 12 and 17, drawn from 11 schools in one province in North Western Spain.
The teens were weighed twice - once without coats and other items likely to add weight, such as mobile phones, ...
Advice to breastfeed exclusively for 6 months may be 'unhelpful' and too idealistic
2012-03-15
Advising women to breastfeed exclusively for six months may be "unhelpful" and far too idealistic, suggests a qualitative study of new mothers, their partners, and close relatives, published in the online journal BMJ Open.
Exclusive breastfeeding for six months is known to confer considerable health benefits for mother and baby, and many governments around the world endorse the World Health Organization recommendations to do so.
But more realistic, incremental, and achievable goals should be set instead, particularly in countries that have struggled to meet targets ...
Dietary cadmium may be linked with breast cancer risk
2012-03-15
PHILADELPHIA — Dietary cadmium, a toxic metal widely dispersed in the environment and found in many farm fertilizers, may lead to an increased risk of breast cancer, according to a study published in Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Cadmium occurs at low concentrations naturally, but scientists are concerned because contamination of farmland mainly due to atmospheric deposition and use of fertilizers leads to higher uptake in plants.
"Because of a high accumulation in agricultural crops, the main sources of dietary cadmium ...
Lung doctors expect respiratory diseases will worsen with global climate change
2012-03-15
Worldwide increases in the incidences of asthma, allergies, infectious and cardiovascular diseases will result from a variety of impacts of global climate change, including rising temperatures, worsening ozone levels in urban areas, the spread of desertification, and expansions of the ranges of communicable diseases as the planet heats up, the professional organization representing respiratory and airway physicians stated in a new position paper released today.
The paper is published online and in print in the Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society. The society ...
Food stamp customers buy more at farmers' markets when point-of-sale system is available
2012-03-15
Philadelphia, PA, March 15, 2012 – Record numbers of Americans are receiving Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) benefits, as food stamps are now known, and many SNAP participants live in neighborhoods with little or no access to healthy food. A study conducted at the Clark Park Farmers' Market, in Philadelphia, PA, has found that making it easier for vendors to collect SNAP payments with electronic point-of-sale systems increased fresh produce sales to SNAP recipients by 38%. However, the costs associated with such systems may put them out of reach for farmers. ...