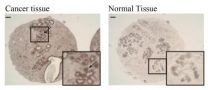
(Press-News.org) Troy, N.Y. – Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Biologist Lee Ligon has found a previously unknown connection between breast cancer tumor cells and the surrounding healthy tissue. The results provide new information on the earliest stages of breast cancer metastasis.
The results were published March 7, 2012, in the journal PLoS One, in a paper titled "Cadherin-23 Mediates Heterotypic Cell-Cell Adhesion between Breast Cancer Epithelial Cells and Fibroblasts." Ligon was joined in the research by Rensselaer doctoral student Maria Apostolopoulou. The research was funded by the American Cancer Society.
The research shows that a specialized type of molecule called Cadherin-23 can be found in and around breast cancer tumors. The molecule, which had never been associated with breast tissue or cancer, helps connect cancerous tumor cells to its neighboring healthy tissue, called the stroma.
"Something happens once cancerous cells enter the stroma and the cancer can very quickly become invasive," Ligon said. "Pathologists studying cancerous tissues have often noted that tumor cells make contact with the cells in the stroma, but they assumed the connections were unimportant."
Ligon and her team sought to uncover exactly what molecules were involved in attaching the tumor cells to the surrounding tissue to determine if those initial points of contact play a role in the progression of cancer through the body.
In the human breast, tumors most often originate in what are known as epithelial tissues. These tissues are made up of a specialized type of cell called epithelial cells. Epithelial cells line the interior of many structures and organs within the human body. In the breast, they line the interior of milk ducts. When epithelial cells start to divide uncontrollably, they eventually break out of the duct and literally spill into the surround tissue or stroma. The stroma is comprised of cells called fibroblasts and extracellular material such as collagen fibers. In many cases, the invading cancerous epithelial cells will glom onto nearby fibroblasts in the stroma.
Ligon and Apostolopoulou worked to pick apart how the epithelial cells attached themselves to the fibroblasts. One of the primary tools the body uses to glue cells together is a family of molecules called cadherins. In the human genome there are over 80 different cadherin family members. In most cases, cadherins stick two cells of the same type together. In the case of the breast cancer tumor cells and fibroblasts, two very different cells were sticking together. Ligon sought to determine which cadherins were involved in this odd interaction.
At first, their findings were not surprising. They found cadherins associated with epithelial cells as well as cadherins associated with fibroblasts. It was the discovery of the highly specialized and unusual cadherin, Cadherin-23, that really surprised them, according to Ligon.
"Cadherin-23 has never before been associated with cancer," Ligon said. "In fact, it has previously only been shown in the sophisticated inner workings of the ear and retina."
It is still largely unknown what happens once the cells have made a connection, but the appearance of Cadherin-23 in elevated levels in cancerous tissues suggests that it might play a real role in the earliest stages of metastasis, according to Ligon. Cadherin-23 is a new and potentially very important new component in the progression of cancer for scientists to investigate, she said.
INFORMATION:
Ligon is a member of the Center for Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies and the Department of Biology at Rensselaer.
Biologists uncover surprising connection between breast cancer cells and surrounding tissue
American Cancer Society-funded research reveals molecule called Cadherin-23 could play a role in the earliest stages of breast cancer
2012-03-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Increased collaboration between nursing home RNs and LPNs could improve patient care
2012-03-15
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Researchers estimate nearly 800,000 preventable adverse drug events may occur in nursing homes each year. Many of these incidents could be prevented with safety practices such as medication reconciliation, a process in which health care professionals, such as physicians, pharmacists and nurses, review medication regimens to identify and resolve discrepancies when patients transfer between health care settings. In nursing homes, both registered nurses (RNs) and licensed practical nurses (LPNs) often are responsible for this safety practice. A recent study ...
Researchers send 'wireless' message using elusive particles
2012-03-15
A group of scientists led by researchers from the University of Rochester and North Carolina State University have for the first time sent a message using a beam of neutrinos – nearly massless particles that travel at almost the speed of light. The message was sent through 240 meters of stone and said simply, "Neutrino."
"Using neutrinos, it would be possible to communicate between any two points on Earth without using satellites or cables," said Dan Stancil, professor of electrical and computer engineering at NC State and lead author of a paper describing the research. ...
Macdonald Hotels Announces New Market Lunch Menu at the Macdonald Compleat Angler
2012-03-15
Macdonald Compleat Angler, which overlooks the River Thames at Marlow, Buckinghamshire, has introduced a new market lunch menu including some of the best fresh, spring provenance. The tempting dishes, created by Head Chef David Smith, will be served in the hotel's AA two rosette Bowaters restaurant Monday to Saturday from 12.30 until 2.30pm.
The restaurant in Marlow will offer a choice of four delicious dishes for each course with vegetarian options. For starters there's pressed ham hock, John Ross Jnr smoked salmon fishcake, cream of cauliflower soup or a classic Caesar ...
Fielding questions about climate change
2012-03-15
This press release is available in French.Montreal -- Canada defines itself as a nation that stretches from coast to coast to coast. But can we keep those coasts healthy in the face of climate change? Yves Gélinas, associate professor in Concordia's Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, has found the solution in a surprising element: iron.
In a study published in Nature, Gélinas — along with Concordia PhD candidate Karine Lalonde and graduate Alexandre Ouellet, as well as McGill colleague Alfonso Mucci — studies the chemical makeup of sediment samples from around ...
Hiding emotions may exacerbate depression among black men who confront racial discrimination
2012-03-15
Enduring subtle, insidious acts of racial discrimination is enough to depress anyone, but African-American men who believe that they should respond to stress with stoicism and emotional control experience more depression symptoms, according to new findings from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
The study, "Taking It Like a Man: Masculine Role Norms as Moderators of the Racial Discrimination–Depressive Symptoms Association Among African-American Men," was published online March 8, 2012, in the American Journal of Public Health.
"We know that traditional ...
New study of pine nuts leaves mystery of 'pine mouth' unsolved
2012-03-15
A new study of the composition of pine nuts, including those associated with "pine mouth," leaves unsolved the decade-old mystery of why thousands of people around the world have experienced disturbances in taste after eating pine nuts. The report on pine nuts or pignolia — delicious edible nuts from pine trees enjoyed plain or added to foods ranging from pasta to cookies — appears in ACS' Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry.
Ali Reza Fardin-Kia, Sara M. Handy and Jeanne I. Rader note that more than 20,000 tons of pine nuts are produced each year worldwide. "Pine ...
Killer silk: Making silk fibers that kill anthrax and other microbes in minutes
2012-03-15
A simple, inexpensive dip-and-dry treatment can convert ordinary silk into a fabric that kills disease-causing bacteria — even the armor-coated spores of microbes like anthrax — in minutes, scientists are reporting in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. They describe a range of potential uses for this new killer silk, including make-shift curtains and other protective coatings that protect homes and other buildings in the event of a terrorist attack with anthrax.
Rajesh R. Naik and colleagues explain that in adverse conditions, bacteria of the Bacillus species, ...
Corn insecticide linked to great die-off of beneficial honeybees
2012-03-15
New research has linked springtime die-offs of honeybees critical for pollinating food crops — part of the mysterious malady called colony collapse disorder — with technology for planting corn coated with insecticides. The study, published in ACS' journal Environmental Science & Technology, appears on the eve of spring planting seasons in some parts of Europe where farmers use the technology and widespread deaths of honeybees have occurred in the past.
In the study, Andrea Tapparo and colleagues explain that seeds coated with so-called neonicotinoid insecticides went ...
Alleged robo-calling may have significantly impacted voting
2012-03-15
In a new paper, a Simon Fraser University economist finds that robo-calling, if the phenomenon did occur, could have significantly influenced voter turnout and ballot results in the last federal election.
Anke Kessler's discussion paper is available on her website and on Worthwhile Canadian Initiative, an economics blog.
Elections Canada is investigating New Democrat and Liberal party allegations that the Conservatives hired companies to robo-call voters in ridings across Canada, thereby influencing the Tories' 2011 federal election win.
The term robo-calling describes ...
Tennessee's urban forests valued in the billions
2012-03-15
NASHVILLE, Tenn. — Tennessee's urban forests, currently valued at about $80 billion, also provide almost $650 million in benefits such as carbon storage, pollution removal, and energy reduction according to a new U.S. Forest Service report.
The authors of Urban Forests of Tennessee, 2009 found there are 284 million trees in urban areas in the state, with canopies covering 33.7 percent of 1.6 million acres of urban area. Those urban forests provide an estimated $204 million per year in pollution removal and $66 million per year in energy savings. The study is the first ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
[Press-News.org] Biologists uncover surprising connection between breast cancer cells and surrounding tissueAmerican Cancer Society-funded research reveals molecule called Cadherin-23 could play a role in the earliest stages of breast cancer