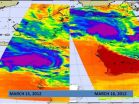
(Press-News.org) Northern Australia's Pilbara coast is under warnings, alerts and watches as powerful Cyclone Lua nears for a landfall. NASA's Aqua satellite has been providing infrared, visible and microwave data on Lua that have shown forecasters the storm is strengthening on its approach to land.
Two of the most recent infrared images of Cyclone Lua were captured from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument onboard NASA's Aqua satellite. The AIRS instrument captured infrared images of Cyclone Lua on March 15 at 1741 UTC and March 16 at 0553 UTC. The later image appeared to show that Lau was becoming more organized and more compact, signs that the storm was strengthening. Bands of thunderstorms are also wrapping into the low-level center, another sign of strengthening. Over that time period the storm had grown from a tropical storm to a cyclone. Aqua captured an infrared image of the storm's cloud top temperatures using the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument. AIRS data showed that the coldest (purple) cloud top temperatures (colder than -63F/-52.7C).
The list of warnings, watches and alerts are numerous. A Cyclone Warning is current for coastal areas from Cape Leveque to Dampier, including Port Hedland, Karratha, Dampier and Broome, as well as inland parts of the eastern Pilbara and far western Kimberley. A Cyclone Watch is current for the central and eastern inland Pilbara including Telfer, Newman and Paraburdoo, the western inland Kimberley, the eastern Gascoyne including Meekatharra, and the far western Interior.
Yellow and Blue Alerts are also in effect. A Yellow Alert is in effect for residents between Broome and Whim Creek including Bidyadanga, Port Hedland, South Hedland, Warralong, Yande Yarra, Marble Bar and adjacent pastoral and mining leases. A Blue Alert is in effect for residents in coastal communities between Whim Creek and Dampier including Karratha, Dampier, Roebourne, Wickham and Point Samson as well as inland communities including Nullagine, Newman and Jigalong and surrounding pastoral and mining leases.
ABC Online Melboure reports that flights have been canceled and roads have been closed. Officials have also closed Karijini National Park because of flash flooding risk.
On March 16, 2012 at 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EST), Tropical cyclone Lua's maximum sustained winds were near 75 knots (86 mph/139 kph). Cyclone-force winds extended out 30 nautical miles (34.5 miles/55.5 km) from the center, while tropical storm-force winds extended out to 160 nautical miles (184 miles/296.3 km) from the center.
Lua was located near 16.5 South and 116.6 East, about 260 miles north-northwest of Port Hedland, Australia. Lua was moving to the east-southeast at 10 knots (11.5 mph/18.5 kph).
Lua is forecast to strengthen to 90 knots (103.6 mph/166.7 kph) before making landfall around midday (local time) on March 17 just north of Port Hedland. By March 19, Lua is expected to dissipate in central or southern Western Australia. The Australian Bureau of Meteorology is issuing updates every three hours. To see the updates, visit: http://www.bom.gov.au/cyclone/.
INFORMATION:
NASA sees cyclone Lua strengthening for March 17 landfall
2012-03-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Top Los Angeles Appliance Repair Company, AM PM Appliance Repair, is now Offering Specialty Services for High End Appliances
2012-03-19
There are quite a few things around the house that many take for granted, no matter how often they are used. Individuals will find themselves enjoying the features and utility of high end appliances to cook their food, clean dishes, and help to wash clothes. When these appliances begin to break down, it is going to put an immediate halt to almost everything in the household. For locals that are going to need these devices back up in working condition as quickly and affordably as possible, the leading Los Angeles appliance repair company, AM PM, is now offering specialty ...
Closing hole in the heart no better than drugs in preventing strokes
2012-03-19
MAYWOOD, Il. -- Loyola University Medical Center is one of the major enrollers in a landmark clinical trial that found that plugging a hole in the heart works no better than drugs in preventing strokes.
The study is published in the New England Journal of Medicine. Loyola enrolled 24 patients, one of the highest patient enrolments in the multicenter trial, and more than any other Chicago-area hospital. Principal investigators at the Loyola site are stroke specialist Dr. Michael Schneck and interventional cardiologist Dr. Fred Leya.
About 1 in 4 adults has a small hole ...
2012 Internal Medicine Residency match virtually unchanged from 2011
2012-03-19
PHILADELPHIA -- The number of U.S. medical student seniors at medical schools choosing internal medicine residencies leveled in 2012 after two years of significant increases. According to the 2012 National Resident Matching Program, 2,941 U.S. medical school seniors matched internal medicine, nearly unchanged from 2011 when 2,940 matched internal medicine.
"After seeing increases in 2010 and 2011 for the internal medicine residency match for U.S. medical students, we are disappointed that there was not a bigger increase this year," said Virginia L. Hood, MBBS, MPH, FACP, ...
Mesquite trees displacing Southwestern grasslands
2012-03-19
As the desert Southwest becomes hotter and drier, semi-arid grasslands are slowly being replaced by a landscape dominated by mesquite trees, such as Prosopis velutina, and other woody shrubs, a team of University of Arizona researchers has found.
In a "leaf-to-landscape" approach, the team combined physiological experiments on individual plants and measurements across entire ecosystems to quantify how well grasslands, compared to mesquite trees and woody shrubs, cope with heat and water stress across seasonal precipitation periods.
"Our results show that even the smallest ...
Researchers reveal how a single gene mutation leads to uncontrolled obesity
2012-03-19
Washington, D.C. -- Researchers at Georgetown University Medical Center have revealed how a mutation in a single gene is responsible for the inability of neurons to effectively pass along appetite suppressing signals from the body to the right place in the brain. What results is obesity caused by a voracious appetite.
Their study, published March 18th on Nature Medicine's website, suggests there might be a way to stimulate expression of that gene to treat obesity caused by uncontrolled eating.
The research team specifically found that a mutation in the brain-derived ...
Need for speed
2012-03-19
Like any law-abiding train passenger, a molecule called oskar RNA carries a stamped ticket detailing its destination and form of transport, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have found. They show that for this molecule, moving in the right direction isn't enough: speed is of the essence. Their study, published online today in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, also provides clues as to how a single molecule could receive tickets for different destinations, depending on what type of cell it is in.
For a fruit fly ...
Miami Defense Attorney Diana Gonzalez Runs for Judge
2012-03-19
Ferrer Shane, PL is proud to announce that one of its attorneys, Diana E. Gonzalez, is running for Miami-Dade County Court Judge.
Starting her career in 2004, Diana Gonzalez was rapidly promoted up the ranks in the Public Defender's Office, first handling misdemeanor charges, then defending young people in the juvenile division, to ultimately defending clients charged with the most serious felonies - all in the span of just five years, trying everything from a traffic ticket to a murder case.
Having traveled abroad with the U.S. Department of Defense and with USAID ...
New insight into mechanisms behind autoimmune diseases suggests a potential therapy
2012-03-19
LA JOLLA, Calif., March 18, 2012 – Autoimmune diseases, such as Type I diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis, are caused by an immune system gone haywire, where the body's defense system assaults and destroys healthy tissues. A mutant form of a protein called LYP has been implicated in multiple autoimmune diseases, but the precise molecular pathway involved has been unknown. Now, in a paper published March 18 in Nature Chemical Biology, researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham) show how the errant form of LYP can disrupt the immune system. ...
UMass Amherst theoretical physicists find a way to simulate strongly correlated fermions
2012-03-19
AMHERST, Mass. – Combining known factors in a new way, theoretical physicists Boris Svistunov and Nikolai Prokof'ev at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, with three alumni of their group, have solved an intractable 50-year-old problem: How to simulate strongly interacting quantum systems to allow accurate predictions of their properties.
It could open the door to practical superconductor applications, as well as to solving difficult "many-body" problems in high-energy physics, condensed matter and ultra-cold atoms.
The theoretical breakthrough by Prokof'ev and ...
Improving Your Doctor's Hygiene
2012-03-19
When people don't feel well, they see a doctor. They probably assume that the doctor will not spread anything to them to make them sicker. Ohio residents may be disturbed to find out that hygiene in hospitals is not as high of a priority as one would expect.
Hospital-acquired infections are the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. A 2004 study done by the American College of Physicians found that only 57 percent of doctors washed their hands when they were supposed to. The study also showed that the busier the doctor was and the more patients needing ...