(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- Although women continue to lag behind men in pay, the gender wage gap has narrowed considerably since the 1960s. Now a new University of Michigan study is the first to quantify the impact of the pill on women's labor market advances.
The study shows that roughly one-third of women's wage gains through the 1990s are due to the availability of oral contraceptives.
Published online this week by the National Bureau of Economic Research as a working paper, the study was conducted by U-M economist Martha Bailey and colleagues Brad Hershbein at U-M and Amalia Miller at the University of Virginia.
"We found that women who had early access to the pill in the 1960s and 1970s earned 8 percent more on average by the 1980s and 1990s than women without early access," said Bailey, an assistant professor of economics in the U-M College of Literature, Science, and the Arts and a research affiliate at the U-M Institute for Social Research.
Bailey and colleagues analyzed the careers of approximately 4,300 women, born from 1943 to 1954, using the National Longitudinal Survey of Young Women. These women varied in their legal ability to obtain the pill from their doctors between the ages of 18 and 21
"The difficulty of parsing the pill's effect on women's careers relates to the timing of its appearance," Bailey said. "By cause or coincidence, the pill's diffusion coincided with important changes in norms and ideas about women's work and the end of the baby boom."
Bailey and colleagues developed a novel analytic strategy to answer this question. After the U.S. Federal Drug Administration approved the pill in 1960, laws in different states placed different age limits on when women could legally obtain it. As these laws changed in almost every state in the country, largely due to reducing the legal voting age to 18, the inadvertent side-effect was that women could obtain the pill at younger ages. This meant that women no longer had to decide between looking for a mate (and the risk of pregnancy) and investing in their educations and careers. They could do both.
The researchers found that early access laws doubled contraceptive pill use among women between the ages of 18 and 20 – precisely the ages affected by access laws – but not beyond age 21, when the laws did not bind. Pill use by age 18 was 140 percent higher, and by age 20 was 43 percent higher than national mean use at those ages.
"As the pill provided younger women the expectation of greater control over childbearing, women invested more in their human capital and careers," Bailey said. "Most affected were women with some college, who benefitted from these investments through remarkable wage gains over their lifetimes."
Their analysis shows that nearly two-thirds of these pill-access induced gains in wages were due to increasing labor-market experience; another third came through to greater educational attainment and entry in non-traditionally female occupations.
But even these results may not do justice to the over-arching importance of the pill.
"Our results may understate the pill's broader influence because they do not explore the effect of changes in access to the pill beyond age 20 and fail to capture the potentially large social multiplier effects," Bailey said. "The pill's availability likely altered norms and expectations about marriage and childbearing. It also likely affected the decisions of companies to hire and promote women."
###
The study is forthcoming in the American Economic Journal: Applied Economics in July.
Related Links:
Martha Bailey http://www-personal.umich.edu/~baileymj/
U-M Institute for Social Research (ISR) http://www.isr.umich.edu
NBER Paper: http://www.nber.org/papers/w17922
Established in 1949, the University of Michigan Institute for Social Research (ISR) is the world's largest academic social science survey and research organization, and a world leader in developing and applying social science methodology, and in educating researchers and students from around the world. ISR conducts some of the most widely-cited studies in the nation, including the Thomson Reuters/University of Michigan Surveys of Consumers, the American National Election Studies, the Monitoring the Future Study, the Panel Study of Income Dynamics, the Health and Retirement Study, the Columbia County Longitudinal Study and the National Survey of Black Americans. ISR researchers also collaborate with social scientists in more than 60 nations on the World Values Surveys and other projects, and the Institute has established formal ties with universities in Poland, China, and South Africa. ISR is also home to the Inter-University Consortium for Political and Social Research (ICPSR), the world's largest digital social science data archive. Visit the ISR Web site at http://www.isr.umich.edu for more information.
Parsing the Pill's impact on women's wage
2012-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mustard -- not just for hotdogs anymore, research shows
2012-03-27
University of Alberta researcher Christina Engels has discovered how to extract a compound from mustard seeds that can protect against food spoilage.
Engels recovered a particular compound—sinapic acid—from mustard seed meal, which shows antibacterial effects against such strains as Staphylococcus aureus, E. coli and Listeria monocytogenes, all of which can cause grave illness and death in humans. Canada is the world's largest exporter of mustard seed.
The results published recently in the European Food Research & Technology journal>.
Engels' isolation of sinapic ...
Smyrna GA Hotel Offers Close Lodging to the 2012 Spring Jonquil Festival
2012-03-27
Hampton Inn & Suites Atlanta Galleria Hotel, a premier Smyrna Georgia Hotel, offers convenient lodging for guests and vendors attending the Spring Jonquil Festival. The event will take place April 28-29, 2012 on the beautiful Village Green in downtown Smyrna, GA. The event will showcase arts and crafts by more than 150 artists/crafters from across the country. It will also feature:
- Featured Artist's Market
- Live entertainment including country music performer J. Scott Thompson
- Children's section with Peter's festival puppet show and inflatable actives
- ...
LaMichael James Brings Tools for Success to His Alma-Mater High School
2012-03-27
Yesterday, pro football prospect LaMichael James surprised students at Liberty-Eylau High School, his alma mater in Texarkana, Texas, with tools for achieving their best on the field and in life. James and representatives from SKLZ, the athletic training company for which he is a brand ambassador, shared how hard work and dedication can lead to academic and athletic successes. In addition to the words of encouragement, James donated $5,000 of SKLZ training equipment to the Liberty-Eylau High School to help its student athletes elevate their athleticism.
"When you're ...
Poor colonoscopy prep hides pre-cancerous polyps
2012-03-27
What happens on the day before a colonoscopy may be just as important as the colon-screening test itself.
Gastroenterologists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found that when patients don't adequately prep for the test by cleansing their colons, doctors often can't see potentially dangerous pre-cancerous lesions.
Reporting in the journal Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, the researchers say that doctors often missed at least one pre-cancerous growth in about one-third of patients who did not properly prepare for their colonoscopy. Those polyps ...
Research into children with autism published in JoVE
2012-03-27
Though the prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) has been steadily climbing— from 6 in 1,000 children in 2002, to nearly 10 in 1,000 children in 2006, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention— little is known about the disorder. But, research with young kids can lead to important insights in how children with developmental abnormalities view the world. This month in the Journal of Visualized Experiments, researchers demonstrate how to use eye-tracking in very young children with autism.
"Generally, individuals new to this method often struggle, ...
Harvard’s Wyss Institute creates living human gut-on-a-chip
2012-03-27
Researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University have created a gut-on-a-chip microdevice lined by living human cells that mimics the structure, physiology, and mechanics of the human intestine—even supporting the growth of living microbes within its luminal space. As a more accurate alternative to conventional cell culture and animal models, the microdevice could help researchers gain new insights into intestinal disorders, such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, and also evaluate the safety and efficacy of potential ...
Sandia National Laboratories' Ion Beam Laboratory looks at advanced materials for reactors
2012-03-27
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M — Sandia National Laboratories is using its Ion Beam Laboratory (IBL) to study how to rapidly evaluate the tougher advanced materials needed to build the next generation of nuclear reactors and extend the lives of current reactors.
Reactor operators need advanced cladding materials, which are the alloys that create the outer layer of nuclear fuel rods to keep them separate from the cooling fluid. Better alloys will be less likely to deteriorate from exposure to everything from coolant fluids to radiation damage.
Operating a reactor causes progressive ...
Boston University researchers develop microfluidic chip to stem flu outbreaks
2012-03-27
BOSTON -- The H1N1 flu pandemic in 2009 underscored weaknesses in methods widely used to diagnose the flu, from frequent false negatives to long wait times for results. Now Boston University researchers have developed a prototype of a rapid, low-cost, accurate, point-of-care device that promises to provide clinicians with an effective tool to quickly diagnose both seasonal and pandemic strains of influenza, and thus limit the spread of infection.
Boston University Biomedical Engineering Associate Professor Catherine Klapperich led the team of engineering and medical researchers ...
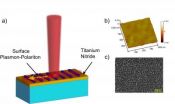
Researchers discover a new path for light through metal
2012-03-27
WASHINGTON -- Helping bridge the gap between photonics and electronics, researchers from Purdue University have coaxed a thin film of titanium nitride into transporting plasmons, tiny electron excitations coupled to light that can direct and manipulate optical signals on the nanoscale. Titanium nitride's addition to the short list of surface-plasmon-supporting materials, formerly comprised only of metals, could point the way to a new class of optoelectronic devices with unprecedented speed and efficiency.
"We have found that titanium nitride is a promising candidate ...
WTFast.com Destroys Lag and Gives First-Person Shooter Gamers a Competitive Advantage From Anywhere Around the World
2012-03-27
Using unique proprietary technology, WTFast accelerates the online connection between gamers and servers, dramatically increasing performance for the world's most popular franchises. WTFast users can see drastic improvements in performance boosting game connection speeds by as much as 70 per cent. This is vital for gamers who live remotely from the host game servers.
"Our service gives its users a huge advantage in multiplayer FPS games regardless of where you are in the world," said Rob Bartlett, CEO of WTFast. "In some cases we've seen ping rates drop ...