(Press-News.org) SAN DIEGO, March 28, 2012 — Scientists today described development of a new explosives detector that can sense small amounts of TNT and other common explosives in liquids instantly with a sensitivity that rivals bomb-sniffing dogs, the current gold standard in protecting the public from terrorist bombs. They reported on the technology, suitable for incorporation into a TNT test strip, at the 243rd National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS), being held here this week.
The sensor also has potential uses in detecting water pollution involving TNT, according to Yu Lei, Ph.D., and Ying Wang, who developed the sensor. Such contamination can occur from production, obsolete storage facilities and other sources. TNT contamination of drinking water carries a risk of serious health disorders.
Wang, a graduate student in Lei's laboratory at the University of Connecticut, said there has been a long-standing need for a fast, simple, accurate way to detect so-called "nitroaromatic compounds" in salt water, fresh water and other liquids. That family of compounds includes 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene — TNT — which is so widely used in construction, agriculture and military applications that it has become the standard for measuring explosive force, even for nuclear weapons.
"Law enforcement or homeland security officials concerned about the presence of TNT in a harbor at docks need an answer quickly so they can take steps to protect people and property," Wang pointed out. "That's not easy with traditional testing methods."
Those tests involve taking a sample of water and shipping it to a full-scale laboratory. The sample must be concentrated because water currents dilute the explosive, leaving only minute amounts in the sample. And water samples must be prepared in other ways before analysis with expensive laboratory instruments.
"Our new sensor promises to provide answers on-the-scene almost immediately," Wang added, noting that it is based on a color change that occurs when a sensing molecule in the device attaches to an explosive. Lei explained that the device can detect very small amounts of TNT, as well as larger amounts. The broad sensing range, high sensitivity and dual action make this new sensor unique among those that work on water-based samples, he noted.
So far, Lei and Wang have been able to detect concentrations of explosives, such as TNT, ranging from about 33 parts per trillion (equivalent to one drop in 20 Olympic-sized swimming pools) to 225 parts per million.
Lei and Wang explained that the sensor is already easy to use, but they plan to make it even more user-friendly by incorporating it into a paper strip, similar to the test strips used to test for pregnancy. That way, an explosives expert or airport screener would simply dip the filter paper into a sample of ocean water or other liquid, and put that filter paper into a machine that would read the fluorescence and detect the presence of explosives in real time. The sensor also could be used to detect TNT that leaches into the environment, in streams or rivers near munitions testing sites and manufacturing facilities.
INFORMATION:
The scientists acknowledged funding from the National Science Foundation.
The American Chemical Society is a non-profit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 164,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society contact newsroom@acs.org.
Abstract
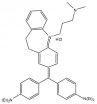
Sensitive and selective detection of explosives is crucial for homeland security and civilian safety. The fluorescence-based methods for explosives hold much promise to satisfy all the requirements as an effective platform for trace detection of explosives. In this work, a novel fluorescence polymer is synthesized by facile side-chain reaction in one synthetic step with high conversion, and characterized by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, UV-vis and fluorescence spectroscopy. In aqueous solution, this new polymer forms a highly emissive hydrogel and undergoes a dramatic fluorescence quenching when nitroaromatics (i.e., 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT)) molecules bind to the polymer through fluorescent resonance energy transfer (FRET)-amplified effects. This amplification was demonstrated by the quantitative analysis of the fluorescence titration profiles. Down to ppt level of TNT could be discriminated, representing the most sensitive response among the reported fluorescence sensors for nitroaromatics. Moreover, this polymer gives a fast response to nitroaromatics and could be used in real-time detection.
END
Patients can enjoy discounted dental treatments to improve the appearance of their smiles with recent promotions offered by Dr. Joon Sun, dentist in Naperville, IL, at White Eagle Family Dentistry. Dr. Sun is pleased to offer patients discounts on multiple dental treatments, including Invisalign, and teeth whitening in Naperville.
"I want my patients to be able to afford the smiles they have always desired. To do this, I have created special promotions for teeth whitening and Invisalign treatments, in addition to a credit for new patients when they receive their ...
SAN DIEGO, March 28, 2012 — If eccentric candy-maker Willy Wonka could leap from the pages of Roald Dahl's classic, Charlie and the Chocolate Factory, and walk these streets, he might make a bee-line for a festival of cocoa and chocolate on the menu today at the 243rd National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS).
As the world's largest scientific society, ACS is hosting a celebration of scientific discoveries about the food that could lay claim to being the world's favorite treat, comfort food and indulgence. The ACS symposium, titled "Cocoa: Science ...
SAN DIEGO, March 28 — Scientists today described a new and more efficient version of an innovative device the size of a home washing machine that uses bacteria growing in municipal sewage to make electricity and clean up the sewage at the same time. Their report here at the 243rd National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's largest scientific society, suggested that commercial versions of the two-in-one device could be a boon for the developing world and water-short parts of the U.S.
"Our prototype incorporates innovations so that ...
Gambling City, a premier online gambling portal, has announced completion of plans for expanding the site to better serve visitors. "We feel visitors should constantly have new and fresh resources available to them to enable them to make the best online gambling choices," stated Graeme Levin, CEO of the Gambling City Network.
Features of this important expansion effort include an advanced bonus search, an advanced casino search and improved voting procedures to allow users to weigh in with their own opinions and experiences at online casinos. With over 600 ...
SAN DIEGO, March 28, 2012 — The standard test used to detect milk-protein residues in processed foods may not work as well as previously believed in all applications, sometimes missing ingredients that can cause milk allergy, the most common childhood food allergy, which affects millions of children under age 3, a scientist reported here today at the 243rd National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society's (ACS), the world's largest scientific society.
Joseph L. Baumert, Ph.D., who headed the study, explained that thermal and non-thermal processing of foods ...
Patients can further expand their dental health care knowledge with the help of Dr. Todd Armstrong, Kenosha cosmetic dentist, and his interactive website. When patients are in search of more information on various dental topics, they can now turn to the extensive education library accessible via Dr. Armstrong's website at http://www.dentalcarekenosha.com.
"I want my patients to be well-informed about dental problems and treatments, because informed patients make better decisions about their health and well being. This is why I am happy to offer an extensive section ...
WASHINGTON -- A first-of-its kind series of brain studies shows how an adult learning a foreign language can come to use the same brain mechanisms as a native speaker. The research also demonstrates that the kind of exposure you have to the language can determine whether you achieve native-language brain processing, and that learning under immersion conditions may be more effective in reaching this goal than typical classroom training. The research also suggests that the brain consolidates knowledge of the foreign language as time goes on, much like it does when a person ...
This press release is available in French, Portuguese and Spanish.
LONDON (28 March 2012) — Nearly one billion people in the world are undernourished, while millions suffer from chronic disease due to excess food consumption. Global demand is growing for agricultural products and food prices are rising, yet roughly one-third of food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted. Climate change threatens more frequent drought, flooding and pest outbreaks, and the world loses 12 million hectares of agricultural land each year to land degradation. Land clearing and inefficient ...
For over three years, Shari has been a temp at Hendry Dental, providing support for Dr. Robert Hendry, Littleton dentist, and quality care for patients of all ages. Dr. Hendry is now happy to announce that Shari is no longer a temp for Hendry Dental, but is now a full time hygienist with his office.
"It is an honor to welcome Shari as a full-time member to my dental team. She truly has been a breath of fresh air for my patients because she spends quality time with each patient to make sure they fully understand their treatment and the health of their teeth. I look ...
Treating invasive brain tumors with a combination of chemotherapy and radiation has improved clinical outcomes, but few patients survive longer than two years after diagnosis. The effectiveness of the treatment is limited by the tumor's aggressive invasion of healthy brain tissue, which restricts chemotherapy access to the cancer cells and complicates surgical removal of the tumor.
To address this challenge, researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University have designed a new treatment approach that appears to halt the spread of cancer cells into ...