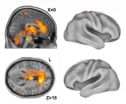
(Press-News.org) An international team of scientists, including four at Simon Fraser University, has made a discovery that will change the way the most deadly form of breast cancer is treated.
The journal Nature has just published the team's findings online in the paper The clonal and mutational evolution spectrum of primary triple negative breast cancers.
The study is the largest genetic analysis of what were thought to be triple negative breast cancer tumours.
The 59 scientists involved in this study expected to see similar gene profiles when they mapped on computer the genomes of 100 tumours.
But to their amazement they found no two genomes were similar, never mind the same. "Seeing these tumours at a molecular level has taught us we're dealing with a continuum of different types of breast cancer here, not just one," explains Steven Jones, co-author of this study.
The SFU molecular biology and biochemistry professor, who heads up bioinformatics research at the BC Cancer Agency, adds: "The genetic diversity of these tumours, even though they're clinically similar, probably explains why they are so difficult to treat. These findings prove the importance of personalizing cancer drug treatment so that it targets the genetic make up of a particular tumour rather than presuming one therapy can treat multiple, similar-looking tumours."
Triple negative breast cancer lacks surface cell receptors for estrogen, progesterone and herceptin — a hormone, steroid and protein, respectively, linked to breast cancer. It strikes 16 per cent of women who develop breast cancer and targets mainly those under age 40.
Scientists consider it the most deadly form of breast cancer because it doesn't respond well to modern drug therapies, which knock out receptors found in most breast cancers but not this one.
Typically, triple negative breast cancer patients need everything thrown at them — surgery, chemotherapy and radiation — to have any hope of going into remission.
Jones credits the affordability of genetic sequencing — a process that now takes tens of thousands rather than millions of dollars to do — with making tumour analysis at the molecular level more readily available.
###Other researchers associated with SFU involved in this research are Marco Marra, Martin Hirst and Gregg Morin. As well as being researchers at the Michael Smith Genome Sciences Centre, they are SFU adjunct professors of molecular biology and biochemistry.
Scientists uncover multiple faces of deadly breast cancer
2012-04-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Arsenic turns stem cells cancerous, spurring tumor growth
2012-04-05
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health have discovered how exposure to arsenic can turn normal stem cells into cancer stem cells and spur tumor growth. Inorganic arsenic, which affects the drinking water of millions of people worldwide, has been previously shown to be a human carcinogen. A growing body of evidence suggests that cancer is a stem-cell based disease. Normal stem cells are essential to normal tissue regeneration, and to the stability of organisms and processes. But cancer stem cells are thought to be the driving force for the formation, growth, and ...
New forage plant prepares farmers for climate changes
2012-04-05
Sorghum, or durra, is an important forage crop in many countries, for example the USA, Africa, China and Australia.
The plant is grown instead of corn because it produces more biomass and better withstands long periods of drought.
However, when exposed to drought, the sorghum plant produces large amounts of dhurrin, which forms toxic cyanide, i.e. Prussic acid.
Forced to discard crops
Farmers thus face a big dilemma. During a period of drought when they most need food for their animals, they are often forced to discard their sorghum because they do not know how ...
Growing nitrous oxide levels explained
2012-04-05
Australian, Korean and US scientists have generated a 65-year record of Southern Hemisphere nitrous oxide measurements establishing a new benchmark against which to compare changes in the long-lived greenhouse gas that is also a major ozone-depleting substance.Published this week in the journal Nature Geoscience, the record is drawn from atmospheric sampling at the Cape Grim Baseline Air Pollution Station, Tasmania, and air extracted from the Antarctic ice sheet
Its significance, says co-author CSIRO's Dr David Etheridge, will be its contribution to the development of ...
Treatment hope for muscular dystrophy
2012-04-05
An international team led by the University of Melbourne Australia, has found that increasing a specific protein in muscles could help treat Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), a severe and progressive muscle wasting disease that affects young boys.
Approximately one in every 3,500 boys worldwide is afflicted with DMD. There is no cure for the disease which causes muscle fragility, spinal curvature and premature death.
Results from the studies published in Nature today showed that by increasing levels of 'heat shock protein 72' (HSP72) in the muscles of animal models ...
Scientists solving the mystery of human consciousness
2012-04-05
Awakening from anesthesia is often associated with an initial phase of delirious struggle before the full restoration of awareness and orientation to one's surroundings. Scientists now know why this may occur: primitive consciousness emerges first. Using brain imaging techniques in healthy volunteers, a team of scientists led by Adjunct Professor Harry Scheinin, M.D. from the University of Turku, Turku, Finland in collaboration with investigators from the University of California, Irvine, USA, have now imaged the process of returning consciousness after general anesthesia. ...
George Williams College Expands Online Degree Offerings to Attract New Students
2012-04-05
George Williams College of Aurora University (GWC) has expanded its online education offerings to include two degree programs for working professionals pursuing new and advanced job opportunities. The Master of Science in Recreation Administration and the Doctorate in Social Work are now available in a convenient online format for students seeking an alternative way to continue their education and achieve their career goals.
The Master of Science in Recreation Administration is an accelerated degree program focused on advancing a professional's career in the field of ...
Elusive Producers Dumbpunx Release 'Get On The Floor'
2012-04-05
This one came out of nowhere but seems to be getting a cult following on YouTube. Check out the video in its tame and not so tame versions...
Warning this video contains SWEARING and scenes of scantly clad girls.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gq_NtNE2-4Q
Dumbpunx is an elusive group of producers who operate through a middle man to deliver their brand of twisted electro anthemic house to their adoring fans. According to the middle men who wish to be nameless, Dumbpunx have a long line of hits under their belts having been involved with projects that have scored over ...
The long arm of the dendritic cell
2012-04-05
Individuals who suffer from autoimmune diseases also display a tendency to develop atherosclerosis – the condition popularly known as hardening of the arteries. Clinical researchers at LMU, in collaboration with colleagues in Würzburg, have now discovered a mechanism which helps to explain the connection between the two types of disorder. The link is provided by a specific class of immune cells called plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs). pDCs respond to DNA released from damaged and dying cells by secreting interferon proteins which stimulate the immune reactions that underlie ...
62 percent of men and 37 percent of women over the age of 65 are sexually active
2012-04-05
A study based on the National Health and Sexuality Survey, involving nearly 2000 people, describes the sexual practices of senior citizens in Spain. The most common are kisses, caresses and vaginal penetration. The main causes of sexual inactivity are physical illness and widowerhood.
A new study published in one of the world's biggest sexuality journals the Journal of Sexual Medicine analyses the factors that influence sexual activity amongst elderly people in Spain.
"This research lets us know the reality of a social phenomenon which is not tackled enough in Spain: ...
Colchis Bar & Restaurant Furnished by Hill Cross Furniture
2012-04-05
Recently launched in the heart of Notting Hill, 'Colchis' Georgian Restaurant and Bar has not disappointed it's rich neighbouring surroundings. Hill Cross Furniture was delighted to fully furnish and work with appointed interior design firm, Design LSM and owner Giorgi Sulkanishvilli in transforming this 150 sq ft interior into a classic regency dining experience.
Exploring Georgia�EUR s affluent heritage, both in location and design, Colchis boasts beautifully adorned dark wooden panelling, marble table tops, bold upholstery and candle-lit ambience at its best. The ...