SAN LUIS OBISPO, CA, April 10, 2012 (Press-News.org) WirelessTimeClock.com, a trusted source for web-based time clocks, has re-launched its website (http://www.wirelesstimeclock.com) with a more intuitive and streamlined design, promising a more enriching experience for businesses searching for reliable employee time clocks and time and attendance management solutions.
"Our customers have been asking for a more intuitive, resourceful site," says Scott Tobin, owner of WirelessTimeClock.com. "We wanted to make sure they could find exactly the clocks and monthly plans that would fit their business needs."
With the new website, visitors will see the products and services front and center, with quick descriptions of the employee time clocks, prices and detailed pictures that call out advanced technical features of each time clock. The updated site also offers help pages, an online contact form, and phone customer services support for any questions customers have while shopping.
"Our primary goal is to provide customers with the time and attendance solution that works best for their business and their budget," notes Mr. Tobin. "Providing an easy-to-use site and worry-free customer are essential."
Many customers want to learn more about how the employee time clocks integrate with time tracking software. The redesigned site offers information explaining how WirelessTimeClock.com's web-based time clocks work, including initial setup and time data management in most popular payroll systems.
For those unfamiliar with web-enabled clocks, employees can punch in either through the clock itself, through the clock management website, through a mobile phone app or by phone. Managers then login to the website to view hours, run reports, make any changes and manage the system. That data is immediately available to be exported to payroll or an external payroll company.
The new website also has a dedicated page to special low-cost service plans for purchasing WirelessTimeClock.com's employee time clocks. For businesses with 1-9 active employees, the cost is $18 a month; for 10-19 active employees, the cost is $29 a month; for 20-49 active employees the cost is $49 a month; for 50-99 active employees the cost is $79 a month; and for 100 plus employees the price is $99 a month.
"One of the biggest areas of growth over the past year has been in biometric time clocks," adds Mr. Tobin. "This option ensures that only the employee is punching in and out through the use of a fingerprint reader integrated into the device. Our BN4000 model offers both fingerprint identification and wireless capability, making it the ideal choice for a growing number of businesses."
Like their easy-to-use time clocks, WirelessTimeClock.com's new and improved website will be a snap for visitors to navigate and easily find the right product for them. With honest service, a lifetime replacement policy, and affordable pricing, WirelessTimeClock.com is the go-to destination for all employee time clock needs.
WirelessTimeClock.com (http://www.wirelesstimeclock.com) has provided hundreds of businesses with reliable, low-cost employee attendance solutions. Based in San Luis Obispo, California, the company has served businesses worldwide with web-based time clocks and state-of-the-art biometric time clocks.
WirelessTimeClock.com Launches Redesigned Site
Offering cost-effective employee time and attendance solutions, WirelessTimeClock.com improves upon its web shopping experience with a complete overhaul of its site.
2012-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High-resolution atomic imaging of specimens in liquid by TEM using graphene liquid cell
2012-04-10
Daejeon, the Republic of Korea, April 9, 2012—The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) announced that a research team from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering has developed a technology that enables scientists and engineers to observe processes occurring in liquid media on the smallest possible scale which is less than a nanometer.
Professor Jeong Yong Lee and Researcher Jong Min Yuk, in collaboration with Professor Paul Alivisatos's and Professor Alex Zettl's groups at the University of California, Berkeley, succeeded in making ...
Normalizing tumor blood vessels improves delivery of only the smallest nanomedicines
2012-04-10
Combining two strategies designed to improve the results of cancer treatment – antiangiogenesis drugs and nanomedicines – may only be successful if the smallest nanomedicines are used. A new study from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) researchers, appearing in Nature Nanotechnology, finds that normalizing blood vessels within tumors, which improves the delivery of standard chemotherapy drugs, can block the delivery of larger nanotherapy molecules.
"We found that vascular normalization only increases the delivery of the smallest nanomedicines to cancer cells," says ...
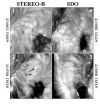
SDO and STEREO spot something new on the sun
2012-04-10
One day in the fall of 2011, Neil Sheeley, a solar scientist at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C., did what he always does – look through the daily images of the sun from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO).
But on this day he saw something he'd never noticed before: a pattern of cells with bright centers and dark boundaries occurring in the sun's atmosphere, the corona. These cells looked somewhat like a cell pattern that occurs on the sun's surface -- similar to the bubbles that rise to the top of boiling water -- but it was a surprise to find this ...
Atlanta Hardwood Flooring Can Be "Baby-Proof" If Done By FlooringAtlantaNow.com
2012-04-10
It shouldn't be surprising to those who have children, that Atlanta Hardwood Flooring is constantly in harm's way from rambunctious babies! The experts at FlooringAtlantaNow are truly masters of the trade, and most recommend using more durable types of wood for high-traffic areas of your home which are prone to scratches or abrasions.
Most Atlanta Flooring specialists agree that winter is the best time to do these types of installations and upgrades to your home. Because metro-Atlanta is known for its mild winters, the season offers a perfect climate which tends to be ...
Black flies may have a purpose after all
2012-04-10
Athens, Ga. – Black flies drink blood and spread disease such as river blindness—creating misery with their presence. A University of Georgia study, however, proves that the pesky insects can be useful.
Don Champagne, an entomology professor with the UGA College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, discovered a way to use the black fly's blood-sucking tactics for medical advancement. The results of his research were published in the journal PLoS One.
"In order to feed on blood, these insects have to contend with our natural defense agents against blood loss—like ...
Sexual reproduction brings long-term benefits, study shows
2012-04-10
Courtship rituals can be all-consuming, demanding time and effort – but now scientists have discovered why it might be worth it.
Attracting a mate – which can take significant effort, such as in a peacock's show of feathers or the exhaustive rutting of stags – can produce benefits for a species in the long term, a study suggests.
Scientists have shown that animals and plants which reproduce sexually are at a considerable advantage to those species – such as some insects and reptiles – that reproduce without a partner.
Researchers at the University of Edinburgh studied ...
Genetic regulator of fat metabolism and muscle fitness discovered
2012-04-10
While exercise is accepted universally as the most beneficial prescription physicians can write for patients, little is known about the molecular mechanisms that generate its widespread health benefits. Researchers from Case Western Reserve School of Medicine have shed light on this mystery by discovering that a genetic factor, Kruppel-like Factor 15 (KLF15), governs the body's ability to burn fat during exercise.
Previous research from the laboratory of Mukesh Jain, MD, FAHA, identified the importance of KLF15 in the metabolism of two of the three basic nutrients used ...
Head and body lice appear to be the same species, genetic study finds
2012-04-10
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new study offers compelling genetic evidence that head and body lice are the same species. The finding is of special interest because body lice can transmit deadly bacterial diseases, while head lice do not.
The study appears in the journal Insect Molecular Biology.
Scientists have long debated whether human head and body lice are the same or different species. The head louse (Pediculus humanus capitis) is a persistent nuisance, clinging to and laying its eggs in the hair, digging its mouthparts into the scalp and feeding on blood several times a ...
A bit touchy: Plants' insect defenses activated by touch
2012-04-10
HOUSTON -- (April 9, 2012) -- A new study by Rice University scientists reveals that plants can use the sense of touch to fight off fungal infections and insects. The study, which will be published in the April 24 issue of Current Biology, finds that plant defenses are enhanced when plants are touched.
"From previous studies, we knew that plants change their growth in response to touch but we didn't know how these growth changes were activated," said Wassim Chehab, a faculty fellow in Rice's Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology and lead author of the new study. ...
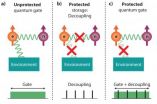
Opening the gate to robust quantum computing
2012-04-10
AMES, Iowa -- Scientists have overcome a major hurdle facing quantum computing: how to protect quantum information from degradation by the environment while simultaneously performing computation in a solid-state quantum system. The research was reported in the April 5 issue of Nature.
A group led by U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory physicist Viatsheslav Dobrovitski and including scientists at Delft University of Technology; the University of California, Santa Barbara; and University of Southern California, made this big step forward on the path to using the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
[Press-News.org] WirelessTimeClock.com Launches Redesigned SiteOffering cost-effective employee time and attendance solutions, WirelessTimeClock.com improves upon its web shopping experience with a complete overhaul of its site.