(Press-News.org) Lifting less weight more times is just as effective at building muscle as training with heavy weights, a finding by McMaster researchers that turns conventional wisdom on its head.
The key to muscle gain, say the researchers, is working to the point of fatigue.
"We found that loads that were quite heavy and comparatively light were equally effective at inducing muscle growth and promoting strength," says Cam Mitchell, one of the lead authors of the study and a PhD candidate in the Department of Kinesiology.
The research, published in the Journal of Applied Physiology, challenges the widely accepted dogma that training with heavy weights—which can be lifted only six to 12 times before fatigue—is the best avenue to muscle growth.
"Many older adults can have joint problems which would prevent them training with heavy loads," says Mitchell. "This study shows that they have the option of training with lighter and less intimidating loads and can still receive the benefits."
For the study, a series of experiments were conducted on healthy, young male volunteers to measure how their leg muscles reacted to different forms of resistance training over a period of 10 weeks.
The researchers first determined the maximum weight each subject could lift one time in a knee extension. Each subject was assigned to a different training program for each leg.
In all, three different programs were used in combinations that required the volunteers to complete sets of as many repetitions as possible with their assigned loads – typically eight to 12 times per set at the heaviest weights and 25-30 times at the lowest weights.
The three programs used in the combinations were:
one set at 80% of the maximum load
three sets at 80% of the maximum
three sets at 30% of the maximum
After 10 weeks of training, three times per week, the heavy and light groups that lifted three sets saw significant gains in muscle volume—as measured by MRI—with no difference among the groups. Still, the group that used heavier weights for three sets developed a bit more strength.
The group that trained for a single set showed approximately half the increase in muscle size seen in both the heavy and light groups.
"The complexity of current resistance training guidelines may deter some people from resistance training and therefore from receiving the associated health benefits," says Stuart Phillips, a professor in the Department of Kinesiology and supervisor of the study. "Our study provides evidence for a simpler paradigm, where a much broader range of loads including quite light loads can induce muscle growth, provided it is lifted to the point where it is difficult to maintain good form."
###
McMaster University, one of four Canadian universities listed among the Top 100 universities in the world, is renowned for its innovation in both learning and discovery. It has a student population of 23,000, and more than 156,000 alumni in 140 countries.
For more information, please contact:
Stuart Phillips
Professor of Kinesiology
McMaster University
905-525-9140 ext. 24465
phillis@mcmaster.ca
@mackinprof
Michelle Donovan
Public Relations Manager
McMaster University
905-525-9140 ext. 22869
donovam@mcmaster.ca
Wade Hemsworth
Public Relations Manager
McMaster University
905-525-9140, ext. 27988
hemswor@mcmaster.ca
END
Ann Arbor, Michigan… Regional differences in rates of cardiac procedures have increased in Michigan over the past decade—not fully explained by differences in health risk factors, heart attack or cardiac mortality rates—according to a report released today by the Center for Healthcare Research & Transformation (CHRT). The report compares the state's hospital referral regions (HRRs) using claims data from Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan's (BCBSM's) under-65 commercial subscribers and Medicare data from The Dartmouth Atlas of Health Care in Michigan.
According to the ...
Vitamin D may be known as the sunshine vitamin, but a new research report appearing in the Journal of Leukocyte Biology shows that it is more than that. According to the report, insufficient levels of vitamin D are related to a deficiency in our innate immune defenses that protect us from infections, neoplasias or autoimmune diseases. Since vitamin D levels decrease during autumn and winter when days are shorter and sunlight is relatively weak, this may explain why people are more prone to viral infection during these times. It also suggests that vitamin D supplementation, ...
New research published online in the FASEB Journal suggests that a specific enzyme, called 5-lipoxygenase, plays a key role in cell death induced by microgravity environments, and that inhibiting this enzyme will likely help prevent or lessen the severity of immune problems in astronauts caused by spaceflight. Additionally, since space conditions initiate health problems that mimic the aging process on Earth, this discovery may also lead to therapeutics that extend lives by bolstering the immune systems of the elderly.
"The outcomes of this space research might be helpful ...
Scientists of KIT and the University of Birmingham have identified relevant new functions of a gene that plays a crucial role in Fanconi anemia, a life-threatening disease. The FANCM gene is known to be important for the stability of the genome. Now, the researchers found that FANCM also plays a key role in the recombination of genetic information during inheritance. For their studies, the scientists used thale cress as a model plant. Their results are newly published by the journal The Plant Cell.
Stability of the genome is ensured by a series of mechanisms. If these ...
Are you connected to college friends on Facebook? Research from North Carolina State University shows that these social networks tend to form around graduation year or university housing – rather than other interests.
Researchers examined the first 100 colleges and universities to have students, faculty or staff join Facebook when the site exclusively contained .edu email addresses. As students, faculty and staff joined Facebook, social networks were formed. Each university, in essence, formed its own network – ranging in size from 762 to 50,000.
"We wanted to see what ...
Removing a child's ruptured appendix sooner rather than later significantly lowers hospital costs and charges, according to a recently published study.
An estimated $10,000 in hospital charges was saved when pediatric general surgeons removed the ruptured appendix within the first 24 hours, compared to the alternative treatment, called an interval appendectomy, which involved removing the appendix six-eight weeks later.
The study was published in the April issue of the Journal of American College of Surgeons, and was led by Martin Blakely, M.D., MS, associate professor ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Today's hybrid corn varieties more efficiently use nitrogen to create more grain, according to 72 years of public-sector research data reviewed by Purdue University researchers.
Tony Vyn, a professor of agronomy, and doctoral student Ignacio Ciampitti looked at nitrogen use studies for corn from two periods -- 1940-1990 and 1991-2011. They wanted to see whether increased yields were due to better nitrogen efficiency or whether new plants were simply given additional nitrogen to produce more grain.
"Corn production often faces the criticism from ...
Toronto will be the site of an incredible exchange of ideas between artists, music industry professionals, thinkers and developing artists at the Toronto International Music Summit. This one-day event, to be held at the Fairmont Royal York, will provide the tools and knowledge necessary to gain a foothold in the music industry and promote your band, your brand and yourself to the best of your ability.
The Summit will host a huge variety of influential industry professionals from all over the music business. Speakers will focus on four specific aspects of the music industry: ...
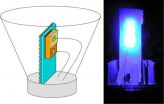
WASHINGTON, April 30--Like a coffee enthusiast who struggles to get a buzz from that third cup of morning joe, light-emitting diodes (LEDs) seem to reach a point where more electricity no longer imparts the same kick and productivity levels-off. Now a team of researchers from California and Japan has devised a new design for green and blue LEDs that avoids much of this vexing efficiency droop. The findings will be presented at the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO: 2012), taking place May 6-11 in San Jose, Calif.
By changing the orientation of the crystal ...
The IEEE Robotics and Automation Society today announced that press registration is now open for the 2012 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). The event, which runs at the Paul River Centre in Saint Paul, MI on May 14-18, 2012, attracts the world's leading robotics and automation experts. The theme of the annual robotics conference is "Robots and Automation: Innovation for Tomorrow's Needs". The event website is http://www.icra2012.org.According to ICRA 2012 Program Chair Paul Oh, "The conference theme for the 2012 ICRA event, 'Robots ...