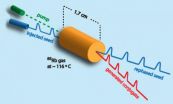
(Press-News.org) Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have developed a novel way of producing light pulses that are "superluminal"—in some sense they travel faster than the speed of light.* The technique, called four-wave mixing, reshapes parts of light pulses and advances them ahead of where they would have been had they been left to travel unaltered through a vacuum. The new method could be used to improve the timing of communications signals and to investigate the propagation of quantum correlations.
According to Einstein's special theory of relativity, light traveling in a vacuum is the universal speed limit. No information can travel faster than light.
But there's kind of a loophole. A short burst of light arrives as a sort of (usually) symmetric curve like a bell curve in statistics. The leading edge of that curve can't exceed the speed of light, but the main hump, the peak of the pulse, can be skewed forward or backward, arriving sooner or later than it normally would.
Recent experiments have generated "uninformed" faster-than-light pulses by amplifying the leading edge of the pulse and attenuating, or cutting off, the back end. The method introduces a great deal of noise with no great increase in the apparent speed. Four-wave mixing produces cleaner, less noisy pulses with a greater increase in speed by "re-phasing" or rearranging the light waves that make up the pulse.
In four-wave mixing, researchers send 200-nanosecond-long "seed" pulses of laser light into a heated cell containing atomic rubidium vapor along with a separate "pump" beam at a different frequency from the seed pulses. The vapor amplifies the seed pulse and shifts its peak forward so that it becomes superluminal. At the same time, photons from the inserted beams interact with the vapor to generate a second pulse, called the "conjugate" because of its mathematical relationship to the seed. Its peak, too, can travel faster or slower depending on how the laser is tuned and the conditions inside the laser.
In the experiment, the pulses' peaks arrived 50 nanoseconds faster than light traveling through a vacuum.
One immediate application that the group would like to explore for this system is quantum discord. Quantum discord mathematically defines the quantum information shared between two correlated systems—in this case, the seed and conjugate pulses. By performing measurements of quantum discord between fast beams and reference beams, the group hopes to determine how useful this fast light could be for the transmission and processing of quantum information.
INFORMATION:
* R. Glasser, U. Vogl and P. Lett. Stimulated generation of superluminal light pulses via four-wave mixing. Physical Review Letters, published online April 26, 2012.
First light: NIST researchers develop new way to generate superluminal pulses
2012-05-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fabrication method can affect the use of block copolymer thin films
2012-05-04
A new study by a team including scientists from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) indicates that thin polymer films can have different properties depending on the method by which they are made. The results* suggest that deeper work is necessary to explore the best way of creating these films, which are used in applications ranging from high-tech mirrors to computer memory devices.
Thin films spread atop a surface have many applications in industry. Inexpensive organic solar cells might be made of such films, to name one potential use. Typically ...
Science nugget: Lightning signature could help reveal the solar system's origins
2012-05-04
Every second, lightning flashes some 50 times on Earth. Together these discharges coalesce and get stronger, creating electromagnetic waves circling around Earth, to create a beating pulse between the ground and the lower ionosphere, about 60 miles up in the atmosphere. This electromagnetic signature, known as Schumann Resonance, had only been observed from Earth's surface until, in 2011, scientists discovered they could also detect it using NASA's Vector Electric Field Instrument (VEFI) aboard the U.S. Air Force's Communications/Navigation Outage Forecast System (C/NOFS) ...
Ultrasound idea: Prototype NIST/CU bioreactor evaluates engineered tissue while creating it
2012-05-04
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have developed a prototype bioreactor—a device for culturing cells to create engineered tissues—that both stimulates and evaluates tissue as it grows, mimicking natural processes while eliminating the need to stop periodically to cut up samples for analysis. Tissue created this way might someday be used to replace, for example, damaged or diseased cartilage in the knee and hip.
Conventional methods for evaluating the development and properties of engineered tissue are time-consuming, destructive ...
Prompt Proofing Blog Post: Revisiting Homophones 3
2012-05-04
In this month's grammar post we are taking another look at some frequently confused homophones. All of the homophones below have been recently spotted, used erroneously, in business communications or copy!
Click here for our first homophones blog post, and here for our second.
insure / ensure
You only insure something in the legal sense - dealing with an insurance company. If you want to make sure something happens you will ensure it. Hence: You insure your car to ensure you will not lose out financially if it is stolen or damaged.
precede / proceed
If something ...
Study examines necessity of additional imaging in PET/CT oncologic reports
2012-05-04
Radiologists and nuclear medicine physicians recommended additional imaging about 30% of the time in oncologic PET/CT reports, with about half of those recommendations being unnecessary, a new study shows.
The study, conducted at Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston, included 250 patients. The study found that there were 84 recommendations made for additional imaging. When study reviewers examined the patients' records, they concluded that 43 of those recommendations were unnecessary, said Atul Shinagare, MD, one of the authors of the study. No adverse patient outcome ...
6 month follow-up of patients with benign MRI-guided breast biopsies may not be necessary
2012-05-04
Short term follow-up of patients who have had a negative (benign) MRI-guided vacuum assisted breast biopsy may not be necessary, a new study indicates.
The study, conducted at Yale New Haven Hospital in Connecticut, included 144 patients with 176 lesions that were followed anywhere from three months to 36 months. The study found no malignancies on follow-up MR imaging, said Jaime Geisel, MD, one of the authors of the study. Two patients had suspicious findings at follow-up and underwent a second biopsy six months after the initial biopsy; one yielded benign results and ...
Preop MRI valuable in detecting additional malignancies in dense & not dense breasts
2012-05-04
Newly diagnosed breast cancer patients should undergo a preoperative MRI exam even if their breasts are not dense, a new study indicates. The study found no difference between the usefulness of 3T breast MRI in detecting additional malignancies and high risk lesions in dense versus non-dense breasts.
"There are currently no guidelines that define the role of breast density in determining if a preoperative MRI should be performed. However, anecdotally, we know that preoperative MRI exams tend to be ordered more frequently in younger patients and/or patients with dense ...
Spain's Balearic Islands Now Open to Charter Yachts
2012-05-04
The Balearic islands of Mallorca, Ibiza, Minorca and Formentera, along with mainland cities such as Barcelona, Valencia and Marbella can now be added to Europe's established 'charter' destinations.
With the longest summer season in Europe, and reliable sunshine from April through until late Autumn, these exclusive destinations can now add as much as 75 days to the European cruising season - This now brings a season that incorporates Easter through until the famous "Club closing parties of Ibiza" and the late Autumn sunshine on the southern Iberian peninsula. ...
Radiologists study necessity of additional imaging recommendations in PET/CT oncologic reports
2012-05-04
Advanced imaging has been identified as one factor that contributes to the overall rising cost of healthcare in the US. Unnecessary or inappropriate imaging utilization magnifies the cost burden associated with advanced imaging studies like MRIs and PET/CT scans. Though these studies often provide the best clinical information for making a diagnosis or planning treatment, experts suspect that a significant number of unnecessary studies are performed. Determining the rate of unnecessary imaging can help guide both policy-makers and physicians to develop guidelines that would ...
Comorbidities increase risk of mortality in COPD patients
2012-05-04
Comorbidities are common among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and a number of these comorbidities are independently associated with an increased mortality risk, according to a new study.
"We followed 1,664 COPD patients recruited from five pulmonary clinics in the United States and Spain for a median of 51 months," said lead author Miguel Divo, MD, a physician in the Pulmonary and Critical Division at Brigham and Women's Hospital and Instructor in Medicine at Harvard Medical School. "Among the 79 comorbidites we observed in these patients, ...