(Press-News.org) Alexandria, VA — A study in the May 2012 issue of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery suggests a threshold for when to choose surgery over medical therapy for recurrent acute rhinosinusitis (RARS) based on the patients' lost productivity in response to RARS and each treatment strategy.
The authors compare the burden of surgery and the burden of disease. On one hand, "Surgery and postoperative convalescence for comprehensive endoscopic sinus surgery can take 5 to 7 days or 3 to 5 workdays…," they write. However, the impact of each bout of infection also diminishes quality of life through absenteeism and partial productivity.
In this study, the authors find that the productivity lost to surgery is outweighed by the productivity lost to illness when patients suffer 4 or more episodes of RARS a year. To counteract the fact that patients may have difficulty distinguishing between an episode of RARS and the 2 viral upper respiratory infections suffered by the average North American each year, the authors suggest using a threshold of 6 episodes per year.
The authors caution, "…productivity is not a perfect surrogate for quality of life… and is not the only way people are affected by a disease. …variability in the degree of debilitation with each infection requires discussion between the clinician and patient to fully appreciate the impact of the disease on an individual basis…" Nonetheless, this threshold provides the first step to a meaningful discussion in patient-centered decision making.
###Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery is the official scientific journal of the American Academy of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery Foundation (AAO-HNSF). The study's authors are Randy Leung, MD; Robert C. Kern, MD; David B. Conley, MD; Bruce K. Tan, MD, and Rakesh K. Chandra, MD.
Reporters who wish to obtain a copy of the study, "Establishing a Threshold for Surgery in Recurrent Acute Rhinosinusitis: A Productivity-Based Analysis" should contact Mary Stewart at 1-703-535-3762, or newsroom@entnet.org.
About the AAO-HNS
The American Academy of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery (www.entnet.org), one of the oldest medical associations in the nation, represents nearly 12,000 physicians and allied health professionals who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the ears, nose, throat, and related structures of the head and neck. The Academy serves its members by facilitating the advancement of the science and art of medicine related to otolaryngology and by representing the specialty in governmental and socioeconomic issues. The organization's vision: "Empowering otolaryngologist-head and neck surgeons to deliver the best patient care."
Establishing a threshold for surgery in recurrent acute rhinosinusitis
2012-05-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Screening for esophageal disease with unsedated transnasal endoscopy is safe and feasible
2012-05-11
OAK BROOK, Ill. – May 10, 2012 – Researchers report that unsedated transnasal endoscopy is a feasible, safe, and well-tolerated method to screen for esophageal disease in a primary care population. This study is the largest reported experience with transnasal endoscopy in the United States. The study appears in the May issue of GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, the monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE).
Esophageal cancer is the most rapidly increasing type of neoplasia in terms of incidence in the United ...
Smoking ban reduced maternal smoking and preterm birth risk
2012-05-11
New Rochelle, NY, May 10, 2012—A citywide ban on public smoking in Colorado led to significant decreases in maternal smoking and preterm births, providing the first evidence in the U.S. that such interventions can impact maternal and fetal health, according to an article in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Women's Health website at http://www.liebertpub.com/jwh.
Prenatal exposure to tobacco smoke–whether the mother is a smoker or exposure is from environmental ...
Discovery in cell signaling could help fight against melanoma
2012-05-11
The human body does a great job of generating new cells to replace dead ones but it is not perfect. Cells need to communicate with or signal to each other to decide when to generate new cells. Communication or signaling errors in cells lead to uncontrolled cell growth and are the basis of many cancers.
At The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) Medical School, scientists have made a key discovery in cell signaling that is relevant to the fight against melanoma skin cancer and certain other fast-spreading tumors.
The scientists report that ...
Economic theory actually works in health care
2012-05-11
WASHINGTON – A study of 7,424 privately insured colon cancer patients found that managed care presence in the market and hospital competition increased the likelihood laparoscopic surgery to treat colon cancer lowered costs, a national team of researchers led by a professor at the George Washington University School of Public Health and Health Services reported in the journal Cancer, May 8, 2012.
Colon cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in the U.S., and surgical resection is the standard of care. In 2004, there were approximately 134,000 colectomies performed ...
Research reveals novel transport mechanism for large ribonucleoproteins
2012-05-11
WORCESTER, Mass. — The movement of genetic materials, such as RNA and ribosomes, from the nucleus to the cytoplasm is a critical component in a cell's ability to make the proteins necessary for essential biological functions. Until now, it was believed the nuclear pore complex was the sole pathway between the cell nucleus and cytoplasm for these materials. New evidence published in Cell by Vivian Budnik, PhD, Melissa J. Moore, PhD, and colleagues at the University of Massachusetts Medical School, reveals a novel budding mechanism, similar to the process used by some viruses, ...
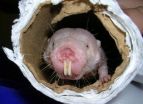
Long-lived rodents have high levels of brain-protecting factor
2012-05-11
SAN ANTONIO (May 10, 2012) — The typical naked mole rat lives 25 to 30 years, during which it shows little decline in activity, bone health, reproductive capacity and cognitive ability. What is the secret to this East African rodent's long, healthy life?
Scientists from the United States and Israel found a clue. From infancy to old age, naked mole rats are blessed with large amounts of a protein essential for normal brain function.
"Naked mole rats have the highest level of a growth factor called NRG-1 in the cerebellum. Its levels are sustained throughout their life, ...
Helping Hands reaches out to patients with cerebral palsy
2012-05-11
HOUSTON – (May 9, 2012) – With the aid of multiple force sensors and a digital dinosaur, a team of Rice University seniors known as Helping Hands hopes to restore strength and flexibility to the hands and wrists of children with cerebral palsy.
"These kids have a real problem with their hands," said Jenna Desmarais, a senior at Rice majoring in mechanical engineering. "The fingers and wrists are locked into a sort of claw-like position. Even after surgery to correct it, they need physical therapy to get stronger."
The team's rehabilitation device, the Dino-Might, was ...
New twist on ancient math problem could improve medicine, microelectronics
2012-05-11
ANN ARBOR, Mich.—A hidden facet of a math problem that goes back to Sanskrit scrolls has just been exposed by nanotechnology researchers at the University of Michigan and the University of Connecticut.
It turns out we've been missing a version of the famous "packing problem," and its new guise could have implications for cancer treatment, secure wireless networks, microelectronics and demolitions, the researchers say.
Called the "filling problem," it seeks the best way to cover the inside of an object with a particular shape, such as filling a triangle with discs ...
ICU stays for worst asthma drop 74 percent, review finds
2012-05-11
SAN ANTONIO (May 10, 2012) — A review of 30 years of life-threatening asthma cases in a San Antonio intensive care unit found that annual ICU admissions for the condition have dropped 74 percent. The study, by UT Medicine San Antonio physicians who reviewed cases at University Hospital between 1980 and 2010, also showed intubation in the emergency department to help patients breathe did not result in longer hospital stays.
UT Medicine is the clinical practice of the School of Medicine at The University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio.
Faculty studied inpatient ...
UF study finds logging of tropical forests needn't devastate environment
2012-05-11
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — Harvesting tropical forests for timber may not be the arch-enemy of conservation that it was once assumed to be, according to a new study led by a University of Florida researcher.
Selective logging may be one of the few feasible options left for conserving tropical forests given the huge financial incentives pushing tropical landholders to convert primary forests into cash-generating agricultural plantations.
The report analyzed data from more than 100 studies of tropical forests on three continents that had been harvested for timber. Results ...